Gerd presentation ( Case study )
- 2. GERD
- 3. Presentation outline PART I DISEASE’S PATHALOGY & MANGEMENT 1- introduction 2- Causes 3- Sings & Symptoms 4- Complication 5- Diagnosis 6- Management
- 4. Presentation outline PART II CASE’S EXEPLATION
- 5. PART I DISEASE’S PATHALOGY & MANGEMENT
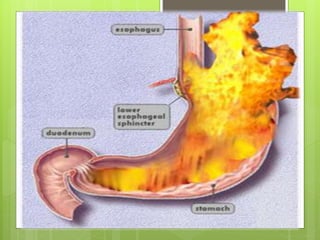
- 6. What is GERD GERD states it is a condition that occurs when the refluxed stomach contents lead to trouble. Disorder in lower esophagus sphincter GERD affects all ages especially after 40 years
- 7. The gender doesn't play a role in the disease . The mortality of GERD is rare . Death occur in Barrett’s esophagus that lead to esophagus adenocarcinoma
- 8. Diagnosis Symptoms (Heartburn , Regurgitation) Barium Swallow An upper endoscopy Esophageal manometry Ambulatory–pH monitoring test
- 9. Barium Swallow Barium sulfate is a metallic compound that shows up on X- rays
- 10. The X-rays track its path through patient digestive system . o Patient drink a preparation containing this solution
- 11. An upper endoscopy visually examine upper digestive system with a tiny camera on the end of a long, flexible tube.
- 12. Esophageal manometry Esophageal manometry is a test to measure how well the esophagus is working. A thin, pressure-sensitive tube is passed through patient nose, down the esophagus, and into patient stomach.
- 13. What is GERD ? GERD states it is a condition that occurs when the refluxed stomach contents lead to trouble symptoms and/or complications. GERD affects all ages espacially after 40 years. The gender doesn't play a role in the disease The mortality of GERD is rare .
- 14. Phathophysiology The main problem in the development of GERD is the abnormal reflux of gastric contents from the stomach into the esophagus.
- 15. This is due to : 1- Lower Esophageal Sphincter Pressure 2- anatomical causes
- 17. GERD Causes *Lower Esophageal Sphincter Pressure Different mechanisms by which defective LES pressure lead gastroesophageal reflux.
- 18. 1- LES relaxations that are not associated with swallowing. Although the exact mechanism is unknown. 2- postprandially, may play an important role in symptom-based esophageal reflux syndromes. 3- intraabdominal pressure (stress reflux)
- 19. Anatomical factor Disruption of the normal anatomic barriers by a hiatal hernia (when a portion of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm into the chest) was once thought to be a primary etiology of gastroesophageal reflux
- 21. Special case Pregnancy 1- hormonal effects on esophageal muscle 2- physical factors (increased intraabdominal pressure)
- 22. Composition of Refluxate the combination is gastric acid, pancreatic enzymes pepsin, and/or bile is a potent refluxate in producing esophageal damage. The composition, pH , volume of the refluxate are important aggressive factors in determining the GERD
- 23. Defensive mechanism Esophageal clearance Mucosal resitance Gastric empting
- 24. Food & Medications may worse GERD causjGERD
- 25. Sings & Symptoms Heartburn Regurgitation Water brash ( hyper salivation) belching
- 26. Atypical Symptoms Nonallergic asthma Hoarseness Pharyngitis Chest pain Dental erosions
- 27. Complication Alarm symptoms symptoms may be indicative of complications of GERD such as Stricture Barrett’s esophagus esophageal adenocarcinoma
- 29. Other alarm symptoms Dysphagia Odynophagia Bleeding Weight loss
- 30. Diagnosis Symptoms (Heartburn , Regurgitation) Barium Swallow An upper endoscopy Esophageal manometry Ambulatory–pH monitoring test
- 31. Barium Swallow Barium sulfate is a metallic compound that shows up on X- rays
- 32. The X-rays track its path through patient digestive system . o Patient drink a preparation containing this solution
- 33. An upper endoscopy visually examine upper digestive system with a tiny camera on the end of a long, flexible tube.
