2 23 Gases Review
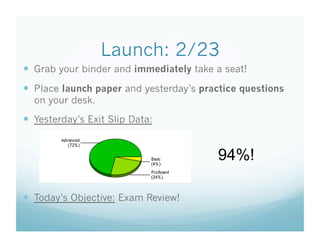
- 1. Launch: 2/23 Grab your binder and immediately take a seat! Place launch paper and yesterday’s practice questions on your desk. Yesterday’s Exit Slip Data: 94%! Today’s Objective: Exam Review!
- 2. Launch: 2/23 Grab your binder and immediately take a seat! Place launch paper and yesterday’s practice questions on your desk. Yesterday’s Exit Slip Data: 87% Today’s Objective: Exam Review!
- 3. Launch: 2/23 Grab your binder and immediately take a seat! Place launch paper and yesterday’s practice questions on your desk. Yesterday’s Exit Slip Data: 93%! Today’s Objective: Exam Review!
- 4. Launch: 2/23 Grab your binder and immediately take a seat! Place launch paper and yesterday’s practice questions on your desk. Yesterday’s Exit Slip Data: N/A Today’s Objective: Exam Review!
- 5. Launch 2/23 1. What is the combined gas law?
- 6. Launch 2/23 3. Choose the right equation. At a constant temperature, a sample of CO2 gas occupies a volume of 20mL at 2 atm. What will the volume of the gas be if the pressure is increased to 20 atm? a. P1 P2 = V T1× V1 = T2× V2 V1 2 b. V1 V2 P1× V1 = P2× V2 = T T1 2
- 7. Launch 2/23 3. The temperature of a gas at 80mmHg is decreased from 100K to 50K at constant volume. What is the new gas pressure? a. 40 mmHg b. 50 mmHg c. 500 mmHg d. 800 mmHg
- 8. Announcements Today is a really important day! 50 points for A-level review notes 50 points for A-level review worksheet Exam on Thursday! Jeopardy tomorrow? For extra help, come in: Before school (7:15am – 8:05am) At lunch
- 9. February Calendar Quiz! Today Exam!
- 10. Unit #7 Exam Review: Gases Mr. Heffner 2/22/10
- 11. What is kinetic molecular theory? Kinetic molecular theory states that… gas molecules move fast and randomly
- 12. What is diffusion? Diffusion is… the process by which gases mix Gas B Gas A random movement
- 13. Example #1 If gas molecules are fast, why is there a delay in smelling vinegar across a room?
- 14. What is temperature? Temperature is… movement a measure of the kinetic energy in a substance °C and K K = °C + 273
- 15. Example #2 Convert 37°C to Kelvin. plug & chug K = °C + 273 K = (37) + 273 K = 310 310 K
- 16. What is pressure? Pressure is… created by random collisions with a surface atm & mmHg temperature = collisions = pressure T & P are directly related
- 17. What is Absolute Zero & STP? standard temperature & pressure Absolute Zero STP all motion stops! standard for experiments Temp = 0K -273°C Temp = 0°C 273K Pressure = 0 atm Pressure = 1 atm 760mmHg
- 18. Example #3 Which of the following correctly show the conditions at STP? a. 0 atm and 0°C b. -273°C and 1 atm c. 0K and 760mmHg d. 760mmHg and 273K
- 19. What is volume? Volume is… the space that an object takes up L & mL temperature = volume T & V are directly related
- 20. What is the combined gas law? The combined gas law is… P1× V1 P2× V2 = T1 T2 There is a 3 step process for solving gas equations: 1. Write down the combined gas law 2. Circle given units and cross out the extras 3. Re-write the equation, plug-in, and solve!
- 21. Example #4 At constant volume, a gas at 100K and 8 atm is cooled to 25K. What is the new gas pressure? Step 1: Write down the combined gas law P1× V1 P2× V2 = T1 T2
- 22. Example #4 At constant volume, a gas at 100K and 8 atm is cooled to 25K. What is the new gas pressure? Step 2: Circle the given units and cross out the extras P1× V1 P2× V2 = T1 T2
- 23. Example #4 At constant volume, a gas at 100K and 8 atm is cooled to 25K. What is the new gas pressure? Step 3: Re-write the equation, plug-in, and solve!. cross- P1 8atm P2 multiply = T ✕ 25K T1 100K 2 (P2)(100K) = (8 atm)(25K) 100K 100K P2 = 2 atm
- 24. Practice Questions Review worksheet
- 25. Closing Study Hard! Unit #7 Exam in 2 days!
- 26. Exit Slip 1. How do gas molecules move? a. in a random pattern, colliding with other gas molecules as they move around b. they move in a straight line c. they always move from areas of low concentration to high concentration d. like ions found in a crystal lattice of NaCl
- 27. Exit Slip 2. Water boils at 373K. What is that temperature in Celsius? a. -100K b. 100K c. 173K d. 646K
- 28. Exit Slip 3. Would you expect a gas at 100°C to have a higher pressure than a gas at 0°C? a. No, because it has less kinetic energy b. No, because it has a higher temperature c. Yes, because it has more random collisions d. Yes, because it has less kinetic energy
- 29. Exit Slip 4. How are P & V related? a. They are directly related. b. An increase in volume increases pressure. c. They change in the opposite direction d. They are indirectly related
- 30. Exit Slip 4. The volume of 400mL of Ne gas at 100mmHg is decreased to 200mL at constant temperature. What is the new gas pressure? a. .5 mmHg b. 200 mmHg c. 200 mL d. 2000 mmHg
- 31. Homework Finish practice questions