Survival English grammar
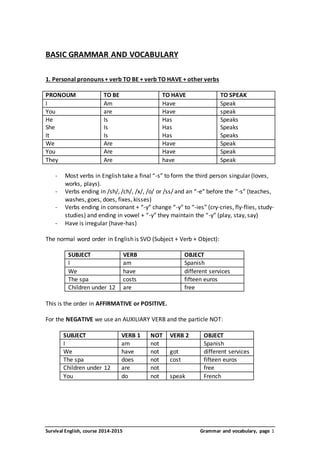
- 1. BASIC GRAMMAR AND VOCABULARY 1. Personal pronouns + verb TO BE + verb TO HAVE + other verbs PRONOUM TO BE TO HAVE TO SPEAK I Am Have Speak You are Have speak He Is Has Speaks She Is Has Speaks It Is Has Speaks We Are Have Speak You Are Have Speak They Are have Speak - Most verbs in English take a final “-s” to form the third person singular (loves, works, plays). - Verbs ending in /sh/, /ch/, /x/, /o/ or /ss/ and an “-e” before the “-s” (teaches, washes, goes, does, fixes, kisses) - Verbs ending in consonant + “-y” change “-y” to “-ies” (cry-cries, fly-flies, study-studies) and ending in vowel + “-y” they maintain the “-y” (play, stay, say) - Have is irregular (have-has) The normal word order in English is SVO (Subject + Verb + Object): SUBJECT VERB OBJECT I am Spanish We have different services The spa costs fifteen euros Children under 12 are free This is the order in AFFIRMATIVE or POSITIVE. For the NEGATIVE we use an AUXILIARY VERB and the particle NOT: SUBJECT VERB 1 NOT VERB 2 OBJECT I am not Spanish We have not got different services The spa does not cost fifteen euros Children under 12 are not free You do not speak French Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 1
- 2. We usually contract the form: I’m not Spanish We haven’t got different services The spa doesn’t cost fifteen euros Children under 12 aren’t free You don’t speak French We use HAVE differently in BrE (British English) and AmE (American English): BrE: We have got two cats/ Have we got two cats? / We haven’t got two cats AmE: We have two cats / Do we have two cats? / We don’t have two cats YES/NO questions: - to be, to have…: verb +subject + object Example: He is Spanish ------------ Is he Spanish? You have got a cat ----- Have you got a cat? - other verbs: auxiliary + subject + verb +object Example: I live in Sant Cugat ----- Do you live in Sant Cugat? He plays football------- Does he play football? The auxiliary is DO or DOES (3rd person singular) in PRESENT. Different examples of word order in English: Affirmative She is my friend Negative She isn’t my friend / She isn’t my friend Question Is she my friend? Affirmative We have got a lot of books/ We have a lot of books* Negative We haven’t got a lot of books/ We don’t have a lot of books * Question Have we got a lot of books?/ Do we have a lot of books?* Affirmative They live in a nice house Negative They don’t live in a nice house Question Do they live in a nice house? Affirmative He drives his car every day Negative He doesn’t drive his car every day Question Does he drive his car every day? Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 2
- 3. 2. Ordinal numbers 1 ONE 11 ELEVEN 2 TWO 12 TWELVE 3 THREE 13 THIRTEEN 4 FOUR 14 FOURTEEN 5 FIVE 15 FIFTEEN 6 SIX 16 SIXTEEN 7 SEVEN 17 SEVENTEEN 8 EIGHT 18 EIGHTEEN 9 NINE 19 NINETEEN 10 TEN 20 TWENTY 21 TWENTY-ONE 30 THIRTY 22 TWENTY-TWO 40 FOURTY 23 TWENTY-THREE 50 FIFTY 24 TWENTY-FOUR 60 SIXTY 25 TWENTY-FIVE 70 SEVENTY 26 TWENTY-SIX 80 EIGHTY 27 TWENTY-SEVEN 90 NINETY 28 TWENTY-EIGHT 100 A HUNDRED 29 TWENTY-NINE 1000 A THOUSAND 1435 A THOUSAND FOUR HUNDRED (AND) THIRTY-FIVE 721.011 SEVEN HUNDRED TWENTY-ONE THOUSAND (AND) ELEVEN 111.111 ONE HUNDRED ELEVEN THOUSAND ONE HUNDRED (AND) ELEVEN 3. Parts of the day, days, months, years Parts of the day Morning Before 12 Midday/Noon 12 Afternoon 12-18 Evening 18 and until you go to bed Night When you go to bed or is really late Midnight 00 Days of the week: Sunday - Monday - Tuesday - Wednesday - Thursday - Friday - Saturday (we start the week saying Sunday and not Monday in English) Months of the year: January, February, March,. April, May, June, July, August, September, October, November, December Seasons of the year: Spring, Summer, Autumn, Winter Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 3
- 4. How to read years in English: 4. Pronunciation tips listen: /lisen/ kiss /kis/ keys /ki:s/ often: /offen/ live /lif/ leave /li:f/ walk: /uoc/ shit /shit/ sheet /shi:t/ talk: /toc/ ship /ship/ sheep /shi:p/ often: /offen/ this: /dis/ these: /di:s/ live: /lif/ write: /rait/l life: /laif/ right: /rait/ 5. There is / There are Singular: there is + a/an/one …. Plural: there are + some/(number) ……. How many toys are there on the floor? There are three Is there a dog in the picture? No, there isn’t any 6. Some / any Any: in negatives and questions Some: in affirmatives Do you need any help? Yes, please. I need some help No, thank you. I don’t need any. Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 4