- 34. Esophageal manometry Esophageal manometry is a test to measure how well the esophagus is working. A thin, pressure-sensitive tube is passed through patient nose, down the esophagus, and into patient stomach.
- 35. After the tube is in the stomach, the tube is pulled slowly back into patient esophagus. At this time, patient is asked to swallow The pressure of the muscle contractions is measured along several sections of the tube. While the tube is in place, other studies of your esophagus may be done. The tube is removed after the tests are completed.
- 36. Ambulatory–pH monitoring test Small tube passed through the nose into the esophagus at the level of the LES. A pH sensor at the tip of the tube collected on a portable computer.
- 37. Treatment 1) Non-Pharmacologic treatment Lifestyle changes 2) Pharmacologic treatment therapy with antacids, nonprescription H2-receptor antagonists, and/or nonprescription proton pump inhibitors Provide symptomatic relief, and prescription strength acid-suppression therapy . 3) Anti-reflux surgery .
- 38. Elevating the head end of the bed by approximately (15 to 20 cm) with a foam wedge under the mattress . Weight loss Avoid food that may decrease lower esophageal sphincter like ( fat, chocolate, cola, spearmint, alcohol(wine), pepper, Garlic, onion ) Avoid food that have the direct irritant of esophageal mucosa like (spicy, citrus juice, tomato, coffee, Tobacco ) Include protein rich meal in diet (augment ( increase ) lower esophageal sphincter ) Always take drugs in the setting upright . Avoidance of tight-fitting clothes . Lifestyle modifications
- 39. DosesRecommended drug 30ml need after meal, and at bedtime 15ml need after meal, and at bedtime Maalox Gaviscon 10mg up to twice daily /2weekFamatodine ( Pepcid Ac ) 75mg up to twice daily /2weekRantidine ( Zentac ) 20mg up to twice daily /2weekOmeprazole ( Prilosec ) 15mg up to twice daily /2weekLanzoprazole ( Prevacid ) Pharmacologic treatment
- 40. The goal of antireflux surgery is to reestablish the antireflux barrier, to position the LES within the abdomen where it is under positive ( intraabdominal ) pressure, and to close any associated defect in the diaphragmatic hiatus by reinforcing the crural muscles . Antireflux surgery should be considered for patients : Who fail to respond to pharmacologic treatment. Who opt for surgery despite successful treatment because of lifestyle considerations, including age, time, or expense of medications. Who have complications of GERD (e.g., Barrett’s esophagus, strictures). Who have atypical symptoms and reflux documented with ambulatory pH monitoring . Anti-reflux surgery
- 41. Management
- 44. Patient with compliant of heartburn Life style modification OTC drug Anti-acid 2 W. H2-receptor antagonist twice daily PPI one a day 4-8 W. PPI twice daily 4-16 W. Reduce or Stop medicine Mano& Amb. pH Endoscopy Surgical intervent ion Maintenance Therapy With minimum eff. dose NO No No No No Yes Yes A L A R M S y m p t o m s
- 45. Chief Complaint “I’m having a lot of heartburn, especially after eating. These pills and liquids I’ve tried seem to work for a little while, but then they wear off.” History of Present Illness George Anderson is a 58-year-old man complaints of heartburn four to five times a week over the last 4 months . episodes of regurgitation, after which he is left with an acidic taste in his mouth symptoms wake him up at night approximately once a week
- 46. tried Extra Strength Maalox liquid first and then Pepcid AC tablets . He took the Pepcid AC 10 mg twice daily for 1 week . This worked intermittently but didn’t provide enough relief Past Medical History HTN × 12 years CKD × 2 years Type 2 DM × 5 years
