More Related Content Similar to Osteosarcoma[2] Similar to Osteosarcoma[2] (20) More from orthoprince (20) 2. Overview
2
Definition
Epidemiology
Pathogenesis Parosteal osteosarcoma
Skeletal distribution Periosteal osteosarcoma
Clinical presentation High grade surface
Evaluation
osteosarcoma
High grade
osteosarcoma
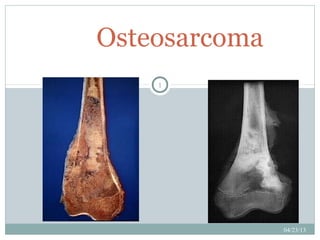
3. Definition
3
2nd most common primary bone tumor
Malignant tumor of mesenchymal origin
Spindle shaped cells that produce osteoid
5. Epidemiology
5
Primary vs secondary
Male : female
Li Fraunie syndrome
6. Pathogenesis
6
Unknown
Modal incidence correlates with rapid bone growth
Radiation exposure
Cancer survivors
Retinoblastoma
9. Clinical Presentation
9
Painful mass arising from bone
Trauma
Metastisize early in evolution
20% clinically detectable mets at dx
10. Evaluation
10
Suspected diagnosis by hx and physical
Supported by xray
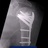
11. Plain Xray
11
Lytic, sclerotic or mixed
Typical characteristics of malignant tumor
Enneking’s 4 questions
13. Local
13
CT
MRI
+/- Angiogram
17. Systemic
17
Bone scan
CT Chest
lab
18. Classic High Grade Osteosarc
18
Age, sex
Presentation
Physical exam
Blood work
Plain films
Site
size
19. Differential Dx
19
Giant Cell Tumor
Aneursymal Bone Cyst
Ewings
Osteoblastoma
Metastasis
Lymphoma
20. Biopsy
20
Principles
Dx “high grade osteosarcoma”
Now What??
21. Chemotherapy
21
Micro metastasis
What we have learned pre chemo (1970’s)
Multi Institutional Osteosarcoma Study
22. Chemotherapy
22
Chemo cannot control clinically detectable disease
Radiation is ineffective
Local control is surgical
23. Chemotherapy
23
Best protocol is subject of ongoing trials
Drugs
Doxorubicin
Cisplatin
Ifosfamide
Methotrexate
Cyclophosphamide
Side effects
24. Induction Chemotherapy
24
Arose in conjunction with development of limb
sparing surgery
Increase survival
prognostic
25. Surgery
25
Limb salvage the norm
Now safer procedure
Wide surgical margin
26. Surgical options
26
Articular surface removed
Osteoarticular allograft replacement
Custom modular prosthesis
Allograft prosthesis composite
Allograft arthodesis
Segment of diaphysis missing
Intercalary allograft
27. Surgery
27
Young patient with open growth plate
Rotatioplasty
Conventional amputation
29. Surgery
29
Indication for amputation
Grossly displaced pathologic fracture
Encasement of neurovascular bundle
Tumor that enlarges during preop chemo and is adjacent
to neurovascular bundle
30. Current Standard of Care
30
Pretreatment radiologic staging
Bx to confirm diagnosis
Preoperative chemotherapy
Repeat radiologic staging
(access chemo response, finalize surgical tx plan)
Surgical resection with wide margin
Reconstruction using one of many technoques
Post op chemo based on preop response
32. Parosteal
32
5% of osteosarcomas
Posterior metaphysis of distal femur
Slow growing large ossified mass
Confused with osteochondroma
String sign
Low grade
treatment
35. Periosteal Osteosarcoma
35
Arises from surface of diaphysis
Characterized by bony spicule formation
perpendicular to shaft
Sunburst
Low grade
Wide excision
36. High grade surface
36
Very rare
20-30’s
Appearance as parosteal but histology high grade
Tx as classic intermedullary