Study of Plants Introduction and Photosynthesis Lesson PowerPoint, Biology
- 1. What is the 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight Carbon Dioxide Water Oxygen Sugar
- 3. New Area of Focus: Kingdom Plantae.
- 4. • Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food
- 5. Plants: Have cell walls and make their own food (photosynthesis), and lack the power of locomotion. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 6. Plants are divided into Divisions instead of Phylums. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 7. “If you see that King Phillip, Tell him that King David wants his head.” Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 8. • What is a plant? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 9. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 10. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 11. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 12. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having a cell wall made of cellulose, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 13. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having a cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 14. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having a cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 15. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having a cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 16. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having a cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 17. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having a cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 18. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having a cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 19. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having a cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 20. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having a cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 21. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having a cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 22. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having a cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 23. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. – Photosynthetic – Makes sugar from light. – Eukaryotic – Cells with a nucleus. – Multi-cellular – Made of many cells. – Embryo – Young organism that grows inside. – Chloroplast – An organelle that does photosynthesis. – Cellulose – A complicated and strong sugar. – Locomotion – To move. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 24. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. – Photosynthetic – Makes sugar from light. – Eukaryotic – Cells with a nucleus. – Multi-cellular – Made of many cells. – Embryo – Young organism that grows inside. – Chloroplast – An organelle that does photosynthesis. – Cellulose – A complicated and strong sugar. – Locomotion – To move. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 25. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. – Photosynthetic – Makes sugar from light. – Eukaryotic – Cells with a nucleus. – Multi-cellular – Made of many cells. – Embryo – Young organism that grows inside. – Chloroplast – An organelle that does photosynthesis. – Cellulose – A complicated and strong sugar. – Locomotion – To move. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 26. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. – Photosynthetic – Makes sugar from light. – Eukaryotic – Cells with a nucleus. – Multi-cellular – Made of many cells. – Embryo – Young organism that grows inside. – Chloroplast – An organelle that does photosynthesis. – Cellulose – A complicated and strong sugar. – Locomotion – To move. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 27. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. – Photosynthetic – Makes sugar from light. – Eukaryotic – Cells with a nucleus. – Multi-cellular – Made of many cells. – Embryo – Young organism that grows inside. – Chloroplast – An organelle that does photosynthesis. – Cellulose – A complicated and strong sugar. – Locomotion – To move. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 28. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. – Photosynthetic – Makes sugar from light. – Eukaryotic – Cells with a nucleus. – Multi-cellular – Made of many cells. – Embryo – Young organism that grows inside. – Chloroplast – An organelle that does photosynthesis. – Cellulose – A complicated and strong sugar. – Locomotion – To move. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 29. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. – Photosynthetic – Makes sugar from light. – Eukaryotic – Cells with a nucleus. – Multi-cellular – Made of many cells. – Embryo – Young organism that grows inside. – Chloroplast – An organelle that does photosynthesis. – Cellulose – A complicated and strong sugar. – Locomotion – To move. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 30. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. – Photosynthetic – Makes sugar from light. – Eukaryotic – Cells with a nucleus. – Multi-cellular – Made of many cells. – Embryo – Young organism that grows inside. – Chloroplast – An organelle that does photosynthesis. – Cellulose – A complicated and strong sugar. – Locomotion – To move. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 31. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. – Photosynthetic – Makes sugar from light. – Eukaryotic – Cells with a nucleus. – Multi-cellular – Made of many cells. – Embryo – Young organism that grows inside. – Chloroplast – An organelle that does photosynthesis. – Cellulose – A complicated and strong sugar. – Locomotion – To move. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 32. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. – Photosynthetic – Makes sugar from light. – Eukaryotic – Cells with a nucleus. – Multi-cellular – Made of many cells. – Embryo – Young organism that grows inside. – Chloroplast – An organelle that does photosynthesis. – Cellulose – A complicated and strong sugar. – Locomotion – To move. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 33. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. – Photosynthetic – Makes sugar from light. – Eukaryotic – Cells with a nucleus. – Multi-cellular – Made of many cells. – Embryo – Young organism that grows inside. – Chloroplast – An organelle that does photosynthesis. – Cellulose – A complicated and strong sugar. – Locomotion – To move. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 34. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. – Photosynthetic – Makes sugar from light. – Eukaryotic – Cells with a nucleus. – Multi-cellular – Made of many cells. – Embryo – Young organism that grows inside. – Chloroplast – An organelle that does photosynthesis. – Cellulose – A complicated and strong sugar. – Locomotion – To move. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 35. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. – Photosynthetic – Makes sugar from light. – Eukaryotic – Cells with a nucleus. – Multi-cellular – Made of many cells. – Embryo – Young organism that grows inside. – Chloroplast – An organelle that does photosynthesis. – Cellulose – A complicated and strong sugar. – Locomotion – To move. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 36. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. – Photosynthetic – Makes sugar from light. – Eukaryotic – Cells with a nucleus. – Multi-cellular – Made of many cells. – Embryo – Young organism that grows inside. – Chloroplast – An organelle that does photosynthesis. – Cellulose – A complicated and strong sugar. – Locomotion – To move. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 37. • Activity! Definition of a plant – (Circle the words you don’t know) – Any of various photosynthetic, eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms of the Kingdom Plantae characteristically producing embryos, containing chloroplasts, having cell wall made of cellulose, and lacking the power of locomotion. – Photosynthetic – Makes sugar from light. – Eukaryotic – Cells with a nucleus. – Multi-cellular – Made of many cells. – Embryo – Young organism that grows inside. – Chloroplast – An organelle that does photosynthesis. – Cellulose – A complicated and strong sugar. – Locomotion – To move. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 38. • The most familiar Eukaryotic cells are Plants Cells and Animal Cells
- 39. • The most familiar Eukaryotic cells are Plants Cells and Animal Cells
- 40. • The most familiar Eukaryotic cells are Plants Cells and Animal Cells
- 41. • This is a picture of a plant cell. It has… Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 42. • This is a picture of a plant cell. It has… – Protective cell walls. – Chloroplast for photosynthesis. – Large storage vacuole that serves many purposes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 43. • This is a picture of a plant cell. It has… – Protective cell walls. – Chloroplast for photosynthesis. – Large storage vacuole that serves many purposes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 44. • This is a picture of a plant cell. It has… – Protective cell walls. – Chloroplast for photosynthesis. – Large storage vacuole that serves many purposes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 45. • This is a picture of a plant cell. It has… – Protective cell walls. – Chloroplast for photosynthesis. – Large storage vacuole that serves many purposes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 46. • This is a picture of a plant cell. It has… – Protective cell walls. – Chloroplast for photosynthesis. – Large storage vacuole that serves many purposes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 47. • This is a picture of a plant cell. It has… – Protective cell walls. – Chloroplast for photosynthesis. – Large storage vacuole that serves many purposes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 48. • Plant (Draw One instead of a definition ) – Include that it has plant cells instead of animal cells. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 49. • There are many varieties of plants called Divisions.
- 50. • Plants are extremely important to our lives. – Can you name 20 products that use materials from plants or the remains of plants. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 51. • Plants are extremely important to our lives. – Can you name 20 products that use materials from plants or the remains of plants. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 52. • Generated Class list.