- 47. Social History • He drinks one to two beers a day after work, 4–5 days per week. • He has a 25 pack-year history of tobacco use and currently smokes 1 ppd. Medication history Amlodipine 5 mg once daily Glyburide 5 mg twice daily Aspirin 81 mg daily Ibuprofen 200–400 mg PRN for headaches and pain
- 48. Reports occasional tension Headaches but no visual changes, aura, or dizziness . (–) Shortness Of Breath , cough, or hoarseness . (+) frequent episodes of a burning pain in his stomach area and travels up his chest associated with an acidic taste in his mouth . (–) N/V (–) Bright red blood per rectum or dark/tarry stools (–) dysuria, nocturia, or frequency; Reports some mild ankle swelling in both ankles He has gained approximately 8 pounds over the last 6 months
- 49. Physical Examination VS : BP 149/89, P 87, RR 17, T 36°C; Wt 99 kg, Ht 5'10'' Abd : Obese; (+) BS; MS/Ext : No CVA tenderness; ( 1+) pitting LE edema bilaterally Labs Fasting Glu 200mg/dL ( high) TC 230 mg/dL ( high) LDL 146 mg/dL ( high) TG 187 mg/dL ( high) HDL 39 mg/dL ( Low )
- 50. Assessment man presenting with uncontrolled GERD symptoms despite self-treatment with OTC H2RA and antacid therapy .
- 51. Problem Identification : Drug therapy problems Identification Efficacy Safety Compliance
- 52. SOAP Notes GERD ★Insufficient drug therapy S: Uncontrolled GERD symptoms (Heartburn (4-5)times in week , regurgitation, acidic taste in his mouth) . O: ____________ A: May be due to the patient didn’t take enough dose & time of Pepcid AC therapy . Usual adult dose for GERD :20mg orally /twice daily up to 6 weeks . Or the patient didn’t take the first line therapy of GERD ( PPI)
- 53. P: Aim / a- Alleviate the patient symptoms b- Decrease frequency of recurrent disease . c- Prevent GERD complications (strictures, Barrett’s esophagus, or possibly adenocarcinoma ) Therapy / Non pharmacological therapy : Pharmacological therapy : Using PPI, the drug of choice for patient with moderate to severe GERD Omeprazole 20mg orally twice daily up to 4 weeks .
- 54. Monitoring : Efficacy of PPI ( Omeprazole ) : according to relied of symptoms in the patient or Ambulatory PH monitoring . Toxicity of Omeprazole ( Ca+2, Mg+2, Vit B12 Levels ) .
- 55. ★Unsafe drug therapy S: Uncontrolled GERD symptoms O: ____________ A: also, may result from using CCB (Amlodipine ), which decrease lower esophageal sphincter pressure & delay gastric emptying . P: Aim : • Alleviate the patient symptoms • Decrease frequency of recurrent disease . • Prevent GERD complications (strictures, Barrett’s esophagus, or possibly adenocarcinoma ) .
- 56. Therapy : • Stop Amlodipine, & start to use ACEI for HTN treatment • ACEI : are recommended as the first line therapy of Hypertension in patient with CKD & DM .
- 57. S: GERD symptoms O: ____________ A: Maalox antiacid ( Al(OH)3 + Mg(OH)2 ) ( This drug contain Al+3 which lead to toxicity in this patient, who is suffering from CKD ) . Toxicity due to accumulation Al+3 in patient with CKD : Osteomalacia Alzehimers disease P: Aim : To prevent toxicity of Al+3 Therapy : Stop Maalox
- 58. ★Improper Drug Selection : S: Headache, Pain . O: ____________ A: Ibuprofen 200mg PRN for headache & pain The use of NSAID drugs or aspirin is an additional risk factor that may suitable to the development or worsening of GERD complication . ( NSAIDs cause direct irritation ) P:
- 59. Aim : • Alleviate the patient symptoms • Decrease frequency of recurrent disease . • Prevent GERD complications (strictures, Barrett’s esophagus, or possibly adenocarcinoma ) . Therapy : Stop Ibuprofen and replaced with Paracetamol for headache and pain when needed .