- 5. 7. Short answers Has she got a pink T-shirt? No, she hasn’t got any Do you speak English? Yes, I do Are you American? Yes, I am 8. Basic verbs To have + a meal: to have breakfast to have lunch to have dinner to have a coffee/tea to watch TV/a tennis match/a ski competition to play a game cards the piano/violin/flute/drums to ride a bike/a horse/ a scooter/ a motorbike to drive a car/a bus/a train/a plane… Phrasal verb: a verb which goes with certain prepositions: to look at mirar to look around donar un cop d’ull to look after cuidar de (una persona, una casa, un animal, una planta, un negoci…) to look down to mirar de forma despectiva Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 5
- 6. VOCABULARY: THE FAMILY Immediate Family Masculine Feminine father mother son daughter brother sister husband wife When you have children, you are a parent. One collective word to describe brothers and sisters is siblings. Different Generations Masculine Feminine Forefathers Great-great grandfather Great-great grandmother Great grandfather Great grandmother Grandfather Grandmother Father Mother Son Daughter Grandson Granddaughter Great grandson Great granddaughter Great-great grandson Great-great granddaughter Descendents Relatives and Extended Family grandparents: the parents of your parents grandfather: the father of your father/mother grandmother: the mother of your father/mother grandchildren: the children of your children grandson: the son of one of your children granddaughter: the daughter of one of your children great grandfather: the father of your grandfather/grandmother great grandmother: the mother of your grandfather/grandmother uncle: the brother (or brother-in-law) of your mother/father aunt: the sister (or sister-in-law)of your mother/father cousin: the child of your aunt/uncle nephew: the male child of your brother/sister niece: the female child of your brother/sister Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 6
- 7. The In-Laws father-in-law: the father of your spouse mother-in-law: the mother of your spouse son-in-law: the husband of your daughter daughter-in-law: the wife of your son brother-in-law: the husband of your sister sister-in-law: the wife of your brother The Family Mix "Step-" means that you are related as a result of one parent marrying again stepfather: the (new) husband of your mother stepmother: the (new) wife of your father stepson: the son of your (new) husband / wife stepdaughter: the daughter of your (new) husband / wife stepsister: the daughter of your stepmother or stepfather stepbrother: the son of your stepmother or stepfather Sometimes one of your parents gets married again and they have more children. There half-brother: the brother you have only one parent in common with . half-sister: the sister you only have one parent in common with. Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 7
- 8. VOCABULARY: DAILY OBJECTS Furniture in the dining room Sofa Chair Armchair Shelf/shelves Plant Table Bookcase TV/television Carpet Door Window Clock Portrait Picture Lamp Cupboard Irregular plurals Singular plural Woman /wuman/ women /wimin/ Man /man/ men /men/ Child children Mouse /maus/ mice /mais/ Fish fish Sheep sheep Shelf shelves Pronunciation tips Crisps /crisps/ picture /pikcher/ Sausages /sosagis/ culture /culcher/ Architecture /arquitekcher/ Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 8
