23204904
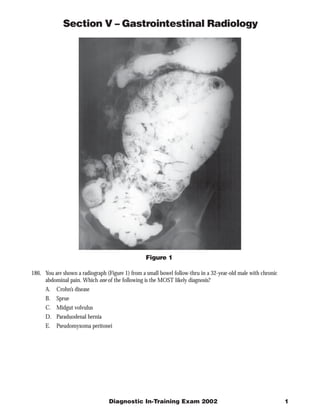
- 1. Section V – Gastrointestinal Radiology Figure 1 186. You are shown a radiograph (Figure 1) from a small bowel follow-thru in a 32-year-old male with chronic abdominal pain. Which one of the following is the MOST likely diagnosis? A. Crohn’s disease B. Sprue C. Midgut volvulus D. Paraduodenal hernia E. Pseudomyxoma peritonei Diagnostic In-Training Exam 2002 1
- 2. Section V – Gastrointestinal Radiology Question #186 Findings: The radiograph demonstrates encapsulation of jejunal loops in the left mid abdomen. Rationales: A. Incorrect. Crohn’s disease involves the small bowel in 75% of patients at the time of presentation. Affected segments show fold thickening and ulceration. Sinus tracts and fistulae are also noted. Although surrounding fibrofatty proliferation may produce a mass effect or displace bowel on SBFT, encapsulation of bowel loops is not noted with Crohn’s disease. B. Incorrect. Sprue or gluten sensitive enteropathy produces villous atrophy and radiographically shows reversal of the normal fold pattern with loss of normal jejunal folds and an increased number of folds per inch in the ilium. Transient intussusceptions, hypomotility and flocculation of barium can also be seen. However, none of these findings are present on this film. C. Incorrect. Midgut volvulus is produced by twisting of small bowel loops around the shortened mesenteric vascular pedicle in patients with congenital small bowel malrotation. A corkscrew deformity of the jejunal loops is noted on SBFT. Obstruction to venous return produces edema and hence thickened folds in the involved bowel. Such changes are not noted on this film. D. Correct. Internal hernias are abnormal protrusions of intraabdominal structures through a normal opening or through a congenital or acquired defect in fascia or mesentery. Encapsulation of jejunal bowel loops in either the right or left mid abdomen is characteristic of paraduodenal hernia - the most common type of internal hernia. The amount of contained small bowel can vary from a few loops to the majority of the small bowel. Patient typically present with intermittent abdominal pain thought to be secondary to episodes of obstruction. Left sided paraduodenal hernia is more common than right sided paraduodenal hernia. E. Incorrect. Pseudomyxoma peritonei results from seeding of the peritoneal cavity by benign or malignant mucin secreting cells. The cells typically come from a ruptured mucinous cystadenoma or cystadenocarcinoma of the appendix or ovary. Though bowel can be distorted, obstructed or tethered by tumor or mucin, encapsulation as noted here is not seen. Citations: Maglinte DDT, Bisset III GS, Congenital and Developmental Anomalies of the Small Bowel in Adolescents and Adults pp 247-251 in Clinical Imaging of the Small Intestine 2nd ed, eds Herlinger H, Maglinte DDT, and Birnbaum BA, Springer, New York, 1999. 2 American College of Radiology
- 3. Section V – Gastrointestinal Radiology Figure 2 187. You are shown a contrast-enhanced CT (Figure 2) in an 84-year-old male with recent weight loss and guaiac positive stool. Which one of the following is the MOST likely diagnosis? A. Desmoid tumor B. Intussusception C. Internal hernia D. Lipomatous ileocecal valve E. Volvulus Diagnostic In-Training Exam 2002 3
- 4. Section V – Gastrointestinal Radiology Question #187 Findings: The CT image demonstrates a long colo-colic intussusception involving the ascending and transverse colon Rationales: A. Incorrect. Desmoid tumors are non metastasizing but locally invasive fibrous tumors. They can occur either in isolation or more commonly in association with Gardner’s syndrome, particularly following abdominal surgery. They may present as an abdominal mass or cause bowel obstruction. On CT they appear as a soft tissue mass in the mesentery either with well circumscribed or infiltrative margins. These findings are not present in this case. B. Correct. The image demonstrates a long segment colo-colic intussusception. The vast majority of adult colo- colic intussusceptions have a malignant lead point with adenocarcinoma being the most common histologic type. The extensive edema seen with the intussusception often makes it difficult to delineate the precise lead point. C. Incorrect. Internal