Engmech 06 (equilibrium of non_concurrent force system)
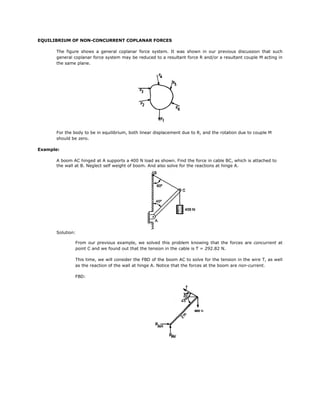
- 1. EQUILIBRIUM OF NON-CONCURRENT COPLANAR FORCES The figure shows a general coplanar force system. It was shown in our previous discussion that such general coplanar force system may be reduced to a resultant force R and/or a resultant couple M acting in the same plane. For the body to be in equilibrium, both linear displacement due to R, and the rotation due to couple M should be zero. Example: A boom AC hinged at A supports a 400 N load as shown. Find the force in cable BC, which is attached to the wall at B. Neglect self weight of boom. And also solve for the reactions at hinge A. Solution: From our previous example, we solved this problem knowing that the forces are concurrent at point C and we found out that the tension in the cable is T = 292.82 N. This time, we will consider the FBD of the boom AC to solve for the tension in the wire T, as well as the reaction of the wall at hinge A. Notice that the forces at the boom are non-current. FBD:
- 2. ∑ MA = 0 (Consider CCW rotation Positive) (T sin 75 o )(2 m) − (400N sin 45 o )(2m) = 0 T = 292.82 N To solve for the reactions at the hinge A; we will take the summation of forces at the horizontal and vertical directions. [∑ F x = 0] → + R AH − (292.82N) cos 30 o = 0 RAH = 253.59 N [∑ Fy ] =0 ↑+ R AV + (292.82N) sin 30 o − 400 = 0 RAV = 253.59 N Assignment: (1) An 8 kg slender rod AB is attached to two collars which may slide along guides without friction shown. Determine for equilibrium of rod AB (a) Angle θ (b) the reactions at A and B. Ans. 49.11o, RA = 45.31 N, RB = 90.62 N (2) A slender rod of length “L” and weight “W” is held in equilibrium position as shown. Determine the angle θ and tension in each cable. Ans. TAB = 0.596W, θ = 59.21o, TCD = 1.164W
- 3. (3) A 3m bar AB of negligible weight is to be kept in horizontal position as shown; Neglecting friction, determine distance ‘x’ if P = 300N. Also find the value of ‘P’ if x = 1.5m. (4) A 200 N cylinder is supported on an 80 N member AB. Find ‘W’ to be attached to the rope neglecting friction mass and size of pulley. Take diameter of cylinder 750 mm and length of member AB to be 3m. What will be components of reaction at end A? Ans. W=117.65N, HA= 98.1N, VA= 221.18N (5) A 150 N weight is held in equilibrium by a 5 kg uniform bar AB hinged at A as shown. Determine (a) components of reactions at A and (b) tension in cable DC. Take length of bar 1m. Ans. T = 604.6 N, HA = 302.3 N, VA = 324.5 N
- 4. (6) Rod AB is bent in the form of arc of a circle of 0.6m radius. Neglecting friction, obtain components of reactions at A and reaction at roller C. Ans. RC = 2W, HA = 0, VA = 1.732W (7) A 18 kg bar has small wheels at ends A and B. Knowing that length of bar AB is 1m, determine the reactions at A and B. Also find tension in cord. Neglect size and weight of rollers. Ans. RB = 152.9N, RA = 0, T = 233.6N Reference: Elements of Civil Engineering and Engineering Mechanics by SP Nitsure © 2007 Technical Publications Pune Textbook in Applied Mechanics by MM Malhotra © 1994 New Age International (P) Ltd., Publishers