Incentives for Ecosystem Services – Colombia
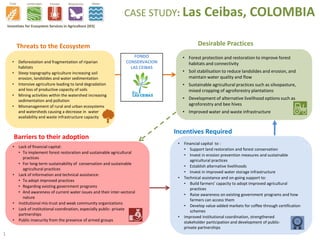
- 1. • Deforestation and fragmentation of riparian habitats • Steep topography agriculture increasing soil erosion, landslides and water sedimentation • Intensive agriculture leading to land degradation and loss of productive capacity of soils • Mining activities within the watershed increasing sedimentation and pollution • Mismanagement of rural and urban ecosystems and watersheds causing a decrease in water availability and waste infrastructure capacity • Lack of financial capital: • To implement forest restoration and sustainable agricultural practices • For long-term sustainability of conservation and sustainable agricultural practices • Lack of information and technical assistance: • To adopt improved practices • Regarding existing government programs • And awareness of current water issues and their inter-sectoral nature • Institutional mis-trust and weak community organizations • Lack of institutional coordination, especially public- private partnerships • Public insecurity from the presence of armed groups • Financial capital to : • Support land restoration and forest conservation • Invest in erosion prevention measures and sustainable agricultural practices • Establish alternative livelihoods • Invest in improved water storage infrastructure • Technical assistance and on-going support to: • Build farmers’ capacity to adopt improved agricultural practices • Raise awareness on existing government programs and how farmers can access them • Develop value-added markets for coffee through certification schemes • Improved institutional coordination, strengthened stakeholder participation and development of public- private partnerships • Forest protection and restoration to improve forest habitats and connectivity • Soil stabilisation to reduce landslides and erosion, and maintain water quality and flow • Sustainable agricultural practices such as silvopasture, mixed cropping of agroforestry plantations • Development of alternative livelihood options such as agroforestry and bee hives • Improved water and waste infrastructure Threats to the Ecosystem Desirable Practices Barriers to their adoption Incentives Required FONDO CONSERVACION LAS CEIBAS CASE STUDY: Las Ceibas, COLOMBIA 1 Incentives for Ecosystem Services in Agriculture (IES)
- 2. COLOMBIA : Financial Investment for Best Practices Forest protection and restoration to protect water recharge area and reduce GHG emissions $ FIDUCIA (water user fees) $ ONU REDD $ CIF Risk management and ecosystem services monitoring $ Fondo Conservacion Las Ceibas Improved primary processing $ ICR $ IAT Reduced agricultural chemical use and improved soil management $ PRONATTA Certified sustainable shade coffee plantations $ Federation Nacional Caféteros de Colombia with improved agroforestry and grazing systems $ ICR $ IAT Alternative livelihood development such as bee-keeping $ Asociación de Apicultores Bioengineering and irrigation to stabilize soils $ EDAT Combined, these efforts result in improved farm productivity and resilience, and food security 2 Key: Public programme | Private sector investment Incentives for Ecosystem Services in Agriculture (IES)
- 3. 3 COLOMBIA: Incentives for Ecosystem Services Incentive Type Key: Conservation and landscape rehabilitation • Forest protection and restoration • Agroforestry plantation development $ FIDUCIA $ ONUREDD & $ CIF • Finance to: • Restore, reforest, conserve and manage watershed forest in protected areas • Invest in sustainable agroforestry management practices • Technological assistance and capacity building to: • Scale-up agroforestry • Maintain tree nurseries $ Federacion Nacional Café $ Asociasion de Apicultores Livelihood diversification and strengthened local capacity • Development of alternative income generation opportunities • Support to: • Develop and market certified sustainable coffee • Train bee keepers and market apiculture products • Create cooperatives and improve access to higher-value market opportunities Increased sustainable agricultural productivity • Improved crop varieties and silvopasture systems • Improved soil management practices $ PRONATTA $ ICR $ IAT • Finance for improved seeds and organic fertilizers • Training in organic land husbandry such as manuring, mulching and composting Incentives from the programmes/ investors:Financed by:Best practices: $ Fondo Conservacion Las Ceibas $ EDAT • Ecosystem monitoring • Soil stabilization measures and improved irrigation • Ecosystem services and social outcomes monitoring • Finance to construct bench terraces to stabilize soils PES IES Incentives for Ecosystem Services in Agriculture (IES)