- 9. SMALL TALK AND INTRODUCTIONS 1. Small talk To be kind To be polite Context: situation relationship Using only first name (Laura, Evan, Tom…) - only in friendly situations (family, friends, children, co-workers or colleagues) - examples: · Hi, Tom. Do you want to go to a film tonight? (a man to his friend) · Excuse me, Mary. What do you think of this presentation? (a woman to a co-worker in the office) · Do you know the answer to number seven, Jack? –(a student to another student) Using title and last name (surname): Mr Smith, Mrs Johnson - at work, with supervisors or managers (talking with superiors) - with senior people - with adult people that you don’t know - in meetings, public speaking - examples: · Good morning Ms Johnson. Did you have a good weekend? (a student to her teacher) · Mr Johnson, I'd like to introduce you to Jack West from Chicago (an employee introducing a colleague to his supervisor) 2. Introductions and social language Title: Mr (Mister, for men) Ms (pronounced “miss”, for women in general) Mrs (pronounced “missis”, for married women) Miss (pronounced “miss”, for unmarried women) Letters and writings: Formal informal Dear Sir/Madam, Dear John, (…) (…) Yours faithfully, Regards Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 9
- 10. A. introducing a person to another one Structure: Example: (name), do you know (name)? Laura, do you know Tom? I'd like you to meet (name) Laura, I’d like you to meet Tom B- greeting that person Ken: Laura, I'd like you to meet Mary. Laura: How do you do? Mary: How do you do / Pleased to meet you / It’s a pleasure Ken: Mary works for ... What do you do? vs How are you? 1st time you meet a person: A - How do you do? B - How do you do? 2nd time you meet that person: A – How do you do? B – Fine, thanks! Formal answers: Nice to meet you Pleased to meet you It’s a pleasure Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 10
- 11. PERSONAL INFORMATION What sort of questions do you ask? type kind Age: How old are you? What’s your age? I’m 40 years old Name: What’s your name? My name’s Sandra I’m Sandra Birth: Where were you born? I was born in Sabadell When is your birthday? My birthday is on 14 May When were you born? I was born on 14 May 1966 Nation: What’s your nationality? I’m Spanish Where are you from? I’m from Spain Live: Where do you live? I live in Sant Cugat What’s your address? 1, Ignasi Barraquer, 2nd-3rd Family: Are you married? Yes, I am married No, I’m single Have you got any brothers or sisters? No, I haven ‘t any Yes, I’ve got one brother and one sister Does your grandfather live with you? Yes, he does No, he doesn’t How old is your sister? She’s 15 Job: What’s your job? I’m a teacher (but I work as a massagist= What do you do? I’m a massagist Where do you work? I work in Barcelona I work in a hotel I work at the fitness area of a hotel in BCN Hobbies: What’s your hobby? I like dancing / listening to music / reading What’s your favourite film? My favourite film is Psicosis Have you got any hobbies? No, I haven’t got any House: How many rooms are there in your house? There are four rooms Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 11
- 12. WORD ORDER in QUESTIONS: a/ question words: to ask for a part of the sentence. (Question word + verb or auxiliary +subject + verb 2 + object) Mandy speaks French: WHO speaks French? I speak German: WHAT do you speak? I go to the beach: WHERE do you go? I get up at 7: WHEN do you get up? This book is mine: WHICH book is yours? The cat is big: HOW is the cat? b/ YES/NO questions: - to be, to have…: verb +subject + object Example: He is Spanish ------------ Is he Spanish? You have got a cat ----- Have you got a cat? - other verbs: auxiliary + subject + verb +object Example: I live in Sant Cugat ----- Do you live in Sant Cugat? He plays football------- Does he play football? The auxiliary is DO or DOES (3rd person singular) in PRESENT. PRONOUNS Personal subject pronoun Possessive adjective Possessive pronoun Personal object pronoun I My Mine Me You Your Yours You He His His Him She Her Hers Her It Its Its It We Our Ours Us You Your Yours You They Their theirs them Personal subject pronoun: We live in Sant Cugat He has two books I am forty years old They speak Chinese Possessive adjective: My father is French This is his book Their car is red What’s your name? Possessive pronoun This car is hers Those books are theirs Your car is red. Mine is green Personal object pronoun This is a present for them Nice to meet you Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 12