- 53. • If a product is made of the following, it is made from plants, or old decomposed plants (oil). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 54. • If a product is made of the following, it is made from plants, or old decomposed plants (oil). – Any wood. – Any fiber / other than metals. – Plastics (most are oil based). – Chemicals (most are from plants). – All food. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 55. • If a product is made of the following, it is made from plants, or old decomposed plants (oil). – Any wood. – Any fiber / other than metals. – Plastics (most are oil based). – Chemicals (most are from plants). – All food. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 56. • If a product is made of the following, it is made from plants, or old decomposed plants (oil). – Any wood. – Any fiber / other than metals. – Plastics (most are oil based). – Chemicals (most are from plants). – All food. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 57. • If a product is made of the following, it is made from plants, or old decomposed plants (oil). – Any wood. – Any fiber / other than metals. – Plastics (most are oil based). – Chemicals (most are from plants). – All food. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 58. • If a product is made of the following, it is made from plants, or old decomposed plants (oil). – Any wood. – Any fiber / other than metals. – Plastics (most are oil based). – Chemicals (most are from plants and oils). – All food. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 59. • If a product is made of the following, it is made from plants, or old decomposed plants (oil). – Any wood. – Any fiber / other than metals. – Plastics (most are oil based). – Chemicals (most are from plants and oils). – All food. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 60. • If a product is made of the following, it is made from plants, or old decomposed plants (oil). – Any wood. – Any fiber / other than metals. – Plastics (most are oil based). – Chemicals (most are from plants and oils). – All food. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 61. • If a product is made of the following, it is made from plants, or old decomposed plants (oil). – Any wood. – Any fiber / other than metals. – Plastics (most are oil based). – Chemicals (most are from plants and oils). – All food. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 62. • If a product is made of the following, it is made from plants, or old decomposed plants (oil). – Any wood. – Any fiber / other than metals. – Plastics (most are oil based). – Chemicals (most are from plants and oils). – All food. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 63. • If a product is made of the following, it is made from plants, or old decomposed plants (oil). – Any wood. – Any fiber / other than metals. – Plastics (most are oil based). – Chemicals (most are from plants and oils). – All food. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 64. • If a product is made of the following, it is made from plants, or old decomposed plants (oil). – Any wood. – Any fiber / other than metals. – Plastics (most are oil based). – Chemicals (most are from plants and oils). – All food. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 65. • The energy flow of life occurs because of plants. Plants harness the energy from the sun, and pass it on to all other life forms. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 66. • The energy flow of life occurs because of plants. Plants harness the energy from the sun, and pass it on to all other life forms. – Except for extreme bacteria on the ocean floor and their predators that use chemosynthesis. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 67. Photosynthesis: Plants make sugar from sunlight. Light energy is turned into chemical energy (sugars are carbon based). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 68. Photosynthesis: Plants make sugar from sunlight. Light energy is turned into chemical energy (sugars are carbon based). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 69. Equation for Photosyntesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2
- 70. Equation for Photosyntesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2
- 71. Equation for Photosyntesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2
- 72. Equation for Photosyntesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2
- 73. Equation for Photosyntesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 Sunlight
- 74. Equation for Photosyntesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 Sunlight
- 75. Equation for Photosyntesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 Sunlight
- 76. • Photosynthesis is the process by which light energy is utilized to convert carbon dioxide and water into food to be used by plants. – Oxygen is released into the air during the process. (O2) – Light or solar energy is captured by chlorophyll (CHLOR-oh-phil), the green pigment in leaves. – It is then converted into chemical energy which is stored as starch or sugar. – These starches and sugars are stored in roots, stems and fruits. They are available to the plant as food or fuel. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 77. • Photosynthesis is the process by which light energy is utilized to convert carbon dioxide and water into food to be used by plants. – Oxygen is released into the air during the process. (O2) – Light or solar energy is captured by chlorophyll (CHLOR-oh-phil), the green pigment in leaves. – It is then converted into chemical energy which is stored as starch or sugar. – These starches and sugars are stored in roots, stems and fruits. They are available to the plant as food or fuel. