Target Population Characteristics"This title is less than 40 characters and clearly conveys the main topic of the document, which is describing the characteristics of the target population for the report. It uses straightforward keyword language ("Target Population Characteristics
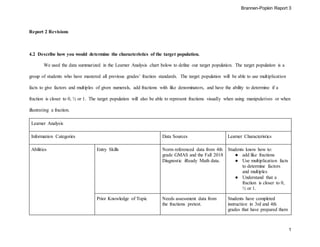
- 1. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 1 Report 2 Revisions 4.2 Describe how you would determine the characteristics of the target population. We used the data summarized in the Learner Analysis chart below to define our target population. The target population is a group of students who have mastered all previous grades’ fraction standards. The target population will be able to use multiplication facts to give factors and multiples of given numerals, add fractions with like denominators, and have the ability to determine if a fraction is closer to 0, ½ or 1. The target population will also be able to represent fractions visually when using manipulatives or when illustrating a fraction. Learner Analysis Information Categories Data Sources Learner Characteristics Abilities Entry Skills Norm referenced data from 4th grade GMAS and the Fall 2018 Diagnostic iReady Math data. Students know how to: ● add like fractions ● Use multiplication facts to determine factors and multiples ● Understand that a fraction is closer to 0, ½ or 1. Prior Knowledge of Topic Needs assessment data from the fractions pretest. Students have completed instruction in 3rd and 4th grades that have prepared them
- 2. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 2 Norm referenced data from 4th grade GMAS and the Fall 2018 Diagnostic iReady Math data. to add like fractions, determine multiples and factors, and to understand if a fraction is closer to 0, ½ or 1. Educational and Ability Levels Permanent records, Snapshot Tracker Documents, IEP and RTI document review Students in this group are average to above average learners. Students in this group are in the RTI process, regular learners and/or gifted learners. General Learning Preferences Student interview and learning preference questionnaire Students enjoy working in small groups, working with manipulatives, and using the computer a resource. Attitudes Attitudes toward content Teacher created survey Students report that they are very anxious to learn about fractions. They report that they are not good at fractions, and they are not looking forward to learning the content. Attitudes toward potential delivery system Teacher created survey Teachers believe that hands on and small group learning will best meet the needs of the students and reduce anxiety. Students report that they are looking forward to playing math games and learning with manipulatives. Motivation for Instruction (ARCS) Teacher created survey and student interview Teachers report that they are aware that students are not
- 3. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 3 motivated to learn how to add fractions with unlike denominators. Attitudes toward school Teacher created survey and student interview Teachers are aware that the majority of the students have a good attitude toward school. They know they can approach the teachers if they have trouble understanding the content. General Group Characteristics Overall Impressions This group of students is a heterogeneous group of 5th grade students. The group is capable of learning even though some mention math anxiety with fractions.
- 4. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 4 REPORT 3 10. Developing Instructional Materials 10.1 For the TO, specify and defend your choice of an appropriate pre-instructional materials. Given that students have received instructions in 4th grade regarding finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM), the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and adding fractions with like denominators, we wanted to see if any students retained that information or could apply that information to adding fractions with unlike denominators using a pretest of the upcoming skills and concepts. Additionally, the Fraction Pre-test will allow us to form groups for differentiated instruction. For example, if only a few students need remediation in LCM, we will provide instruction on that skill with those students only. For group practice, we can use pre-test data to put high, medium and low performing students in appropriate groups. Fractions Pretest Name ________________________ Fractions Pre-test Are you ready for some fractions? Show me what you know! 1. Find the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 4 and 6. 2. Find the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 2 and 5.
- 5. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 5 3. Find the Least Common Denominator (LCD) for ⅓ and ⅗. 4. Find the Least Common Denominator (LCD) for ½ and ⅚. 5. Complete the following equivalent fractions: a. 3 4 = ? 12 b. 1 2 = 5 ? 6. Find the sum of the following. A. 2/3 + 1/2 = B. 2/5 + 1/4 = C. 1/3 + 2/5= D. 5/12 + 2/3 = 7. Find the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of 15 and 10. 8. Find the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of 30 and 12. 9. Simplify 10 15 using the GCF. 10. Simplify 12 30 using the GCF.
- 6. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 6 10.2 Select one SO; specify and defend your choice of an appropriate presentation of materials. SO: Create equivalent fractions for 2 unlike fractions using the common denominator. To provide relevance of the topic of adding fractions for students, the presentation of this objective will begin with students using manipulatives to find the common denominator of two unlike denominators. The use of manipulatives will allow students to see the process at a concrete level first before moving to more abstract representations of fractions without manipulatives. Students will be given a problem such as “Find the common denominator for this problem: ⅔ + 4/9.” The students will then build a model of the addition problem using fraction tower manipulatives. Students will have to find the same color fraction tower that works for both fractions. For example, they will have to discover that the ninth fraction tower piece will need to be used. Students will build a model of the problem, then draw the model on a sheet of paper. Transferring the actual model to a drawn model teaches students to use drawings when manipulatives are not available. This will provide students with confidence in approaching fractions in future practice activities. We will discuss how we can use the least common multiple, and later equivalent fractions, to add unlike fractions. Students will then watch a Brain Pop video clip of adding fractions (https://www.brainpop.com/math/numbersandoperations/addingandsubtractingfractions/). Students will work in small groups to find the common denominator of unlike fractions from page 131 in the textbook. Students will be asked to use the manipulatives for even numbered problems and drawings for odd numbered problems in the textbook to allow students practice using both. The manipulatives will give the students a chance to check their work for accurateness and reasonableness.
