Tuberculosis summary
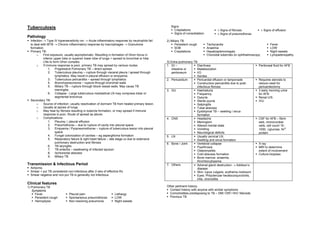
- 1. Tuberculosis Signs Crepitations ± Signs of fibrosis ± Signs of effusion Signs of consolidation ± Signs of pneumothorax Pathology Infection → Type IV hypersensitivity rxn → Acute inflammatory response by neutrophils fail 2) Miliary TB to deal with MTB → Chronic inflammatory response by macrophages → Granuloma Persistent cough Tachycardia Fever formation. SOB Anaemia LOW Primary TB: Crepitations Hepatosplenomegaly Night sweats o First exposure, usually asymptomatic. Resulting in formation of Ghon focus in Choroidal tubercles on ophthalmoscopy Lympadenopathy inferior upper lobe or superior lower lobe of lungs + spread to bronchial or hilar LNs to form Ghon complex. 3) Extra-pulmonary TB o If immune response is poor, primary TB may spread by various routes: 1. GI – Diarrhoea Peritoneal fluid for AFB 1. Progressive Pulmonary TB – direct spread. intestine or Malabsorption 2. Tuberculous pleurisy – rupture through visceral pleura / spread through peritoneum I/O lymphatics. May result in pleural effusion or empyema. Ascites 3. Tuberculous pericarditis – spread through lymphatics 2. Pericardium Pericardial effusion or tamponade Requires steroids to 4. Bronchopneumonia – rupture through bronchial walls Constructive pericarditis due to post- reduce need for 5. Miliary TB – rupture through blood vessel walls. May cause TB infectious fibrosis pericardiectomy meningitis. 3. GU Haematuria 3 early morning urine 6. Collapse - Large tuberculous mediastinal LN may compress lobar or Frequency for AFB segmental bronchus. Dysuria Renal U/S Secondary TB: Sterile pyuria IVU o Source of infection: usually reactivation of dormant TB from healed primary lesion. Salpingitis o Usually at apices of lungs Tubal abscess o May heal by fibrosis resulting in tubercle formation, or may spread if immune Epididymal TB – swelling / sinus response is poor. Route of spread as above. formation o Complications: 4. CNS Headache CSF for AFB – fibrin 1. Pleurisy ± pleural effusion Meningism web, mononuclear 2. Pneumothorax – due to rupture of cavity into pleural space Altered mental state cells, cell count 10- 3. Empyema / Pyopneomothorax – rupture of tuberculous lesion into pleural Vomiting 1000, ↓glucose, N/↑ space Neurological deficits protein 4. Fungal colonization of cavities – eg aspergilloma formation 5. LN Usually cervical LN. 5. Respiratory failure & right heart failure – late stage cx due to extensive Swelling and sinus formation pulmonary destruction and fibrosis 6. Bone / Joint Vertebral collapse X-ray 6. TB laryngitis Pyarthrosis MRI to determine 7. TB enteritis – swallowing of infected sputum. Osteomyelitis extent of involvement 8. Ischiorectal abscess Cold abscess formation Culture biopsies 9. Miliary TB Bone marrow: anaemia, thrombocytopenia Transmission & Infectious Period 7. Others Adrenal gland destruction → Addison’s Airborne. disease Smear + pul TB considered non-infectious after 2 wks of effective Rx Skin: lupus vulgaris, erythema nodosum Smear negative and non-pul TB is generally not infectious. Eyes: Phlyctenular keratoconjunctivitis, iritis, choroiditis Clinical features 1) Pulmonary TB Other pertinent history: Symptoms Contact history with anyone with similar symptoms Fever Pleural pain Lethargy Comorbidities predisposing to TB – DM/ CRF/ HIV/ Steroids Persistent cough Spontaneous pneumothorax LOW Previous TB Hemoptysis Non-resolving pneumonia Night sweats
- 2. Investigations Continuation phase Rifampicin & As above Microbiology Samples: sputum, induced sputum (using nebuliser), laryngeal swab and (4 mths on 2 drugs Isoniazid direct smear, NG aspirate (pump in saline and withdraw in the morning), Ethambutol 15mg/kg/day PO For resistant TB BAL, pleural fluid, pleura, urine, pus, ascites, CSF ZN or auramine stain Common & Important ADRs o + in 30% (up to 70%) Rifampicin Hepatitis Stop if bilirubin rises o Indicates high bacterial population and infectiousness. Cholestasis o Not specific for MTB. May be other mycobacterial spp. Orange discoloration of urine & tears C/S Severe