1. biomechanics of the knee joint basics
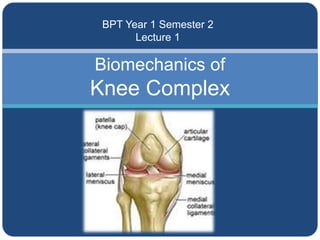
- 1. Biomechanics of Knee Complex BPT Year 1 Semester 2 Lecture 1
- 2. Contents 1. Introduction 2. Function 3. Tibio-femoral joint and Patellofemoral joint 4. Articular surfaces 5. Capsule, ligaments and Menisci 6. Muscles around the knee 2
- 3. Introduction Largest and one of the most complex joints Major stability and mobility roles 3
- 4. Functions: Functional shortening and lengthening of the extremity by flexion and extension Supports body during dynamic and static activities Closed kinematic chain- support body weight in static erect posture Dynamically- moving and supporting body in sitting and squatting activities, supporting and weight transferring activity during locomotion 4
- 5. Knee complex Tibio- femoral Patello-femoral 5
- 6. Tibio-femoral Joint Type of Joint? Double Condyloid joint Degrees of freedom of motion? Flexion/ Extension Medial/ Lateral rotation Adduction/ abduction 6
- 8. Articular surfaces Proximal Articular Surface: femoral condyles Medial condyle larger than lateral Distal Articular Surface: Tibial condyles- medial and lateral 8
- 9. Alignment of knee • The Anatomical axis of femur is oblique directed inferiorly and medially. • Anatomical axis of tibia is vertical. 9
- 10. Alignment of knee Normally knee forms lateral angle of 170o-175o Variation: Genu valgum or Knock knee- lateral angle < 170o Genu vaRum or bow leg- angle > 180o 10 Neumann, 2010
- 13. Menisci: Functions Improves congruence of joint Distributes weight bearing forces Decreases friction between tibia and femur Shock absorber 13
- 14. Nutrition First year of life: contains blood vessels throughout meniscal body Vascularity decreases with age Outer 25% is vasularized by capillaries from joint capsule and synovial membrane Central blood supply by diffusion from synovial fluid 14
- 15. Prolonged immobilization or non-weight bearing? Menisci does not receive appropriate nutrition Avascular nature of central portion of meniscus reduces potential of healing after injury In adults only peripheral portion of meniscus is vasularized hence is capable of inflammation, repair and remodeling after injury or tear. 15
- 16. Compression forces at the knee: While walking- 2.5 – 3 times body weight Ascending stairs: 4 times Menisci triples the surface area by significantly reducing the pressure on the articular cartilage Lateral menisectomy increases pressure at knee by 230% 16 Neumann, 2010
- 17. Mechanisms of meniscal injury Forceful, rotation of femoral condyle on partially flexed and weight bearing knee locked knee syndrome Medial meniscus is injured twice as much as lateral Risk of meniscal injury increases with instability 17
- 18. Test for Miniscal injury Apley’s Grinding Test McMurray’s Test 18
- 19. 19
- 20. • Capsule • Collateral Ligament • Cruciate ligament 20 Capsule and Ligaments
- 21. Capsule Encloses medial and lateral tibio-femoral joint and patello-femoral joint. Two layers of capsule: Fibrous layer Synovial layer 21
- 22. Capsule: Fibrous layer Three layers: 1. Extensor retinaculum: anteriorly 2. Fascial layer: distal quadriceps muscle 3. Deep: medial and lateral retinacula 22
- 23. Capsule: Synovial layer Internal surface of the capsule is lined by synovial membrane. Role: 1. secretion of synovial fluid 2. Absorption of fluid into joint for lubrication 3. Nutrition to avascular structure like menisci 23
- 25. Medial collateral ligament (MCL) • Originates from medial epicondyle of femur • Inserted into medial tibial plateau, medial meniscus, medial proximal tibia. • Restrains excess abduction and lateral rotation stress at knee 25
- 26. MCL: Applied aspect Injury when valgus stress is delivered over a planted foot. Common in football players MCL is rich in blood supply hence has good healing 26