- 13. Introductions (presentacions) Do you know each other? Us coneixeu? Carol, let me introduce John to you: Carol, deixa que et presenti el John Carol, let me introduce you to John: Carol, deixa que et presenti al John Let me introduce myself: Deixa que em presenti Can you introduce yourself? Et podries presentar? Family name = last name = surname (Bosch, Calatayud) First name = given name (Rosa, Meritxell) Peter Sebastian Walker Peter = first name, given name Sebastian = middle name Walker = surname, family name, surname To meet a person = trobar-se a algú To have a meeting = tenir una reunió Reflexive pronouns I Myself I hurt myself when I was cutting the bread You Yourself Emma, did you take the picture by yourself? He Himself Robert made this T-shirt himself She Herself Lisa often speaks to herself It Itself The lion can defend itself We Ourselves We helped ourselves with some cola at the party You Yourselves Tim and Gerry, if you want more milk, help yourselves They Themselves Alice and Doris collected the stickers themselves False friends To present = to make a presentation To introduce = presenter a algú Pronunciation tips Know /nou/ love /lov/ No /nou/ law /lo/ Knowledge /nouleig/ laugh /laf/ Dead /ded/ (adjectiu: mort) kite /kait/ Death /dez/ (substantiu: mort) bike /baik/ Died /daed/ (participi passat: mort) bite /bait/ Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 13
- 14. THE ALPHABET AND SPELLING CLASSROOM LANGUAGE: How do you spell ________________ in English? Can you spell it, please? How do you pronounce _______________ in English? What’s “mesa” in English? Can you repeat it, please? Is it correct? It’s my turn! Can you speak slowly, please? Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 14
- 15. JOBS IN ENGLISH She’s a police officer. She’s a policewoman He’s a police officer. He’s a policeman She’s a nurse She’s a lawyer ENGLISH SPANISH accountant contable actor/actress actor/actriz air hostess azafata architect arquitecto baker panadero butcher carnicero chemist farmacéutico cook cocinero dentist dentista doctor médico driver conductor electrician electricista employee empleado engineer ingeniero farmer granjero fireman bombero fisherman pescador gardener jardinero hairdresser peluquero instructor monitor journalist periodista labourer obrero lawyer abogado mechanic mecánico nanny niñera Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 15
- 16. ENGLISH SPANISH Nun monja nurse enfermero office worker oficinista painter pintor pilot piloto plumber fontanero policeman policía politician político postman cartero psychiatrist psiquiatra psychologist psicólogo receptionist recepcionista salesman vendedor secretary secretario shoemaker zapatero shop assistant dependiente singer cantante student estudiante teacher profesor technician técnico vet veterinario waiter/waitress camarero/a writer escritor Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 16
- 17. Vocabulary Some of my cousins live ABROAD = Some of my cousins live IN ANOTHER COUNTRY To look up a word in the dictionary = buscar una paraula al diccionari I have a work colleague WHO is from Portugal. He’s Portuguese. I have a car THAT is from Japan. It is Japanese. Pronunciation tips Musician /musishan/ euro /iuro/ Electrician /electrishan/ Television /televishon/ Adverbs from adjectives He is SAD. He sings SADLY She is HAPPY. She dances HAPPILY The price is EXACT This is EXACTLY the price Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 17
- 18. Countable and uncountable nouns (I) A noun can be countable: One pen, two pens, forty pens…. Or uncountable: One water, two waters, three waters… We use different words to count uncountable nouns: A bottle of water, two bottles of water, three bottles of water… A glass of water, two glasses of water… Only with uncountable nouns With uncountable and countable nouns Only with countable nouns How much? How much or How many? How many? a little no/none a few a bit (of) not any a number (of) - some (any) several a great deal of a lot of a large number of a large amount of plenty of a great number of - lots of - Examples: I have a little money in my pocket I have a few coins in my pocket We use a large amount or rice to cook a paella We use a great number of eggs to cook a cake Online English practice: Greetings: http://eslgamesworld.com/members/games/grammar/sentences/greetings/greetings. html Film – elementary level: http://film-english.com/category/elementary-a1-pre-intermediate-a2/ Introductions and small talk: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qa44S_B4xWQ Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 18