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 78. • Photosynthesis is the process by which light energy is utilized to convert carbon dioxide and water into food to be used by plants. – Oxygen is released into the air during the process. (O2) – Light or solar energy is captured by chlorophyll (CHLOR-oh-phil), the green pigment in leaves. – It is then converted into chemical energy which is stored as starch or sugar. – These starches and sugars are stored in roots, stems and fruits. They are available to the plant as food or fuel. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 79. • Photosynthesis is the process by which light energy is utilized to convert carbon dioxide and water into food to be used by plants. – Oxygen is released into the air during the process. (O2) – Light or solar energy is captured by chlorophyll (CHLOR-oh-phil), the green pigment in leaves. – It is then converted into chemical energy which is stored as starch or sugar. – These starches and sugars are stored in roots, stems and fruits. They are available to the plant as food or fuel. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 80. • Photosynthesis is the process by which light energy is utilized to convert carbon dioxide and water into food to be used by plants. – Oxygen is released into the air during the process. (O2) – Light or solar energy is captured by chlorophyll (CHLOR-oh-phil), the green pigment in leaves. – It is then converted into chemical energy which is stored as starch or sugar. – These starches and sugars are stored in roots, stems and fruits. They are available to the plant as food or fuel. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 82. • Which of the following statements is false of photosynthesis? A.) Photosynthesis requires sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. B.) Oxygen and glucose are produced in photosynthesis. C.) Carbon Dioxide and water are produced. D.) In photosynthesis, plants use radiant energy from the sun to create chemical energy in the form of sugars. E.) None of the above. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 83. • Which of the following statements is false of photosynthesis? A.) Photosynthesis requires sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. B.) Oxygen and glucose are produced in photosynthesis. C.) Carbon Dioxide and water are produced. D.) In photosynthesis, plants use radiant energy from the sun to create chemical energy in the form of sugars. E.) None of the above. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 84. • Which of the following statements is false of photosynthesis? A.) Photosynthesis requires sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. B.) Oxygen and glucose are produced in photosynthesis. C.) Carbon Dioxide and water are produced. D.) In photosynthesis, plants use radiant energy from the sun to create chemical energy in the form of sugars. E.) None of the above. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 85. • Which of the following statements is false of photosynthesis? A.) Photosynthesis requires sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. B.) Oxygen and glucose are produced in photosynthesis. C.) Carbon Dioxide and water are produced. D.) In photosynthesis, plants use radiant energy from the sun to create chemical energy in the form of sugars. E.) None of the above. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 86. • Which of the following statements is false of photosynthesis? A.) Photosynthesis requires sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. B.) Oxygen and glucose are produced in photosynthesis. C.) Carbon Dioxide and water are produced. D.) In photosynthesis, plants use radiant energy from the sun to create chemical energy in the form of sugars. E.) None of the above. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 87. • Which of the following statements is false of photosynthesis? A.) Photosynthesis requires sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. B.) Oxygen and glucose are produced in photosynthesis. C.) Carbon Dioxide and water are produced. D.) In photosynthesis, plants use radiant energy from the sun to create chemical energy in the form of sugars. E.) None of the above. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 88. • Which of the following statements is false of photosynthesis? And the answer is… A.) Photosynthesis requires sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. B.) Oxygen and glucose are produced in photosynthesis. C.) Carbon Dioxide and water are produced. D.) In photosynthesis, plants use radiant energy from the sun to create chemical energy in the form of sugars. E.) None of the above. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 89. • Which of the following statements is false of photosynthesis? And the answer is… A.) Photosynthesis requires sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. B.) Oxygen and glucose are produced in photosynthesis. C.) Oxygen and glucose are produced. D.) In photosynthesis, plants use radiant energy from the sun to create chemical energy in the form of sugars. E.) None of the above. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 90. • Which of the following equations is true of photosynthesis? Pick the correct color. – 6O2 + C6H12O6 Energy 6CO2 + 6H2O – C6H12O6 + 6O2 Energy + Chloroplasts. – 6O2 + 6CO2 + 6O2 Energy + C6H12O6 – 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 – 6O2 + 6CO2 + Energy + C6H12O6 + 6O2 – Energy + 6H2O Energy + 6O2 + 6CO2 – CO2 + 3H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + O2 – 6CO2 + 6H2O Energy + 6CO2 + 6O2 – Energy 6O2 + C6H12O6 + 6CO2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 91. • The Answer is… – 6O2 + C6H12O6 Energy 6CO2 + 6H2O – C6H12O6 + 6O2 Energy + Chloroplasts. – 6O2 + 6CO2 + 6O2 Energy + C6H12O6 – 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 – 6O2 + 6CO2 + Energy + C6H12O6 + 6O2 – Energy + 6H2O Energy + 6O2 + 6CO2 – CO2 + 3H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + O2 – 6CO2 + 6H2O Energy + 6CO2 + 6O2 – Energy 6O2 + C6H12O6 + 6CO2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 92. • Answer: Blue – 6O2 + C6H12O6 Energy 6CO2 + 6H2O – C6H12O6 + 6O2 Energy + Chloroplasts. – 6O2 + 6CO2 + 6O2 Energy + C6H12O6 – 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 – 6O2 + 6CO2 + Energy + C6H12O6 + 6O2 – Energy + 6H2O Energy + 6O2 + 6CO2 – CO2 + 3H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + O2 – 6CO2 + 6H2O Energy + 6CO2 + 6O2 – Energy 6O2 + C6H12O6 + 6CO2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