- 27. Lateral collateral ligament (LCL) 27 Extracapsular Origin: Lateral femoral condyle Insertion: fibular head Checks Varus stress and excessive lateral rotation of tibia
- 28. Anterior cruciate ligament Posterior cruciate ligament Cruciate ligaments
- 29. 29
- 30. Anterior Cruciate Ligament 30 Inferior attachment: anterior tibial spine Extends superiorly, posteriorly to attach to the postero-medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle Two bands: Anteromedial band (AMB)- taut in flexion Postero-lateral band (PLB)- taut in extension
- 31. Anterior Cruciate Ligament 31 Functions: Restrains anterior translation of tibia on femur Prevents hyperextension of knee Secondary restraint against varus and valgus motion
- 32. Mechanism of injury- ACL Most common injury Football, downhill skiing, basketball and soccer players Mechanism: Common in weight bearing, slight flexion and rotation in either directions Anterior translatory force on proximal tibia Hyperextension injury Hyperflexion in bulky lower extremity muscles 32
- 33. Posterior Cruciate Ligament 33 • Origin: Posterior inter-condylar area of tibia • Insertion: Lateral side of Medial femoral condyle • Anteromedial and posterolateral bands
- 34. Functions- PCL Primary restraint to posterior translation of tibia on femur Limits the anterior translation of femur over fixed tibia in activities such as rapid descending into squat and landing from jump with partially flexed knee 34
- 35. Mechanism of injury- PCL Three mechanisms 1. Pretibial trauma (Dashboard trauma) 2. Hyper flexion (in thin individual) 3. Hyperextension (second ligament to be injured after ACL) 35
- 36. Muscles Aiding Tibial Translation Anterior Translation: 1. Quadriceps 2. Gastrocnemius Posterior Translation: 1. Soleus 2. Hamstring 36
- 37. Other ligaments Oblique popliteal ligament Anterolateral ligament (newer ligament) List out all other ligaments and its function referring to articles and reference text books 37
- 38. Bursae
- 39. Bursae 14 bursae Reduce friction between intertissue junction during movement. Activities that involve excess and repetitive force at inter tissue junctions frequently leads to Bursitis. 40
- 40. Bursae 41 Suprapatellar Prepatellar (Housemaid’s knee) Infrapatellar (Clergyman’s knee)
- 41. Bursitis 42 Prepatellar bursitis (housemaid’s knee) Infrapatellar bursitis (clergyman’s knee)
- 42. Plicae
- 43. Plicae Synovial membrane formation occurs in early embryonic development Synovial membrane separates medial and lateral articular surface into separate cavities By 12th week of gestation synovial septae reabsorbs to form a single joint cavity 44
- 44. Plicae Failure of complete resorption results in persistent folds called PLICAE Plicae may get inflamed or irritated- Plicae Syndrome 45
- 45. Summary Articular components Menisci Capsule MCL, LCL, ACL, PCL Ligaments Bursae Plicae 46
- 46. References: Neumann DA. Kinesology of musculoskeletal system, Foundation for Physical Rehabilitation , 2nd Edition Norkin C, Levengie P. Joint structure and function. 4th Edition Kapandji IA. The Physiology of Joints. Volume 2, Lower Limb. 5th Edition 47
Notas del editor
- In unilateral stance or during gait, weight bearing line must shift medially across the knee to account or to compensate for small BOS below the centre of mass. This shift increases compressive forces on medial compartment.
- Genu valgum: Mechanical axis shifts laterally Increased compressive forces laterally and tensile forces medially Lateral OA and medial laxity of structures Genu varum Mechanical axis shifts medially Increased compressive forces medially and tensile forces laterally Medial OA and lateral laxity of structures
- Locked knee syndrome- Torsion within the compressed knee can pinch and dislodge the meniscus. This can block knee movement causing locked knee. Medial meniscus is larger and less mobile, so more chances of injuries
- Locked knee syndrome
- Blood supply- middle genicular artery
