Sinus tachycardia
- 2. Sinus Tachycardia • In an adult is characterized by a sinus rate of more than 100 beats/minute • Rate rarely exceeds 160 beats/minute except during strenuous exercise • Each impulse follows the normal pathway of conduction resulting in atrial and ventricular depolarization
- 3. Sinus Tachycardia • How it happens – Depends on the underlying cause • May be of no clinical significance – May be the body’s response to exercise – May be the body’s response to high emotional state • May also occur with hypovolemia, hemorrhage, or pain – When the stimulus for the tachycardia is removed, the arrhythmia spontaneously resolves
- 4. Sinus Tachycardia • Causes – Normal response to • Exercise, pain, stress, fever, or strong emotions – Certain cardiac conditions • Heart failure – Medications • Epinephrine and atropine – Substances • Caffeine, nicotine, and cocaine – Other conditions • Anemia, respiratory distress, pulmonary embolism, sepsis, and hyperthyroidism
- 5. Sinus Tachycardia • Hard on the heart – Not good for those with heart conditions already – Considered a poor prognostic sign if follows MI • Is associated with massive heart damage – Persistent tachycardia may signal impending heart failure or cardiogenic shock – Consequences • Bring on an episode of chest pain in patients with CAD
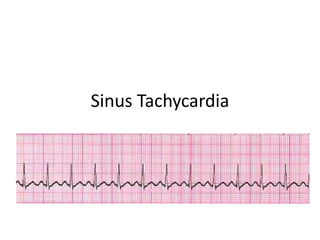
- 6. Sinus Tachycardia • What to look for – Look for a pulse rate of more than 100 beats/minute – Rhythm is regular
- 7. Symptomatic Tachycardia • Pulse rate of more than 100 beats/minute but with regular rhythm – Usually patient is asymptomatic
- 8. Symptomatic Tachycardia • If cardiac output falls and compensatory mechanisms fail – Will experience symptoms • Hypotension • Syncope • Blurred vision • Chest pain and palpitations • Nervousness or anxiety • Heart failure – JVD – crackles
- 9. Symptomatic Tachycardia • Steps to take – Prompt recognition is vital so treatment can be started – Provide the patient with a calm environment; help to reduce fear and anxiety which can fuel the arrhythmia – Tachycardia is commonly the first sign of pulmonary embolism
- 10. Symptomatic Tachycardia • When to call for help and what to do until help arrives – Look at the patient and ask how they are doing – Call for help if heart rate is too fast and/or symptomatic • Compare it their normal heart rate and rhythm – Stay with the patient – If the patient is not breathing and does not respond • Call code • ABCs/CPR
- 11. Sinus Tachycardia • What to look for – Look for a pulse rate of more than 100 beats/minute – Rhythm is regular
- 12. Sinus Tachycardia • Normal – P wave preceding each QRS complex – PR interval – QRS complex – T wave – QT interval
- 13. Sinus Tachycardia • P wave – Normal size and shape and precedes each QRS, but it may increase in amplitude – As the heart rate increases, the P wave may be superimposed on the preceding T wave and difficult to identify
- 14. Sinus Tachycardia • PR interval – Normal indicating that the impulse is following normal conduction pathways • 0.12-0.20 seconds
- 15. Sinus Tachycardia • QRS complex • Normal duration representing normal ventricular impulse conduction and recovery – Less than 0.12 seconds
- 16. Sinus Tachycardia • T wave – Upright in lead II, confirming that normal repolarization has taken place
- 17. Sinus Tachycardia • QT interval – Within normal limits • 0.36 to 0.44 seconds • QT normally shortens with tachycardia
