English Tences
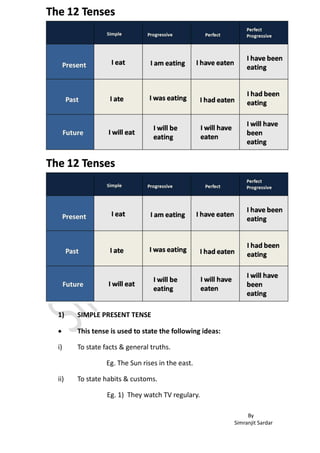
- 1. By Simranjit Sardar 1) SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE This tense is used to state the following ideas: i) To state facts & general truths. Eg. The Sun rises in the east. ii) To state habits & customs. Eg. 1) They watch TV regulary.
- 2. By Simranjit Sardar 2) Our company produce food color. iii) For instructions or direction. Eg. Open the packet and pour contents into boil water. Common time expression in SPT. Usually, always, every Sunday, twice a week, once a month, in general, every other day, everyday. Ex. i) In general, I believe that all people can live in peace. ii) Vidhi goes to badminton practice every Monday. 3rd person singular (he,she,it) add s, es or ies to the verb. i) To regular verb just add an “S” Ex. Travel – Travels, Give – Gives ii) To Verbs that end with (s, ss, sh, ch ,o) add an “es”. Ex. Wash - Washes, Mix – Mixes iii) To verbs that end with “y” after consonant change “y” into “i” and add “es”. Ex. Study – Studies, Fly – Flies Sentence formation : Subject + v1 + object Type of sentence 1) Affirmative(positive) : I always study hard for exams. 2)Interrogative : Do you surf the Internet every day? Does your boss give you positive feedback? Does Jonathan always turn off the lights? Don’t you ever clean your room? 3)Negative: I don’t like the food they serve at that restaurant. Jim doesn’t work on Fridays. 4)Wh Questions: When do you want to meet me?
- 3. By Simranjit Sardar Why does Beth always complain so much? How much does the ticket cost? Why don’t you ever go on vacation? 5)Tag Que: John likes me, doesn’t he? All those girls speak French, don’t they? Keisha doesn’t speak Spanish, does she? Those boys don’t play sports, do they? 2) PRESENT PROGRESSIVE TENSE To describe incomplete action which is in progress at the moment Ex. I am typing at the moment. Common time expression in PPT. Now, at the moment, currently, right now, at the present. To describe a plans or arrangement in the near future usually with time expression such as: tonight, tomorrow, this week, this month. Ex. Jimi is leaving for meeting tonight. Sentence formation : Subject + am/is/are +verb(ing) Type of sentence 1)Affirmative(positive) : We are discussing the project at the moment. Her husband is always complaining for his job. 2)Interrogative : Am I talking too much? Is that your dog barking? Are you participating in the competition next week? 3)Negative: I’m not listening to you. Roger isn’t eating with us tonight. The Smiths aren’t going to France this year. They’re going to Thailand. He is not coming with me dressed like that! 4)Wh Questions: Which route are you taking to the conference this week? Why is it bleeding? Who am I sending to the meeting? 5)Tag Que: Terry is driving to the post office, isn’t she? Latika’s not working at IBM anymore, is she? Tom and Gill aren’t going on the trek to South America, are they?
- 4. By Simranjit Sardar 1) PRESENT PERFECT TENSE To describe action that occurred in the past but still relevant to the present. Ex. Rani has broken her mobile Ex. I have already made so many calls. (till now) Describe action that were repeated many times in the past. Useful tip Use since with a specific year or a period in the paste. Eg. since 2000/since I was a child Use for with a number of years. Eg. For twenty years. Use ever and yet in question and negative. Eg. Have you ever/ hasn’t been yet Use already and never just between have/has and the verb. Eg. Has already finished/have just been. Use before, since, for, already, many times, so far, yet at the end of a sentence or question. Ex. Have you been there before? Sentence formation: Subject have/has +v3 +….. Use Ever and Yet Ex.1) Have you ever seen tiger? 2) Has Jerry presented his idea to the CEO yet? Use Already, Never & Just Ex.1) I have already finished my work. 2) I have never seen tiger. 3) Pooja has just gone to the Market. Type of sentence 1)Affirmative(positive) : The girls have played tennis at the club since 2005. 2)Interrogative : Have you ever gone to Paris? 3)Negative : I haven’t eaten at that restaurant yet. Jim hasn’t worked on Fridays since he joined the company. My friends haven’t ever gone to France. I have not forgiven you!
