Role of p 53 and p-rb protein in cell cycle regulation
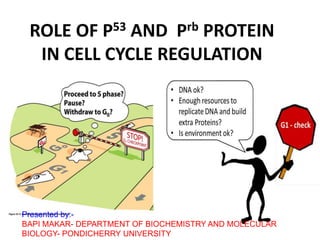
- 1. ROLE OF P53 AND Prb PROTEIN IN CELL CYCLE REGULATION Presented by:- BAPI MAKAR- DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY- PONDICHERRY UNIVERSITY
- 4. R point Cell cycle control involves several checkpoints and checkpoint (molecular breaking) mechanisms
- 5. Cyclins G0 G1 S G2 M Cyclin D Cyclin E Cyclin A Cyclin B determined by mitogenic growth factors • Cyclines and cyclin-dependent kinases (cdks) – The cyclines have oscillating levels during cell cycle – The cyclines are regulatory subunits of the CDK-kinases • cyclines+ cdk cell cycle-dependent variations in the activity of the kinases
- 7. M G1 G2 S R E2F released S-phase genes expressed Rb Cdk4/6 Cyclin D Gate keeper model
- 8. pRb: What does it do? pRb is a nuclear protein that undergoes phosphorylation and dephospharylation in concert with the cell cycle
- 9. Hypo-phosphorylated or un-phosphorylated pRb inhibits the cell from entering a new cell cycle The guardian of the cell at early-mid G1 Upon further phosphorylation at the R point, hyper-phosphorylated pRb becomes inert and the cell cycle can proceed
- 10. Hypo-phosphorylated Rb inhibits activity of the E2F family of transcription factors Hyper-phosphorylation of Rb sequesters Rb, and releases E2Fs E2Fs are needed for transcription of genes that are essential for the cell to enter the cell cycle
- 11. Hypo-phosphorylated Rb binds to E2Fs and: - Inhibits their transcription activation sites - Recruits proteins that will “close” the chromatin down
- 12. PLGA dissolved in acetone (for ENP).PLGA+ DRUG(10:1) dissolved in acetone for CNP/BDMCANP) Synthesis GO FOR CHARACTERISATION PREPARATION OF NANO- PARTICLE
- 13. Releasing Rb from the E2Fs leads to: - Release of their transcription activation sites - Recruitment of proteins that will “open up” the chromatin
- 14. Rb, the retinoblastoma protein regulates the cell cycle Cell cycle = OFF Rb binds to E2F: no transcription, no entry into S phase Cell cycle = ON Rb does not bind to E2F: transcription and entry into S phase
- 15. Rb activity is tightly regulated by the cell cycle clock Hypo-phosphorylation is catalyzed by cycD-CDK4/6 Hyper-phosphorylation is catalyzed by cycE-CDK2
- 16. pRb is hyper-phosphorylated and inhibited (and released from its role as a guardian), only upon cycE expression
- 17. Rb activity is tightly regulated by the cell cycle clock However, E-CDK2 can phosphorylate Rb, only AFTER Rb is phosphorylated by cycD-CDK4/6
- 18. Only after we have enough mitogen signaling (and, as a result, enough cycD-CDK4/6 activity), cycE can phosphorylate Rb and allow entry to the cell cycle
- 19. E2Fs have more than 100 target genes, mostly involved in the first steps of DNA replication One of the targets: the cycE gene Transcription of cycE starts a positive feedback loop
- 20. As E2Fs are necessary for expression of cycE, think how critical negative regulation by Rb is for cell cycle control E2Fs
- 21. Uncontrolled crossing of the R site can be due to loss of Rb function (e.g. mutation), loss of CKIs or oncogenic activity of cyclins E and D
- 22. Rb gene alteration is involved many tumors In the majority of tumors you will find mutation involved in the R site
- 24. Effect of mutant p53 alleles in the mouse germ line
- 26. p53 is a transcription factor, active only as a homotetramer
- 27. In normal cells we find only low concentrations of the p53 protein - p53 protein is actually synthesized all the time, but is degraded very fast via the ubiquitine system
- 28. p53 protein is ubiquitinated by the E3 ligase MDM2
- 29. p53 DNA damage Hyperproliferative stress Many agents induce p53 activity Grouped into two classes
- 30. DNA damage is sensed by sensor proteins and repaired by the DNA repair machinery Extensive DNA damage recruits the DNA damage response machinery Two key players: The protein kinases ATM and ATR Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated Ataxia Telangiectasia and rad3 related
- 31. ATM and ATR are recruited to distinct sites and phosphorylate downstream effectors
- 32. ATR is recruited to single - stranded DNA - ATR-dependent phosphorylation of the Rad9 adaptor protein is needed for activating Chk2 - Activated Chk2 is released to phosphorylate its effectors ATR Rad9 Chk2 (inactive) Chk2 (active)
- 33. Phosphorylation of p53 (by ATM/ATR and/or Chk2) makes it insusceptible to MDM2 binding Phosphorylated p53 acts as a transcription factor
- 34. DNA damage response activates p53 by stabilizing the protein via phosphorylation (and additional mechanisms) Additional inhibitory phosphorylation of MDM2
- 36. Hyperproliferative stress response is mediated through the ARF protein - E2Fs induce transcription of the ARF gene - ARF binds to and sequesters MDM2 - p53 is stabilized
- 37. Over activity of oncogenes stimulates apoptosis through ARF
- 38. Two reactions for the price of one
- 39. - p53 is a transcription factor, acting as a homotetramer Summary - Transcribed constitutively, but has a very short half life - DNA damage and a stalled replication fork induce p53 phosphorylation and activation - Hyperproliferative stress (e.g. oncogenic signaling, hypoxia) activates p53 via ARF - Ubiquitinated by the E3 ligase MDM2
- 40. p53 DNA damage Cell cycle arrest Apoptosis What about outputs? Hyperproliferative stress