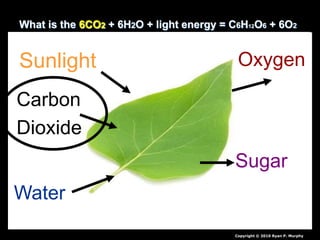
- 93. What is the 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight Carbon Dioxide Water Oxygen Sugar
- 94. What is the 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight Carbon Dioxide Water Oxygen Sugar
- 95. What is the 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight Carbon Dioxide Water Oxygen Sugar
- 96. What is the 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight Carbon Dioxide Water Oxygen Sugar
- 97. What is the 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight Carbon Dioxide Water Oxygen Sugar
- 98. What is the 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight Carbon Dioxide Water Oxygen Sugar
- 99. What is the 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight Carbon Dioxide Water Oxygen Sugar
- 100. What is the 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight Carbon Dioxide Water Oxygen Sugar
- 101. What is the 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight Carbon Dioxide Water Oxygen Sugar
- 102. What is the 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight Carbon Dioxide Water Oxygen Sugar
- 103. What is the 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight Carbon Dioxide Water Oxygen Sugar
- 104. • Activity! Use the white boards to memorize the equation for photosynthesis. Keep writing and erasing until you can do it repeatedly. • 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight Carbon Dioxide Water Oxygen Glucose
- 105. “Oh-No!” “We have to do it for the teacher.”
- 106. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 107. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 108. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 109. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 110. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 111. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 112. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 113. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 114. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 115. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 116. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 117. “Oh-No!” “Some people didn’t get to share their knowledge.”
- 118. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 119. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 120. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 121. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 122. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 123. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 124. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 125. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 126. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 127. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 128. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sunlight 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water 6 Oxygen Sugar C6H12O6
- 129. • Video Music Link! Photosynthesis Song – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wj8TGhcCnxs
- 130. “Oh-No!” “We are doing it again differently.”
- 137. • Which of the following equations is the correct equation for photosynthesis? • A) 6O2 + 6H2O + light energy = C12H6O6 + 6O2 • B) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • C) 6CO2 + 6O2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • D) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • E) 6CO2 + H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • F) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H2O6 + 6O2 • G) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • H) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O3 + 6O2 • I) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • J) C6H12O6 = 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 138. • Answer! Which of the following equations is the correct equation for photosynthesis? • A) 6O2 + 6H2O + light energy = C12H6O6 + 6O2 • B) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • C) 6CO2 + 6O2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • D) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • E) 6CO2 + H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • F) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H2O6 + 6O2 • G) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • H) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O3 + 6O2 • I) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • J) C6H12O6 = 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 140. • Try Again! Which of the following equations is the correct equation for photosynthesis? • A) 6O2 + 6H2O + light energy = C12H6O6 + 6O2 • B) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • C) 6CO2 + 6CO2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • D) 6CO2 + 6H2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • E) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • F) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H2O6 + 6O2 • G) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • H) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • I) 6CO2 + H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • J) C6H12O6 = 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 141. • Try Again! Which of the following equations is the correct equation for photosynthesis? • A) 6O2 + 6H2O + light energy = C12H6O6 + 6O2 • B) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • C) 6CO2 + 6CO2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • D) 6CO2 + 6H2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • E) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • F) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H2O6 + 6O2 • G) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • H) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • I) 6CO2 + H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • J) C6H12O6 = 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 142. • Almost finished! One more try. Find the Photosynthesis equation. • A) 6O2 + 6H2O + light energy = C12H6O6 + 6O2 • B) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • C) 6CO2 + 6O2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • D) 6CO2 + 12H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • E) 6O2 + 6H2O + light energy = C12H6O6 + 6O2 • F) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H2O6 + 6O2 • G) 6CO2 + 6H2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • H) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O6 • I) 6CO2 + 6H6O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • J) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = CH12O6 + 6CO2 • K) CO2 + 6H2O2 + light energy = CH12O6 + 6O2 • L) 6CO2 + 6H2O + no energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • M) 6O2 + 6H2O + light energy = C12H6O6 + 6O2 • N) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • O) 6CO2 + 6O2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • P) 6CO2 + 12H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • Q) 6O2 + 6H2O + light energy = C12H6O6 + 6O2 • R) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H2O6 + 6O2 • S) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • T) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O6 • U) 6CO2 + 6H6O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • V) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = CH12O6 + 6CO2 • W) CO2 + 6H2O2 + light energy = CH12O6 + 6O2 • X) 6CO2 + 6H2O + no energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • Y) 6CO2 + 6H2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • Z) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O6 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 143. • Answer! Almost finished! One more try. Find the Photosynthesis equation. • A) 6O2 + 6H2O + light energy = C12H6O6 + 6O2 • B) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • C) 6CO2 + 6O2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • D) 6CO2 + 12H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • E) 6O2 + 6H2O + light energy = C12H6O6 + 6O2 • F) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H2O6 + 6O2 • G) 6CO2 + 6H2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • H) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O6 • I) 6CO2 + 6H6O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • J) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = CH12O6 + 6CO2 • K) CO2 + 6H2O2 + light energy = CH12O6 + 6O2 • L) 6CO2 + 6H2O + no energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • M) 6O2 + 6H2O + light energy = C12H6O6 + 6O2 • N) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • O) 6CO2 + 6O2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • P) 6CO2 + 12H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • Q) 6O2 + 6H2O + light energy = C12H6O6 + 6O2 • R) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H2O6 + 6O2 • S) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • T) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O6 • U) 6CO2 + 6H6O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • V) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = CH12O6 + 6CO2 • W) CO2 + 6H2O2 + light energy = CH12O6 + 6O2 • X) 6CO2 + 6H2O + no energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • Y) 6CO2 + 6H2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • Z) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O6 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 144. • Remember: Producers create the sugars, then consumers use these sugars. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 145. • Remember: Producers create the sugars, then consumers use these sugars. Plants harness the energy from the sun so we can live. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 146. • Remember: Producers create the sugars, then consumers use these sugars. Plants harness the energy from the sun so we can live. “Thank you tree.” “Thank you for doing photosynthesis.” Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 147. • Remember: Producers create the sugars, then consumers use these sugars. Plants harness the energy from the sun so we can live. “I love your sugars that you produce from photosynthesis.” Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 148. Photosynthesis - - - - - - Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 149. Carbon dioxide is used. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 150. Water is used. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 151. Occurs in light Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 152. Occurs only in cells with chloroplasts. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 153. Produces sugar from light. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 154. Oxygen is released. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 156. • This PowerPoint is one small part of my Taxonomy and Classification Unit. • A Seven Part 3,000+ Slide PowerPoint full of engaging activities, critical class notes, review opportunities, question, answers, games, and much more. • 19 Page bundled homework that chronologically follows the slideshow for nightly review. Modified version provided as well as answer keys. • 24 pages of unit notes with visuals for students and support professionals. • 2 PowerPoint Review Games with Answer Key • Rubrics, videos, templates, materials list, First Day PowerPoint, guide, and much more. • http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Taxonomy_Classification_Unit. html