- 7. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 7 10.3 For the same SO, specify and defend your choice of an appropriate practice materials. Students need to be presented information in multiple ways to reach all types of learners. It is important for teachers to model concepts first using concrete examples before moving to a more abstract way to solve the problem. For instance, students should understand why denominators needs to be the same before adding, instead of just learning the algorithm to add two unlike fractions. In our instruction, we have used concrete manipulatives, modeling, drawing models, and a video before students master the algorithm of adding fractions with unlike denominators. Unit: Adding Fractions with Unlike Denominators Lesson2: Find the common denominator of two unlike fractions Standards: MGSE5.NF.1 Add and subtract fractions and mixed numbers with unlike denominators by finding a common denominator and equivalent fractions to produce like denominators. MGSE5.NF.2 Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions, including cases of unlike denominators (e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem). Use benchmark fractions and number sense of fractions to estimate mentally and assess the reasonableness of answers. For example, recognize an incorrect result 2/5 + ½ = 3/7, by observing that 3/7 < ½. Learning Target Students will be able to find the common denominator of two unlike fractions. Activator Students will be able to use manipulatives in order to find the common denominator of two unlike denominators. Mini-Lesson The teacher will provide students with opportunities to use manipulative to find the common denominator of two unlike fractions. Students will work in small groups for this skill.
- 8. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 8 Practice Students will work in small groups to find the common denominator of unlike fractions from page 131 in the textbook. Students will be asked to use the manipulatives for even numbered problems and drawings for odd numbered problems in the textbook to allow students practice using both. The manipulatives will give the students a chance to check their work for accurateness and reasonableness. Formative Assessment Students will be formally assessed on this learning target with a daily grade. Students will be responsible for finding the common denominator of two unlike fractions. The assessment will include problems such as, but not limited to, the following: 1. Find the common denominator for ¾ and 7/12. 2. Find the common denominator for ⅔ and ½. 3. Find the common denominator for 3/4 and 3/8. 4. Find the common denominator for 2/5 and ½. Extension Students who master this learning target quickly will be able to attempt to add the two unlike fractions together with the use of manipulatives. Note: the algorithm will not be taught at this time. Students will use the manipulatives to find the sum of the two unlike fractions. 10.4 For the TO, specify and defend your choice of an appropriate follow-through materials. Students will be able to use their new skills of finding the common denominator of two unlike fractions to complete their semester project in the STEM lab. Students will have to find the combined lengths of materials needed in order to build a new cage for the quail that they are raising. The materials will be in fraction dimensions consisting of denominators containing ½, ¼, ⅛, and 1/12 of an inch. Students will have to find the common denominator of the fractions before they can find a combined length of the needed materials. Students who needed multiplication support will have access to multiplication charts in the STEM lab. The flow map for steps of the process of adding fractions with unlike denominators will be posted for reference in the STEM lab.
- 9. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 9 Not only will students need this information for their STEM project, but this information will also be presented on the GMAS at the end of the year. We will continuously review this skill throughout the year by incorporating adding fractions into other standards such as finding the perimeter of quadrilaterals, analyzing line plots, and solving problems with the order of operations. Incorporating adding fractions in new skills with act as a memory aid to help students retain the information. 11. Formative Evaluation 11.1 Describe an approach that you might use to carry out formative evaluation for your instructional initiative. Include any instruments for assessment, quiz/rubrics, or other related products used for your evaluation. The final formative assessment will include Post-test that mirrors the Pre-Test to determine if students have mastered all objectives. This will allow us to adequately analyze data based on the same objectives. If students have not mastered the objectives we will adjust the instruction for remediation. Students who master the curriculum will be allowed to continue with the next objectives in the curriculum while other students will be pulled in small groups for remediation. 12. Revision 12.1 Describe your plans for revising your instruction. We utilized the Item by Objective Analysis to first examine how students performed on the actual test. The results allowed us to evaluate the problems on the test and how students performed on them as well as look at individual student performance.
