Sociocognitive model
- 3. The sociocognitive apprenticeship model, developed by Vygotsky says that culture is the prime factor of individual development. Humans are the only species that has formed a culture and each child develops in the context of a culture. Therefore, the development of a child's learning is affected to a greater or lesser extent by the culture (including the family environment) in which it is immersed.
- 4. Cognitive development is a dialectical process in which the child learns through shared experiences of problem solving, generally shared experiences with parents and teachers, but also occasionally with a brother or partner. Initially, the person interacting with child bears most of the responsibility for guiding the process of problem solving, but will gradually transferring responsibility to the child.
- 5. Language is the main form of interaction through which adults transmit to the child the broad body of knowledge that exists in their culture. As learning progresses, the child's own language begins to serve as the primary tool of intellectual adaptation. Eventually, the child can use internal language to direct their own behavior. It refers to the internalization of the learning process, and therefore, to the internalization of a wealth of knowledge and thinking tools that exist outside the child. This happens primarily through language.
- 6. There is a difference between what the child can do for themselves and what they can do to help, Vygotskians call this difference the "zone of proximal development". Because much of what children learn comes from the surrounding culture and much of problem solving is mediated by an adult, would be wrong to focus on a child refugee. The approach does not reveal isolated child processes by which children learn new skills. The interaction with the surrounding culture and social agents such as parents and peers more advanced, contributes significantly to children's intellectual development.
- 7. How Vygotsky's theory impacts learning: Curriculum: As the child learns primarily through interaction, activities should be designed to emphasize the interaction between the learner and the learning subject. Instruction: With appropriate adult help, children can often perform tasks that would otherwise be unable to do. With this in mind, the "scaffolding", in which the adult continually adjusts the level of support in response to the child's level of mastery, is an effective way of teaching.
- 8. Assessment: Assessment methods must consider the zone of proximal development. What they can do for themselves is the current level of development and what they can do to help is their level of potential development. Two children can have the same level of development, but providing adequate assistance of an adult, one may be able to solve many more problems than the other. Evaluation methods should focus on both levels of development, both current and potential.
- 10. This model highlights the question of the meaning or the why of education and thus of learning that seek to promote and in that order, also emphasizes the need to link the academic and social. Within this context, the sociocognitive model is proposed as a conceptual framework and in turn perfectible interesting or improved, to begin entering a new perspective on the learning process, revealing from there and with the contributions of other approaches, the role of medical students in their learning processes.
- 11. The socio-cognitive model defines the key elements inherent in any position or focus on education: • Perspective on the curriculum: since this model curriculum is a vital educational tool, as cultural selection of career and discipline whose content and practical implementation should be directed toward the development of skills and values serving as the purposes of education and content and learning methods that operate as the means to achieve these aims or goals.
- 12. Perspective on Learning: provides a particular view about what is and how learning occurs, revealing the social and cultural aspects involved in its construction. It argues that all learning processes involve the learner in a scenario, their socio-cultural and historical context in which these take place. In this approach, significant learning building must arise from the subject, from how this learning (cognitive paradigm) and what it learns (social paradigm)
- 13. epistemological perspective on knowledge: learning or legitimates knowledge that from the standpoint of cognitive (ability / skills) and affective (values / attitudes) students possess. In fact the mission of teaching, pre- design activities is to identify both. Perspective on educational practice: learning activities are centered learning strategies in the subject. The goal from the socio-cognitive model is that activities such as learning strategies enable the development of skills and values as goals of curriculum, ie, cognitive and affective processes.
- 14. • Perspective on the subject of educational action: from the socio- cognitive model recognizes the importance of viewing the subject of education. This allows contextualise what students in general and in particular pedagogical practice, according to the specific characteristics, knowledge, learning, expectations and demands of specific educability presenting different cohorts of graduate students and residents.
- 15. In the socio-cognitive model argues that learning potential and cognitive dimension is developed through socialization contextualized as socio-cultural dimension, where the dialectical interactions between learners, as protagonists of their learning and reinforce the learning stage and simultaneously create the motivation to contextualize what they learn. For purposes of concreteness and to promote a holistic appreciation of the socio-cognitive model is presented as its main features to be developed in the theory and practice curriculum, the following:
- 16. • As a basic metaphor, the actor tries to integrate learning and cognitive and affective processes in learning scenario. • The institutional culture are both socially reinforced, understanding the curriculum as an integrated cultural selection skills, values, content and methods. Thus social and institutional culture and curriculum have the same basic elements (skills, values, content and methods of learning).
- 17. The teacher model has two dimensions, as mediator of learning and as a mediator of the social culture of the profession and the specialty and institutional culture. This mode uses the contents and methods as a means to develop the skills and values. • The goals and purposes are identified as abilities / skills and cognitive processes and values / attitudes as affective processes, to develop professional and capable people.
- 18. The curriculum will necessarily be open to new learning, educational realities, and also flexible in order to enable a wide range of accommodations and concretions, because culture is plural and changing, while facilitating institutions to develop their own institutional culture, favoring institutional academic freedom and professional educators.
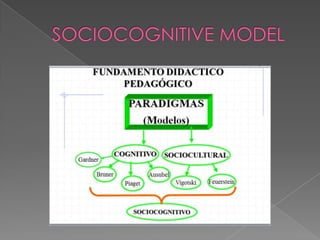
- 20. Pedagogy sociocognitive paradigm relies on the sociocognitive and lies beyond the behavioral paradigm. We define a macromodel theoretical educational paradigm capable of explaining the theory and practice of education in the context of a new society. The sociocognitive paradigm attempts to integrate the cognitive (capacity - values) and social (culture). Therefore we seek more complementarity between the opposed cognitive paradigm and the sociocultural paradigm for these reasons:
- 21. The cognitive paradigm focuses on the teacher's thought processes (how to teach) and student (learn how), while the ecological paradigm, social or contextual environmental worries and classroom life and both aspects can and should be comple ¬ mentary. Globalization (global culture) will be the new scenario and learning (intellectual capital) your goal.
- 22. The cognitive paradigm is more individualistic (focusing on individual processes), while the ecological paradigm (context) is more socializing (focusing on the interaction context - group - individual and vice versa), so we must seek complementarity between the two ..
- 23. The acting apprentice learning is embedded in a learning scenario, which is their niche and their life context (global perspective that integrates global and local). Learn how an apprentice is reinforced in what it learns from a contextualized. The skills and values have not only an individual dimension without also social. The school as a learning organization is to develop, as an agency of socialization and enculturation, "emotional intelligence of the trainees".