Initiation &management of drug therapy
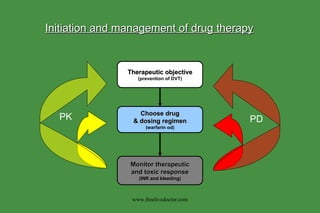
- 1. Therapeutic objective (prevention of DVT) Choose drug & dosing regimen (warfarin od) Monitor therapeutic and toxic response (INR and bleeding) PK PD Initiation and management of drug therapy www.freelivedoctor.com
- 3. Interpatient Variability - Pharmacokinetic factors: Absorption Generally maximal in upper SB - gastric emptying often rate limiting hence …. AUC increased by metoclopramide/erythromycin and reduced by atropinics, phenthiazines and antihistamines The Effect of food often unpredictable - may (INH, rifampicin or captopril) - or (chloroquine) Drugs with high first-pass (verapamil, propranolol) with food intake Specific effects of certain foods milk/antacids - tetracyclines grapefruit juice -felodipine/terfenadine First-pass metabolism * (inactivation before entering the systemic circulation) gut lumen insulin/benzylpenicillin gut wall tyramine/salbutamol liver propranolol, verapamil, lignocaine * Avoided by alternate route e.g. sl GTN, intranasal insulin, pr ergotamine www.freelivedoctor.com
- 4. Interpatient Variability - Pharmacokinetic factors: Elimination Liver disease (eg cirrhosis) affects first-pass by: (1) direct impairment of hepatocellular function; (2) shunting drug directly into the systemic circulation - increased bioavailability may be huge (eg 10-fold for chlormethiazole) - pro-drug activation may be severely impaired eg ACEIs - concomitant hypoalbuminaemia will complicate the picture if free fraction affects clearance - certain liver diseases have little PK impact eg acute viral hepatitis Renal impairment directly affects renal clearance as well as having indirect effects on protein binding and hepatic metabolism: - only binding of acidic drugs (eg warfarin/phenytoin) are affected HD does not restore reduced albumin binding but transplant does - reduced hepatic clearance (eg propranolol/nicardipine) depends on dialyzable factors in uraemic plasma www.freelivedoctor.com
- 6. Factors Affecting Metabolism by P450s: (1) INDUCTION by drugs or other environmental chemicals - increased metabolism reduces availability of parent drugs ( unless the metabolite is active when induction actually increases availability and toxicity) - generally family specific (2) INHIBITION by concommitant drugs - Competitive antagonism of specfic isoforms eg QUINIDINE (2D6) and FURAFYLLINE (1A2) - Haem-Fe binding eg CIMETIDINE, KETOCONAZOLE, ERYTHROMYCIN. - Suicide inhibitors eg OC (ethinyl oestradiol) and SECOBARB. (3) GENETIC POLYMORPHISMs within the CYP genes . - Subjects show extensive or poor metabolism of drugs transformed through specific P450s. Best characterized for CYP2D6 where PMs make up 10% of Caucasian subjects. Up to 20 alleles known and typable by PCR-RFLP (PHARMACOGENOTYPING). Agent Isoform Induced polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in cigarette smoke CYP1A anticonvulsants CYP3A chronic EtOH, acetone and isoniazid CYP2E1 www.freelivedoctor.com
- 8. Monitoring drug therapy 1. By Clinical Response Indication result to result to toxic signs dose dose Frusemide Heart Failure Urea Oedema Severe Dehydration hypotension Carbidopa/DOPA Parkinson’s Dyskinesias Poor Confusion Blepharospasm Control Depression Thiopentone Induction Anaesthesia Insufficient Respiratory Too Deep Anaesthesia Failure www.freelivedoctor.com
- 9. Indication result to result to toxic signs dose dose Warfarin TE disease high INR low INR Bleeding Thyroxine Hypothyroidism low TSH high TSH Hyperthyroidism Statin Raised cholesterol AST/CK high TC Myopathy Monitoring drug therapy 2. By an in Vitro Test of Therapeutic Effect www.freelivedoctor.com
- 17. Enzyme Induction/inhibition by Anticonvulsants: Phenytoin, phenobarb, CBZ Lamotrigine Valproate Felbamate Ethosuximide Gabapentin Tiagabine Vigabatrine * CYP/UGT UGT (weak) UGT/epoxidases/CYP2C 3A4 2C19 No Effect * =inhibition; / =induction (+/++) www.freelivedoctor.com