hernias are abnormal protrusions of intraabdominal structures through a normal opening or through a congenital or acquired defect in fascia or mesentery An internal. The most common type is the paraduodenal hernia shown in the previous question. Although internal hernias can cause distortion of bowel loops they would not produce the bowel within bowel appearance noted here. D. Incorrect. Lipomatous ileocecal valve is caused by submucosal infiltration of fat into the lips of the I-C valve. It is typically seen in older patients and is more common in women. Symptoms are usually absent. Although the mass can mimic an adenocarcinoma its fatty density on CT and smooth contour usually allow differentiation. The mass in this case is predominantly soft tissue density and much larger and more extensive and irregular than a lipomatous I-C valve. E. Incorrect. A volvulus involving the bowel is produced by twisting of small bowel loops around a point of fixation. In midgut volvulus associated with malrotation the point of fixation is the shortened mesenteric vascular pedicle. Volvulus involving fewer bowel loops may also occur around an acquired adhesive band. On CT a swirling appearance of vessels is seen in conjunction with obstructed small bowel loops. Although arcing vessels are seen in this case, they are entering the ascending colon rather than twisting around a point of fixation. Citations: Gore RM, Eisenberg RL, Large Bowel Obstruction pp1247-1260 in Textbook of Gastrointestinal Radiology eds Gore RM, Levine MS, Laufer I, W.B.Saunders, Philadelphia, 1994 4 American College of Radiology
- 5. Section V – Gastrointestinal Radiology Figure 3 188. You are shown a radiograph (Figure 3) of the splenic flexure from a double contrast barium enema in a 35-year-old female with diarrhea and abdominal pain. Which one of the following is the MOST likely diagno- sis? A. Typhlitis B. Ulcerative colitis C. Toxic megacolon D. Crohn’s disease E. Pseudomembranous colitis Diagnostic In-Training Exam 2002 5
- 6. Section V – Gastrointestinal Radiology Question #188 Findings: The radiograph demonstrate areas of irregular colonic narrowing and ulceration. More normal caliber bowel is also noted but demonstrates multiple small aphthous lesions. Rationales: A. Incorrect. Typhlitis refers to an acute enterocolitis associated with immunosuppression and neutropenia. The disease predominantly involves the cecum and right colon and is characterized by marked wall edema and inflammation. Diagnosis is usually suggested by CT or plain film in conjunction with the clinical setting. Barium enema or colonoscopy may place the patient at risk of perforation when inflammation is severe. The appearance of aphthous lesions and irregular areas of colonic narrowing and ulceration in the splenic flexure would not be typical for typhlitis. B. Incorrect. Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease, predominantly limited to the mucosa, with a peak age of onset of 15 to 25 years. The barium enema findings involve the rectum and extend proximally to a variable extent, often involving the entire colon. Mucosal abnormalities in acute active disease include granularity, mucosal stippling, collar button ulceration and inflammatory pseudopolyp formation. In patients with chronic disease, there can be narrowing of the colonic lumen, loss of haustration and shortening of the colon. The discontinuous irregular involvement noted in this case in addition to the presence of aphthous lesions are strongly against the diagnosis of UC. C. Incorrect. Toxic megacolon is characterized by an ill, toxic appearing patient with diffuse colonic dilatation. The colon will also demonstrate loss of haustral folds and an irregular nodular mucosal surface corresponding to ulcerations and inflammatory pseudopolyps. Barium enema is contraindicated in patients with toxic megacolon, because of a risk of perforation. Causes include ulcerative colitis as well as infectious colitis. D. Correct. Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that, like UC has a peak age of onset of 15 to 25 years. Unlike UC however, Crohn’s disease is characterized by transmural inflammation with aphthous lesions and discontinuous areas of mucosal ulceration and narrowing. Sinus tracts and fistulae are also common as is small bowel involvement which occurs in 75% of patients at presentation. The appearance in this case would be typical for colonic involvement with Crohn’s disease. E. Incorrect. Pseudomembranous colitis is produced secondary to toxin producing Clostridium difficile infection. The disease usually follows the administration of broad spectrum antibiotics and produces watery diarrhea, fever, abdominal pain and leukocytosis. Moderate large bowel dilation with thumbprinting is noted on abdominal plain film exam. On barium enema small irregular plaque like filling defects or small nodules are noted. In severe cases the luminal margin may appear irregular from poor mucosal coating. These changes are not noted in this case. Citations: Gore RM, Laufer I, Ulcerative and Granulomatous Colitis: Idiopathic Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Textbook of Gastrointestinal Radiology eds Gore RM, Levine MS, Laufer I, W.B.Saunders, Philadelphia, 1994 6 American College of Radiology
- 7. Section V – Gastrointestinal Radiology Figure 4A Figure 4B 189. You are shown a contrast-enhanced CT (Figure 4A and 4B) of a 25-year-old male with epigastric pain. Which one of the following is the MOST likely diagnosis? A. Mucinous ductectatic malignancy B. Cystic fibrosis C. von Hipple Lindau disease D. Tuberous sclerosis E. Solid and papillary epithelial neoplasm Diagnostic In-Training Exam 2002 7
- 8. Section V – Gastrointestinal Radiology Question #189 Findings: Multiple cysts are identified in the pancreas. A solid enhancing lesion is also noted in the left kidney. In addition an enhancing mass is noted involving the spinal cord. Rationales: A. Incorrect. Mucinous ductectatic tumor is a pancreatic mucinous tumor with an intraductal growth pattern. Both benign and malignant variants are reported. The median age of patients is in the 7th decade but unlike the usual mucinous cystic tumor, the lesion is more common in men than women. On CT cystic areas are noted along with distension of the pancreatic ducts with mucin. The appearance can mimic the changes of chronic pancreatitis. Duct distension is not noted in this case, nor would this entity explain the spinal and renal abnormalities noted above. B. Incorrect. Cystic fibrosis affects multiple epithelial tissues including sweat gland, lung, pancreas, and bowel. It is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait and occurs in 1 in 3000 Caucasian live births in the US. Pancreatic secretions in cystic fibrosis patients have increased viscosity and are thought to cause inspissation and resulting pancreatic atrophy. By 2 years of age more than 80% of patients will have evidence of pancreatic insufficiency. On CT the pancreas often demonstrates diffuse fatty replacement. Less commonly replacement of the gland by multiple macroscopic cysts occurs. Although multiple cysts are seen in this patient, cystic fibrosis would not explain the renal or CNS masses. C. Correct. von Hippel Lindau disease is characterized by cysts and or neoplasm in multiple organs including the pancreas, kidney, liver, epididymis and CNS. It is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion. Onset of symptoms is typically in the third to fifth decade. Commonly associated lesions include hemangioblastomas (seen in retina, cerebrum, cerebellum and spinal cord) renal carcinoma and hemangioblastomas, pancreatic cysts and cystadenomas, and epididymal cysts. The pancreatic cysts, renal carcinoma and spinal hemangioblastoma seen in this case would be typical for von Hippel Lindau disease. D. Incorrect. Tuberous sclerosis is an autosomal dominant syndrome which has skin, CNS, cardiovascular renal, and pulmonary manifestations. Renal lesions including intrarenal aneurysms, carcinoma, cysts and angiomyolipomas, are reported. The latter occur in 40-80% of patients and can cause spontaneous hemorrhage. Diagnosis of AMLs can be made by showing intratumoral fat on CT or MRI. Although CNS lesions occur, tuberous sclerosis would not be expected to present the pancreatic or spinal cord findings noted in this case. E. Incorrect. Solid and papillary epithelial neoplasm is an uncommon pancreatic tumor of young females. More than 95% of cases are found in adolescent or postadolescent girls and young women. The tumor is generally a large cystic and solid mass that frequently contains areas of necrosis and hemorrhage with fluid-debris levels. The sex of the patient and the morphologic appearance of the tumor in the test patient make solid and papillar y epithelial neoplasm an unlikely diagnosis. Citations: Stanley RJ, Semelka RC, Pancreas in Computed Body Tomography with MRI Correlation third ed., eds Lee JKTL, Sagl SS, Stanley RJ, and Heiken JR, Lippincott-Raven, New York 1998. 8 American College of Radiology