- 60. Hypertension ★ Ineffective drug therapy S: ____________ O: B.P = 149/89mmHg A: this drug didn’t effective to decrease SBP< 140mmHg . P : Aim : • Decrease SBP < 140mmhg & DBP < 90mmHg • To reduce renal mortality & morbidity, also decrease CV risk .
- 61. Therapy : Non pharmacology therapy : • Maintain normal body weight ( during weight loss ) ( BMI 18-25 ) • BMI of this patient 31.2 • Eating food rich in Fruits, Vegetables, Grains, Low in fats & cholesterol . • Reduce dietary Na+ :2,4 g/day Na+ (not more ) • Exercise ( Walking ) 30min/day . • Limit alcohol drinking . • Smoking cessation .
- 62. Pharmacological therapy : • Stop Amlodipine ( unsuitable for patient state ) , • Use ACEI ( Enalapril 5mg/twice daily ) . • according to American recommendation, ACEI is used as first line treatment in Hypertension patient with Chronic Kidney Disease ( CKD ) or with Diabetes mellitus • ACEI has beneficial effect on renal function, make efferent arteriolar vasodilatation , decrease intraglomerular pressure . Monitoring : Efficacy of Enalapril : B.P measurement . Toxicity of Enalapril : CrCl, K+ level .
- 63. ★Unsafe drug therapy : S: Mild ankle swelling in both ankles. O: ____________ A: this patient’s adverse effect result from using of Amlodipine therapy . P: Aim : • The removal of this adverse effect . • Enhance quality of life of patient . Therapy : Stop Amlodipine therapy.( replaced with ACEI ) . Monitoring : Disappearance of this adverse effect ( ankle swelling ) .
- 64. ★Inappropriate indication for drug use S: ____________ O: TC 230 mg/dL , LDL 146 mg/dL , TG 187 mg/dL , HDL 39 mg/dL A: This patient has high lipid profile ( Total cholesterol, LDL, TG, Low HDL ) Which is additional risk for CV events, and he doesn't take Anti-hyperlipidemia therapy . P: Aim / • Normal level of lipid profile ( TC=less than 200 mg/dl, LDL=below 100 , TG=below 150 , HDL=40-60 or more • Decrease risk for CV
- 65. Therapy : • non-pharmacological : • Weight loss • Reduce intake of Fat & Cholesterol • Increase intake of Omega 3 • Pharmacological Use of statin : Atorvastatin 20 mg
- 66. Diabetes mellitus ★Insufficient & Improper Drug Selection : S: ____________ O: Fasting glucose = 200 mg/dl A1C = 8,6 % A: Glyburide didn't decrease his blood glucose. This patient didn't use preferred initial agent which is has beneficial effect in this pt. (wt. gain, high risk of CV event )
- 67. ★Unsafe drug therapy : S: ____________ O: BMI = 31.2 obese A: Obesity in this pt. may results from use Glybruide (it's is one of adverse effect: wt. gain), This is risk factor which increase CV events in the other risk factors present in this pt.
- 68. P: Aim Control blood glucose level Prevent DM complications ( nephrophathy, neurpathy & retiropathy ) Therapy : NON pharmacological : • Diet • Weight loss • Physical activity
- 69. Pharmacological : • Stop glyburide ( not effective in decrease glucose level, And has disadvantage : weight gain) • Replaced it with Metformin, initiate with dose 500 mg twice daily No dose adjustment in this patient ( which is suffering from CKD ) .
- 70. According to : Cockreft-gault Eq. CrCl = 59.34 ml/min ( in stage 3 - moderate- ) Dose adjustment of Metformin in renal disease if CrCl<30 ml/min Monitoring of Metformin : Efficacy : Fasting glucose test A1C Toxicity : Vit B12 level ( it cause vit B12 deficiency ) .
- 71. Aspirin 81mg , Why ??!!!