- 19. Addresses in English St Street Av Avenue Blvd Boulevard Rd Road Sq Square Flat (BrE) = Apartment (AmE) 5, Sant Bartomeu St, 1st-2nd (number, street, floor, door) 08172 SANT CUGAT DEL VALLÈS (zip code, town or city) BARCELONA (area) SPAIN (country) Where do you live ? What’s your address ? Do you live in an apartment or in a house? What’s your home/land phone number? Have you got an alternate phone? Have you got an e-mail address? @ = “at” . = “dot” What’s your Social Security Number? What is your marital status? Are you married or single? What’s the title of the job? What’s your birth date? When were you born? I was born on 27th June 1971 (nineteen seventy-one) Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 19
- 20. In, At, On + Time or Date When is your birthday? Mine is ON October 12. When do you eat lunch? I usually eat it AT noon. When does the school year begin in your country? In mine it begins IN September. Do you know which preposition to use before times, days, months and years? Here is a reminder. Don't forget to use... in + month or year- In March, In 2003 on + date (with the year or without it) or day of the week- On April 2, On March 3, 1999, On Saturday at + clock time, midnight, noon- At 3:30 p.m., At 4:01, At noon Remember also... in + season- In the summer, In the winter in + morning, afternoon, evening- In the morning, In the evening at + night- At night Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 20
- 21. POSSESSIVE ADJECTIVES (revision) My car el meu cotxe My cars els meus cotxes Your car el teu cotxe / el vostre cotxe Your cars els teus cotxes / els vostres cotxes His car el seu cotxe (d’ell) Her cars els seus cotxes (d’ella) Their car el seu cotxe (d’ells) Their cars els seus cotxes (d’ells) ADVERBS OF FREQUENCY Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 21
- 22. WH Question Words We use question words to ask certain types of questions. We often refer to them as WH words because they include the letters WH (for example WHy, HoW). Question Word Function Example what asking for information about something What is your name? asking for repetition or confirmation What? I can't hear you. You did what? what...for asking for a reason, asking why What did you do that for? when asking about time When did he leave? where asking in or at what place or position Where do they live? which asking about choice Which colour do you want? who asking what or which person or people (subject) Who opened the door? whose asking about ownership Whose are these keys? Whose turn is it? why asking for reason, asking what...for Why do you say that? why don't making a suggestion Why don't I help you? how asking about manner How does this work? asking about condition or quality How was your exam? how + adj/adv asking about extent or degree see examples below how far distance How far is Pattaya from Bangkok? how long length (time or space) How long will it take? how many quantity (countable) How many cars are there? how much quantity (uncountable) How much money do you have? how old age How old are you? Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 22
- 23. PUBLIC HOLIDAYS IN ENGLAND Federal holiday: public holiday in a federation National holiday: in Catalonia, 11th September Public holiday: a holiday established by law. It’s a non-working day Bank holiday: colloquialism for “public holiday” in England Abans del 1834 el Banc d’Anglaterra va fixar 33 dies i festivals religiosos com a festius, però en 1834 aquests es van reduïr a 4: 1st May (or May Day), 1st November (All Saints Day), Good Friday (divendres Sant) i Christmas Day. Actualment a Anglaterra hi ha vuit festius d’aquest tipus: New Year’s day Good Friday Easter Monday 1st May Last Monday in May Last Monday in August Christmas Day Boxing Day (Saint Stephen’s Day) HALLOWEEN 2014 October 31 is Halloween. On Halloween, children wear costumes and go trick-or-treating. They knock on doors and say "Trick or treat." The person who opens the door gives the children sweets. The children say "Thank you." Adults like Halloween, too. They like to wear costumes to work and attend parties. Orange and black are popular Halloween colours. Orange is the colour of pumpkins and black is the colour of darkness. Halloween is a fun holiday, but it is not a federal holiday. When is Halloween? It is on October 31. In 2014, it is on a Friday. On October 31 we say "Happy Halloween!" Halloween is not a federal holiday. What is the child in this picture doing? He is selecting a pumpkin. On Halloween, people cut faces on pumpkins and put candles inside of them. They light the candles at night. What are these children wearing? They are wearing Halloween costumes. The witch is wearing a black dress and a tall black hat. Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 23