- 9. Section V – Gastrointestinal Radiology Figure 5 190. You are shown an image from an endoscopic retrograde cholangiogram (Figure 5) in a 24-year-old female with painless jaundice. Which one of the following is the MOST likely diagnosis? A. Adenomyomatosis B. Mirizzi syndrome C. Sclerosing cholangitis D. Caroli’s disease E. Klatskin tumor Diagnostic In-Training Exam 2002 9
- 10. Section V – Gastrointestinal Radiology Question #190 Findings: The image demonstrates obstruction and dilation of the intra and extrahepatic biliary tree down to a point just above the juncture with the cystic duct. At this point there is thinning of the contrast column and an apparent filling defect outlined in the cystic duct. The CBD is normal in size. Rationales: A. Incorrect. Adenomyomatosis is characterized by hyperplastic changes in the wall of the gallbladder with formation of intramural diverticuli or Aschoff-Rokitansky sinuses. This may occur in a diffuse or segmental fashion. The clinical significance of this finding is uncertain, although it is important to differentiate it from other causes of gallbladder wall thickening such as carcinoma and cholecystitis. The intramural diverticuli do not typically involve the distal cystic duct and would not be responsible for the findings shown here. B. Correct. Mirizzi syndrome is partial or complete obstruction of the common hepatic duct associated with a stone lodged in the distal cystic duct. It occurs because the distal cystic duct and common hepatic duct are often bound together in a common sheath. The clinical presentation is often progressive jaundice and abdominal pain. The findings depicted here are typical for Mirizzi syndrome. C. Incorrect. Primary sclerosing cholangitis is an idiopathic disorder characterized by inflammation, fibrosis and strictures involving the intra and extrahepatic biliary tree. Ulcerative colitis is the most frequent associated condition and is present in 50-75% of cases. Men are affected twice as often as women. Symptoms are usually insidious in onset and consist of fatigue, right upper quadrant pain, jaundice and pruritus. Multiple short irregular strictures are seen at cholangiography diffusely distributed throughout the biliary tree. A beaded appearance of the ducts is often noted with bandlike strictures and small diverticulum like outpouchings occasionally seen. Such findings are not noted in this case. D. Incorrect. Caroli’s disease is a congenital disorder characterized by diffuse or segmental dilatation of the intrahepatic biliary tree. Two types have been characterized, a simple and a periportal fibrosis type. The latter is more common and is associated with congenital hepatic fibrosis, cirrhosis and portal hypertension. The former is associated with medullary sponge kidney. Patients usually present in early adulthood with symptoms of cholangitis (fever, chills, abdominal pain). An increased incidence of malignant transformation is also noted. The uniform dilation of the biliary tree down to the point of obstruction noted here would not be seen in Caroli’s disease. E. Incorrect. Klatskin tumor refers to a cholangiocarcinoma occurring at the confluence of the right and left bile ducts and common hepatic duct. An increased incidence of cholangiocarcinoma has been noted in patients with PSC and choledochal cyst as well as patients infested with Clonorchis sinensis or Opisthorchis viverrini. Patients usually present with painless jaundice. The peak incidence is around 65 years of age. The tumor typically appears as a short segmental stricture at the bifurcation and would not be consistent with the appearance shown here. Citations: Zeman RK, Cholelithiasis and Cholecystitis in Textbook of Gastrointestinal Radiology eds Gore RM, Levine MS, Laufer I, W.B.Saunders, Philadelphia, 1994 10 American College of Radiology