- 158. Areas of Focus within The Taxonomy and Classification Unit: Taxonomy, Classification, Need for Taxonomy vs. Common Names, What is a Species?, Dichotomous Keys, What does Classification Use?, The Domains of Life, Kingdoms of Life,The 8 Taxonomic Ranks, Humans Taxonomic Classification, Kingdom Monera, Prokaryotic Cells, Types of Eubacteria, Bacteria Classification, Gram Staining,Bacterial Food Borne Illnesses, Penicillin and Antiseptic, Oral Hygiene and Plaque, Bacterial Reproduction (Binary Fission), Asexual Reproduction, Positives and Negatives of Bacteria, Protista, Plant-like Protists, Animal-like Protists, Fungi-like Protists, Animalia, Characteristics of Animalia, Animal Symmetry, Phylums of Animalia (Extensive), Classes of Chordata, Mammals, Subclasses of Mammals, Characteristics of Mammals, Classes of Fish, Fashion a Fish Project, Animal Poster Project, Fungi, Positives and Negatives of Fungi, Divisions of Fungi (Extensive), Parts of a Mushroom, 3 Roles of Fungi, Fungi Reproduction, Mold Prevention, Plant Divisions, Photosynthesis, Plant Photo Tour, Non Vascular Plants, Algae, Lichens, Bryophytes, Seedless Vascular Plants, Cone Bearing Plants, Flowering Plants, Monocotyledons, Dicotyledons and much more. Full Unit can be found at… http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Taxonomy_Classification_Unit.html
- 161. • Please visit the links below to learn more about each of the units in this curriculum – These units take me about four years to complete with my students in grades 5-10. Earth Science Units Extended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Geology Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Geology_Unit.html Astronomy Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Astronomy_Unit.html Weather and Climate Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Weather_Climate_Unit.html Soil Science, Weathering, More http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Soil_and_Glaciers_Unit.html Water Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Water_Molecule_Unit.html Rivers Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/River_and_Water_Quality_Unit.html = Easier = More Difficult = Most Difficult 5th – 7th grade 6th – 8th grade 8th – 10th grade
- 162. Physical Science Units Extended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Science Skills Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Science_Introduction_Lab_Safety_Metric_Methods. html Motion and Machines Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Newtons_Laws_Motion_Machines_Unit.html Matter, Energy, Envs. Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Energy_Topics_Unit.html Atoms and Periodic Table Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Atoms_Periodic_Table_of_Elements_Unit.html Life Science Units Extended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Human Body / Health Topics http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Human_Body_Systems_and_Health_Topics_Unit.html DNA and Genetics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/DNA_Genetics_Unit.html Cell Biology Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Cellular_Biology_Unit.html Infectious Diseases Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Infectious_Diseases_Unit.html Taxonomy and Classification Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Taxonomy_Classification_Unit.html Evolution / Natural Selection Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Evolution_Natural_Selection_Unit.html Botany Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Plant_Botany_Unit.html Ecology Feeding Levels Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Feeding_Levels_Unit.htm Ecology Interactions Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Interactions_Unit.html Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Abiotic_Factors_Unit.html
- 163. • More Units Available at… Earth Science: The Soil Science and Glaciers Unit, The Geology Topics Unit, The Astronomy Topics Unit, The Weather and Climate Unit, and The River Unit, The Water Molecule Unit. Physical Science: The Laws of Motion and Machines Unit, The Atoms and Periodic Table Unit, The Energy and the Environment Unit, and The Introduction to Science / Metric Unit. Life Science: The Diseases and Cells Unit, The DNA and Genetics Unit, The Life Topics Unit, The Plant Unit, The Taxonomy and Classification Unit, Ecology: Feeding Levels Unit, Ecology: Interactions Unit, Ecology: Abiotic Factors, The Evolution and Natural Selection Unit and The Human Body Systems and Health Topics Unit. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 164. • Thank you for your time and interest in this curriculum tour. Please visit the welcome / guide on how a unit works and link to the many unit previews to see the PowerPoint slideshows, bundled homework, review games, unit notes, and much more. Thank you for your interest and please feel free to contact me with any questions you may have. Best wishes. • Sincerely, • Ryan Murphy M.Ed • ryemurf@gmail.com