- 5. By Simranjit Sardar 4)Wh Questions: When have I ever lied to you? Why has Tanya left the country? How much money have you spent so far? 5)Tag Que: John has known her for a couple of years, hasn’t he? They have been in business since 1980, haven’t they? Keisha hasn’t spoken to you yet, has she? Those kids have never played rugby, have they? 2) PRESENT PERFECT PROGRESSIVE TENSE It is used to describe an event that started in the past but is still happening in the present. That event in the present can be. Ex. I have been living in this house for 40 years. (I started living in it 40 years ago and I am still living in it today.) Ex. I have been climbing up this mountain for over two hours. (I started climbing up it two hours ago and at this moment I’m still climbing.) Useful Tip Time Expressions in the Present Perfect Progressive (Continuous) Use since or ever since with a specific month, year or a period in the past . Ex. I have been jogging in this park since 2002 / He has been staring at the wall ever since he heard the news. Use for with a number of hours, days, months, years . Ex. She’s been talking on the phone for 3 hours. Sentence form: Subject have/has +been +verb (ing)+….. Type of sentence 1)Affirmative(positive) : I have been waiting for you since 10 am. I’ve been thinking about you since you called. He’s been singing for two hours. We’ve been helping her out for a few months. 2)Interrogative : Have you been keeping track of sales record? Has jerry been picking fruit from my trees again? 3)Negative I haven’t been feeling well lately. Simon hasn’t been attending class regularly since he got a job. The sales team hasn’t been performing at the top of their game. He has not been paying attention!
- 6. By Simranjit Sardar 4)Wh Questions: What have you been doing since I left? How long has he been waiting? Why the phone has been ringing for the last two hours? 3) SIMPLE PAST TENSE To describe the past activities which no longer part of present . The event started in past and ended in past. Ex. India won world cup. Time expression in SPT Yesterday, last day, the day before previous day, last month, last year, a year ago. Sentence form: Subject + verb 2….. Type of sentences 1) Affirmative (positive): she planned the wedding event all by herself. 2) Interrogative : Did the students came late again last day? 3) Negative : Students didn’t steal the original paper copy. I didn’t talk to my sister yesterday I dint go to that event the day before yesterday. 4) Wh Que: When did you buy that car? How long did the flight journey take? Why didn’t they inform about the accident? 5) Tag Que: You were snoring full night, didn’t you?? Servant didn’t do any mistakes, did they?
- 7. By Simranjit Sardar 6) PAST PROGRESSIVE TENSE: To describe an action that started in the past and was interrupted by another action: Ex. He was writing an e-mail when the phone rang. When the phone rang, he was writing an e-mail. While he was writing an e-mail, the phone rang To describe two actions that were in progress at the same time in the past: Ex. I was preparing dinner while priya was working on project. Priya was working on project while,I was preparing dinner. We use the time expression “while” before the past progressive and the word when before the past simple part of the sentence. use only one of these time expression in each sentence. Sentence form: Sub + was/were + verb ( ing )… Type of sentences 1) Affirmative (positive):she was cleaning kitchen platform when riya came While she was cleaning the kitchen platform, riya came. 2) Interrogative : Was I talking to you? Were you taking lunch when the electricity went off? When you came to the home, was she singing the song? Wasn’t tom playing game when you stood there? 3) Negative : I wasn’t sleeping when you came last night. When Mr. Donald came home, the children weren’t playing. 4) Wh Que: What were you doing when the trouble started? Why wasn’t she waiting at the meeting point Who was I talking to? I can’t remember 5) Tag Que: you were snoring last night, weren’t you?
- 8. By Simranjit Sardar They were all rushing for the exit, weren’t they? Students weren’t trying their best, weren’t they? 7) PAST PERFECT TENSE: The past perfect simple is used to describe one action that happened before another action in the past. Ex. After Sofie had finished her work, she went to lunch. In many cases a complete sentence is written in two parts with two different tenses: 1) The past perfect simple, to refer to the action that happened first or earlier. 2) The past simple to refer to the action that happened second or later. Ex. I washed the floor when the painter had gone The time expressions already, for, since, and yet may be used in the past perfect simple, as they are in the present perfect simple. Remember the following rules for using other time expressions: Use after, as soon as, the moment that, until before using the past perfect simple. Ex: After she had moved out, I found her notes. I didn’t say anything until she had finished talking. Use before, when, by the time before the past simple: Ex. Before I knew it, she had run out the door. By the time he phoned her, she had found someone new. Sentence form: Sub + had + v3 …. Type of sentences 1) Affirmative (positive): After she had moved out, I found her notes. Before I knew it, she had run out the door. 2) Interrogative : Had you cleaned up the room by the time they came home? Had Asha ever spoken to the CEO before he was fired? 3) Negative : I had not eaten at that restaurant before today. Sam hadn’t had time to explain her side of the story