- 10. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 10 We will revise instruction by giving students more opportunities to model and manipulate fractions into simplest form. We will give students more opportunities to model fractions in simplest form, draw diagrams of simplest form, then use the greatest common factor to find simplest form. Scaffolding this concept from concrete (models) to abstract (the use of GCF) will help students visualize how a fraction in simplest form is equivalent to the beginning fraction. We will model and review this concept in small groups. Item by Objective Analysis Objective 1: Find the LCM of 2 unlike fractions Objective 2: Create equivalent fractions for 2 unlike fractions using the common denominator. Objective 3: Add the equivalent fractions. Objective 4: Simplify the sum of the fractions. Objective 5: Check to see if the answer is reasonable . No. of item s % of items corre ct No. of obj. master ed % of obj. master ed Learner #1 #2 #3 #4 #5a #5b #6a #6b #6c #6d #7 #8 #9 #10 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 10 71 4 80 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 13 93 5 100 3 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 12 86 5 100 4 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 12 86 5 100 5 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 10 71 3 60 6 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 13 93 5 100 7 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 12 86 5 100
- 11. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 11 8 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 10 71 3 60 9 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 10 71 3 60 10 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 12 86 5 100 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 11 80 5 100 12 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 12 86 5 100 13 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 11 80 5 100 14 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 9 60 3 60 15 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 10 71 4 80 16 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 12 86 5 100 17 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 10 71 4 80 18 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 11 80 5 100 19 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 7 50 3 60 20 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 9 60 3 60 No. of Ss correct 17 16 16 17 16 16 16 16 16 16 12 14 14 12 % of Ss correct 85 80 80 85 80 80 80 80 80 80 60 70 70 60 % master obj. 82.5% 81.25 80 65 65
- 12. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 12 Key: 1 = correct response; blank = incorrect response; Instructional Revision Analysis Form
- 13. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 13 Instructional Strategy Component Problem Identified Proposed Changes to Instruction Evidence and Source Entry skills test Students who use multiplication charts had difficulty using them during practice activities. A mini lesson on how to use the multiplication chart during classroom practice. Teacher Observation and formative assessment during practice activities. Motivational introductory material Students were not motivated to learn as fractions since it is a difficult concept to learn. Start the lesson with Math vocabulary games Student rating scale Teacher observation Pretest Not Applicable Not Applicable pretest Information presentation Students did not have a concrete understanding of simplest form. When teaching simplest form we will use the phrase equivalent fraction instead of simplest form to decrease vocabulary confusion initially, then use the phrase simplest form or simplify. Post-test Item by Objective Analysis Learner participation Math anxiety when manipulatives were not provided for practice activities. A few students stopped participation. Rating scale to indicate student anxiety level at each step of the instructional process. Student rating scale Teacher observation Posttest We found that students had poor performance, 65% We may increase the number of problems to 4 for each Post-test Item by Objective Analysis
- 14. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 14 mastery rate, on objectives 4 and 5. There were 2 problems for each of those objectives. 60% missed one and 70% missed the other problem giving the 65% mastery level. However, objectives 2 and 3 had more problems per objective. objective to see if that affects the performance rate. Attitude Questionnaire Math anxiety when manipulatives were not provided for practice activities. A few students stopped participation. Rating scale to indicate student anxiety level at each step of the instructional process. Student rating scale Teacher observation 13. Summative Evaluation
- 15. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 15 13.1 Describe an approach that you might use to carry out formative evaluation for your instructional initiative. Include any instruments for assessment, quiz/rubrics, or other related products used for your evaluation. Students will be able to use their new skills of finding the common denominator of two unlike fractions, finding equivalent fractions, and adding unlike fractions to complete their semester project in the STEM lab. Students will have to find the combined lengths of materials needed in order to purchase materials in order to build a new cage for the quail that they are raising. The materials will be in fraction dimensions consisting of denominators containing ½, ¼, ⅛, and 1/12 of an inch. Students will have to measure the perimeter of the base of the rectangular quail pen to determine how much of the needed materials (wire and wood) to order. This step will require students to accurately add unlike fractions before they can find a combined length of the needed materials. Students will complete computations individually and turn them in to the teacher for evaluative purposes first. Students will then compare their results to each other and decide who has the best measurements and complete computations for purchasing materials. Students will need to apply knowledge that was taught during the fractions unit in order to be successful with this project. The following scores indicate mastery levels: At Mastery: 10-12 points Approaching Mastery: 7-9 points Needs Remediation: 4-6 points Rubric for STEM Activity
- 16. Brannen-Popkin Report 3 16 Unacceptable (1 point) Acceptable (2 points) Target (3 points) Points Scored Students accurately find the perimeter of the base of the rectangular quail pen. *related to our fractions unit Students did not accurately measure the length or width of the base of the quail pen to find the perimeter to the nearest ¼ inch. Students accurately measured the length OR width of the base of the quail pen to find the perimeter to the nearest ¼ inch. Students accurately measured the length and width of the base of the quail pen to find the perimeter to the nearest ¼ inch. Students accurately find the height of the sides of the rectangular quail pen. Students accurately measured the height of the side of the quail pen to find the height to the nearest 1 inch. Students accurately measured the height of the side of the quail pen to find the height to the nearest 1/2 inch. Students accurately measured the height of the side of the quail pen to find the height to the nearest ¼ inch. Students will determine the amount of money needed to purchase wire for the quail pen. Students accurately determine the correct amount of money needed to purchased materials to the nearest five dollars. Students accurately determine the correct amount of money needed to purchased materials to the nearest dollar. Students accurately determine the correct amount of money needed to purchased materials to the nearest cent. Students will be able to use a measuring tape to measure dimensions for the new quail pen. Students will be able to measure accurately to the nearest ½ inch. Students will be able to measure accurately to the nearest ¼ inch. Students will be able to measure accurately to the nearest ⅛ inch.