- 24. What are these children doing? They are trick-or-treating. They are waiting for someone to open the door and give them candy. Who are these people? They are pumpkinscarecrows. The woman is on the left and the man is on the right. What kind of house is this? It is a haunted house. A full moon is out. What is the skeleton doing? He is holding a lantern and waiting for the ship. Ghosts live on the ship. Who is this woman? She is a fortune teller. She can tell the future by looking into the crystal ball. Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 24
- 25. ONLINE LISTENING ACTIVITIES Grammar – Simple present: http://www.simpleenglishvideos.com/carters-breakfast/ Greetings and meetings (listen and repeat): http://www.simpleenglishvideos.com/meeting-and-greeting/ Address (AmE) or addrEss (BrE) (la majúscula indica on recau l’accent tònic) http://www.simpleenglishvideos.com/jennifer/ Make or do http://www.simpleenglishvideos.com/make-or-do/ Make or do (fixed expressions) http://www.simpleenglishvideos.com/make-and-do-fixed-expressions/ Wh questions https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mLefVAvKsRk&list=UUicjynhfFw2LiIQFnoS1JTw&i ndex=42 How to pronounce “the” in English https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GTLLy0cftBQ&list=UUicjynhfFw2LiIQFnoS1JTw&i ndex=58 Different ways to say “thank you” in English https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CMIXAqAy5HE&index=61&list=UUicjynhfFw2LiIQ FnoS1JTw Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 25
- 26. Pronunciation tips /dis/ /di:s/ (HERE) El modisme “veritat?” /dat/ Després de la frase posem una coma I afegim el verb canviant el “signe” (en negatiu si la frase està en afirmatiu, I en afirmatiu si la frase està en negatiu) seguit del subjecte: You are Spanish, aren’t you? (ets espanyol, oi?) She isn’t married, is she? (està casada, oi?) You live in Madrid, don’t you? (vius a Madrid, oi?) You don’t speak Chinese, do you? (no parles xinès, oi?) She eats a banana, doesn’t she? (ella menja un plàtan, oi?) She doesn’t go to Paris, does she? (ella no va a París, oi?) Simple present vs present continuous Simple present Present continuous (Verb) (To be + verb + ing) 1. for habitual actions 1. for actions happening now 2. for facts that are always true 2. actions happening in this period of time 3. for feelings or thoughts Example: I run Example: I am running What are they doing? He is buying a newspaper They are running She is eating an ice-cream I am listening to you He is walking slowly Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 26 (THERE) /dous/
- 27. The time in English What time is it? It’s……. 20:15 It’s a quarter past eight 19:45 It’s a quarter to eight 20:00 It’s eight o’clock 20:30 It’s half past eight 20:05 It’s five past eight 20:40 It’s twenty to nine Ten Expressions to say goodbye Expression: How to use the expression: Bye! The most common Goodbye! A little more formal Bye for now! Informal and friendly. They mean that you expect to see the other See you! person again soon. See you later! See you soon! I’m off Informal and not very polite. You are leaving without a farewell greeting Cheerio! Informal and old fashioned Catch you later! Very informal. You expect to see the other person again soon Good night! We only say it at night (when you go home at night or when you go to bed) Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 27
- 28. Other examples with ¨See you…”: See you tomorrow See you in an hour See you at work Vocabulary and expressions Lucky you! Quina sort que tens! Good luck! Bona sort! It seems so Ho sembla To take off enlairar-se To land aterrar Survival English, course 2014-2015 Grammar and vocabulary, page 28