thrombocytopenia o + in 66% Visual changes o Specific for MTB Liver enzyme inducer Caution in concurrent use with o Average 12-14 days for + result to return, another 1-2wks for OCP, warfarin, steroids, OHGA, sensitivity results phenytoin & digoxin. o Culture usually kept for up to 8 wks if negative Isoniazid Hepatitis Radiology CXR: Neuropathy, encephalopathy Give pyridoxine (Vit B6) to prevent o consolidation, cavitations, fibrosis, calcification / tuberculoma, collapse Pyridoxine deficit o Post TB bronchiectasis (usu upper lobes) Agranulocytosis o reticular-nodular opacities in miliary TB Pyrazinamide Hepatitis Mantoux Tests skin sensitivity to tuberculoprotein. + = sensitivity, NOT active infxn Arthralgia, gout Contraindicated in gout test (only 20% of infected individuals devt active infxn). May be + during Ethambutol Optic neuritis Test color vision before initiating Rx dormant OR active infection. Gout Inject 0.1ml of PPD intradermally Streptomycin Vestibular disturbance / ototoxicity Test for hearing before initiating Rx Read at 2-4 days: + if induration >10mm (locally 15mm), − if <5mm Nephrotoxicity False −: in sarcoidosis, malnutrition, Hodgkin’s dz, immunosuppression and overwhelming active TB Second line drugs: False +: atypical mycobacterial infections o Aminosalicylic acid Main use for contact tracing, to treat for latent TB infection o Cycloserine Serology o Ethionamide γ-interferon Eg Quantiferron, Elispot o Ofloxacin / Ciprofloxacin assays More sensitive c.f Mantoux test, but expensive. Not routinely done yet. Meningeal, ureteric and pericardial disease: consider adding steroids to reduce risks of Cx from scarring Monitoring of Rx efficacy – AFB smear & culture @ 2mths of Rx and after completing Rx, Management plus CXR after completing Rx. 1) Isolation For infectious pulmonary TB PTs. 3) Consider HIV testing Stop isolation only after >2 sputum cultures are AFB negative esp if high-risk group, or young (who don’t usually get TB. ?HIV) 2) Chemotherapy 4) Contact tracing & notification Check liver and renal functions, as well as color vision due to ethambutol ocular toxicity. Household contacts of sputum-smear positive PTs Give Pyridoxine throughout treatment to prevent isoniazid induced neuropathy 2/3-step contact tracing Directly Observed Therapy (DOT) to ensure compliance – daily Rx at TB control unit (CDC) o week 0 – do Mantoux, read at day 2-4 and polyclinics. Alternative: Intermittent DOT (3x/week). 97% cure rate ♦ if >15mm, means seroconvert – give prophylaxis ♦ if <15mm, repeat Mantoux Short-course regimen o week 2 – do Mantoux Initial phase (8 wks *Rifampicin 600-900mg PO 3X/wk ♦ if increase cf week 0’s test by >10mm, means that first /2mths on 3-4 drugs) *Isoniazid 15mg/kg PO 3X/wk Mantoux reactivated previously exposed immune system, now *Pyrazinamide 2.5g PO 3X/wk pt is displaying competent immune response – don’t need Monitor LFTs wkly Ethambutol 30mg/kg PO 3X/wk Add ethambutol or prophylaxis Streptomycin 0.75-1g/day IM streptomycin if ♦ if <10mm, do third Mantoux resistance is suspected.
- 3. o week 12 – do Mantoux ♦ if increase >10mm cf week 0, means pt has seroconverted, pt has LTBI, give prophylaxis ♦ if increase <10mm, no need prophylaxis 5) Chemoprophylaxis Consider for: o Severely immunosuppressed PTs (eg HIV +) o Unvaccinated contacts with recent MT + Isoniazid 300mg/day PO for 9 mth/ rifampicin 4 months if Mantoux positive as described 6) BCG vaccination at birth. Only protects against childhood miliary and CNS TB. Repeat vaccination in adolescence not found to affect outcome / risk of TB, and is no longer indicated. 7) Rx of Latent TB Infection Preventive ChemoRx Isoniazid (6mths locally, 9mths in USA) – effective in eradicating latent TB in 70%. Resistance to isoniazid not known to occur in the remainding 30% despite monotherapy. Digitally signed by DR WANA HLA SHWE DN: cn=DR WANA HLA SHWE, c=MY, o=UCSI University, School of Medicine, KT-Campus, Terengganu, ou=Internal Medicine Group, email=wunna.hlashwe@gmail.com Reason: This document is for UCSI year 4 students. Date: 2009.02.24 14:06:33 +08'00'