- 9. By Simranjit Sardar 4) Wh Que: What had they said that made him so angry? Why had he agreed to work for that salary? How much had he drunk before you got to him? 5) Tag Que: John had known about the cancer for a couple of years, hadn’t he? They had been in business together, hadn’t they? Jenifer hadn’t spoken to you about it, had she? They had never eaten a proper Indian meal, had they? 8) PAST PERFECT PROGRESSIVE TENSE: The past perfect progressive (continuous) is used to describe an action that started in the past and was still in progress when a second action started. Both actions began and ended in the past. As in the past perfect simple, the sentence has two parts: 1. The past perfect progressive, to refer to the action that was in process 2. Ex. Ben had been working for three hours when Rachel came home. 3. The past simple to refer to the action that happened after the first action Ex.By the time Sam found an umbrella, it had been raining for ten minutes. Type of sentences 1. Affirmative (positive) Ben had been working for three hours when Rachel came home. I had been feeding the dogs when I tripped and fell. Negative 1. I hadn’t been feeling well, so I sent him away. 2. Simon had not been expecting a positive answer when he got a job. Yes/No questions 1. Had he been drinking when you found him? 2. Had the manager been complaining about Jim before she fired him? Wh-Questions 1. What had you been doing when you cut your finger? 2. Which fax had you been trying to send when the power went off? 3. How long had he been waiting? 9) FUTURE TENSE
- 10. By Simranjit Sardar The future can be expressed in several ways in English. Here are the different possibilities: 1. Future Simple: will + base form of the verb I) She‘ll write the e-mail after lunch. II) Alina won’t help us decorate for the party. 2. Be Going To: am, is, are + going to + base form of the verb I) Dan‘s going to take the from the customer. II) The girls are going to sing ‘national Anthem’ now. III) They aren’t going to buy the house. IV) I am not going to make dinner tonight. We’re going out to a restaurant. 3. Shall: Shall + subject + base form of the verb? Shall is used with the subjects I and we to make suggestions or to offer to do something for someone. It is always used in the form of a question. I) Shall we go for a walk? II) Shall I help you with that? Examples – Future Tense Positive 1. She’ll write the e-mail after lunch. 2. Don’t lift that. You’ll hurt yourself. 3. I’ll see you tomorrow. 4. You’ll get the answer by post. 5. Dan’s going to take the order over to the customer. 6. The girls are going to sing ‘Amazing Grace’ now. 7. I’ll drive you to your lesson at 4 pm. 8. He is going to clean up his room tonight. Negative 1. Alice won’t help us decorate for the party. 2. I won’t see you tomorrow. 3. You will not do that again! 4. They aren’t going to buy the house. 5. I am not going to make dinner tonight. We’re going out to a restaurant. Yes/No Questions
- 11. By Simranjit Sardar 1. Will Dave burn the CD for you? 2. Won’t the girls be late for the party? 3. Am I going to feel bad about my decision? 4. Is he going to watch the film tonight? 5. Are you going to participate in the race tomorrow? 6. Shall we go for a walk? 7. Shall I help you with that? 8. Will Allen be participating in the science fair next week? 9. Won’t you be visiting your mother when I’m in town? 10. Will Ron be visiting you today? Wh- Questions 1. When will he give you an answer? 2. Why won’t you tell him the truth? 3. How much is the computer going to cost? 4. Why aren’t you going to buy that car? Tag Questions 1. John will call her tomorrow, won’t he? 2. You are going to finish that work, aren’t you? 3. That bee is going to sting me, isn’t it? 4. Carey won’t report me, will she? 5. The kids aren’t going to play cricket tomorrow, are they? 6. You’re not working tomorrow, are you? Future Progressive (Continuous) sentence : will + be + verb (ing) Spelling Tip Verbing (Present Participle) • Add ing to most verbs. Ex. play > playing, cry > crying, bark > barking • For verbs that end in e, remove the e and add ing. Ex: slide > sliding, ride > riding • For verbs that end in ie, change the ie to y and add ing. Ex: die > dying, tie > tying We use will/wont + be + verbing (present participle) when we know that an action will be in progress at some time in the future or to describe something that has been pre-arranged. 1) Affirmative : This time next year, we will be living in our new home . You can take my car tomorrow. I won’t be using it
- 12. By Simranjit Sardar 2) Interrogative: Will Amit be participating in the science fair next week ? Won’t you be visiting your mother when I’m in town? 3) Wh question : Where will he be waiting for me? How will you be travelling to the exhibition? How many contestants will be attempting to win the prize? Which runners will be running the race? 11) FUTURE PERFECT TENSE The future perfect simple is used to explain an activity that will be completed by a certain time in the future. We add time expressions such as by the time, by then, by the year 2008, by March 25th to describe these kinds of activities. Sentence form: Sub + will have + v3 … ▪ For the short form, we change will to 'll. But, when we are speaking. ▪ But, when we are speaking, we also make 'have' shorter, so it sounds like I'll've finished. Eg. I'll have finished this book You'll have studied the English tenses Sentences: Affirmative: By this time next year we will have been married for 30 years. If all goes well, by June 2012, I will have finished my university degree. Interrogative: Will she have gotten her passport by then? Won’t you have sent the documents by Thursday? Negative: We won't have met Julie They won't have left Japan