Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Morphology, anatomy and reproduction in Anthoceros

Morphology, anatomy and reproduction in Anthoceros
Morphological, anatomical and reproductive characters of Marchantia

Morphological, anatomical and reproductive characters of Marchantia
Chara algae Morphology Cell Structure Reproduction

Chara algae Morphology Cell Structure Reproduction
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (20)
Similar to Marchantia jb
Similar to Marchantia jb (20)
Marchantia, Dr.V.Vijaya, Assistant Professor of Botany, E.M.G. Yadava Women's...

Marchantia, Dr.V.Vijaya, Assistant Professor of Botany, E.M.G. Yadava Women's...
More from Jayakara Bhandary
More from Jayakara Bhandary (20)
Recently uploaded
Mehran University Newsletter is a Quarterly Publication from Public Relations OfficeMehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024

Mehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024Mehran University of Engineering & Technology, Jamshoro
https://app.box.com/s/7hlvjxjalkrik7fb082xx3jk7xd7liz3TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? webinar
Thursday 2 May 2024
A joint webinar created by the APM Enabling Change and APM People Interest Networks, this is the third of our three part series on Making Communications Land.
presented by
Ian Cribbes, Director, IMC&T Ltd
@cribbesheet
The link to the write up page and resources of this webinar:
https://www.apm.org.uk/news/making-communications-land-are-they-received-and-understood-as-intended-webinar/
Content description:
How do we ensure that what we have communicated was received and understood as we intended and how do we course correct if it has not.Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...Association for Project Management
Recently uploaded (20)
Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx

Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx
TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...
ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.

ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.
Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...

Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...
Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf

Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...
This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.

This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.
Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes

Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes
ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx

ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx
Marchantia jb
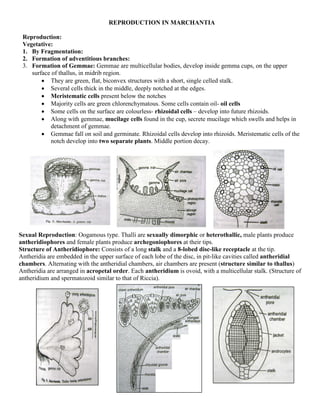
- 1. REPRODUCTION IN MARCHANTIA Reproduction: Vegetative: 1. By Fragmentation: 2. Formation of adventitious branches: 3. Formation of Gemmae: Gemmae are multicellular bodies, develop inside gemma cups, on the upper surface of thallus, in midrib region. • They are green, flat, biconvex structures with a short, single celled stalk. • Several cells thick in the middle, deeply notched at the edges. • Meristematic cells present below the notches • Majority cells are green chlorenchymatous. Some cells contain oil- oil cells • Some cells on the surface are colourless- rhizoidal cells – develop into future rhizoids. • Along with gemmae, mucilage cells found in the cup, secrete mucilage which swells and helps in detachment of gemmae. • Gemmae fall on soil and germinate. Rhizoidal cells develop into rhizoids. Meristematic cells of the notch develop into two separate plants. Middle portion decay. Sexual Reproduction: Oogamous type. Thalli are sexually dimorphic or heterothallic, male plants produce antheridiophores and female plants produce archegoniophores at their tips. Structure of Antheridiophore: Consists of a long stalk and a 8-lobed disc-like receptacle at the tip. Antheridia are embedded in the upper surface of each lobe of the disc, in pit-like cavities called antheridial chambers. Alternating with the antheridial chambers, air chambers are present (structure similar to thallus) Antheridia are arranged in acropetal order. Each antheridium is ovoid, with a multicellular stalk. (Structure of antheridium and spermatozoid similar to that of Riccia).
- 2. Structure of Archegoniophore: Consists of a long stalk and a 8-lobed disc-like receptacle at the tip, the lobes of the receptacle bend downwards and inwards. Hanging structures called rays develop from the margin of the disc. Archegonia are present on the upper surface of the receptacle in young archegoniophore, in acropetal order. They are in median rows on each lobe. After fertilization, the central part of the disc grows rapidly. As a result, the archegonia are pushed to the lower surface and they become pendulous. Between rows of archegonia, a curtain-like tissue called perichaetium or the involucre develops. It is single cell in thickness and fringed in the margins. Structure of Archegonia: Structure is similar to that of Riccia. Only difference is number of Neck Canal Cells is 8 (in Riccia 4). Fertilisation: Splash mechanism due to rain drops. Refer Riccia. Structure of Sporophyte: The diploid zygote develops into the sporophyte inside the venter of the archegonium. Mature sporophyte shows three distinct parts: • Foot: The basal, broad, parenchymatous part. Embedded in the tissue of the archegoniophore. Absorptive and anchoring in function. • Seta: It connects the foot and capsule. Consists of many vertical rows of cells. • Capsule: oval, spore producing structure at the apex of the sporophyte. Covered by a single-layer of cells called capsule wall. Many haploid spores or meiospores and sterile elaters are found inside the capsule. • The spores are small globose structures with a spore wall consisting of exine and intine, a single nucleus and little cytoplasm. They germinate into new thalli. • Elaters long ribbon-like multicellular structures. They are hygroscopic and help in spore dispersal. • Mature sporophyte is protected by three coverings – perigynium, calyptra and perichaetium. Dehiscence and spore dispersal: Mature capsule splits along 4-6 lines. Spores are released due to the hygroscopic movement of elaters. Liberated spores germinate into new thalli, in the presence of water. ©Dr. Jayakara Bhandary M. Associate Professor of Botany Govt. Degree College, Karwar