- 4. The Fondo Conservacion Las Ceibas (FCLC) is a strategic, collective and participatory basin-wide partnership to sustainably manage and protect the Las Ceibas river basin. Integrated co-finance, coordinated through a common fund, Fiducia, is provided from four sources: i) Water user fees from the Neiva water utility, ii) Public funds from the Neiva municipality, III) funds from the departmental government of Huila, and, iv) the Regional development cooperation of the Magdalena River. Legislation requires that the public funds are allocated for watershed protection. Co-investments for the first year in the Las Ceibas basin totaled US$1,622,434, reaching US$2,773,656 in 2012. Using a basin-wide approach to landscape planning, this fund aims to address threats to the Las Ceibas ecosystem from intensive agricultural practices and pressure from growing rural populations on natural resources. Built around a hydrological PES scheme financed by water users, the initiative combines public programs and the private sector, and seeks to achieve mutually-beneficial environmental and rural development targets. Together they finance and support an integrated package of incentives that effectively protects the Las Ceibas ecosystem services and enables the transition to sustainable agricultural practices. The Las Ceibas river basin ecosystem is threatened by: • The reliance on intensive unsustainable agricultural practices such as the felling of valuable timber, cattle ranching within the steep topography of the area and expansion of agricultural areas through slash-and-burn for bean cultivation. These practices have led to: • Deforestation and fragmentation of riparian habitats. • Soil erosion which has increased sedimentation of water courses and increased the risk of landslide and flooding events. This threatens rural livelihoods and disrupts water supplies to cities within the watershed such as Neiva, reliant on Las Ceibas as their sole potable water source. • Reduced soil fertility. A reduced productive capacity of soils forces farmers to convert additional forest areas to rapidly increase productivity for cattle pasture, coffee and cocoa, causing further deforestation and fragmentation of riparian habitats. • Mining activities within the watershed have increased levels of sedimentation, land and water pollution. • Increased population size and the development of sugarcane agrobusiness has increased the demand on rural and urban ecosystem services. • Ineffective coordination and weak community institutions have reduced trust in and ability of their management of rural and urban ecosystems and watersheds, causing disruption in water availability and poor water and waste infrastructure. COLOMBIA: Overview 4 Incentives for Ecosystem Services in Agriculture (IES)
- 5. • Restoration of forest cover can also help to stabilize soil structure, improve forest connectivity and increase carbon storage. Increased vegetation can protect springs, water recharge areas and riparian forests of the Las Ceibas basin and increase habitat for native biodiversity. • Construction of bioengineering to stabilize soils, such as bench terraces, can assist to control soil erosion, reduce the risk of landslides and the potential for sedimentation of water courses. • Implementing land planning for sustainable agricultural production can increase overall production efficiency and environmental protection by reducing pressure on soil fertility from intensive practices. Sustainable practices such as silvopasture, improved agroforestry plantations (such as cirrus, cacao and shaded coffee), improved irrigation systems, and establishing alternative livelihoods such as bee-hives or value-added markets for coffee. This can protect soils, reduce the need to expand agricultural land and increase the long-term income potential for smallholder farmers. • Strengthening grassroots organisations and institutional coordination can support the implementation of integrated land management and improve infrastructure development such as water infrastructure, irrigation and waste management throughout the Las Ceibas basin. • Monitoring and risk management can observe ecosystem services outcomes and reduce the risk of flooding, landslide and other extreme events within the river basin. Smallholder farmers, however, face barriers to adopting these sustainable practices: • A lack of access to information, technological assistance and long-term support to adopt improved practices, such as Farmer Field Schools. • Limited awareness of current water issues and existing government programs that farmers could benefit from. • Financial capital: • A lack of financial capital to invest in soil stabilization measures, implement reforestation, improve infrastructure and invest in alternative livelihoods. The transition cost of implementing sustainable agricultural practices also prevents farmers moving away from unsustainable practices, such as slash and burn to produce beans, or improving water and waste management infrastructure. • Current financial incentives to fence springs (~USD 1,000) lack additional finance to manage them. Cattle, therefore, break through fences or farmers destroy them to expand grazing areas. • Municipal finance for conservation is also insufficient to both purchase and manage land for ecosystem services. • Limited access to higher market opportunities for sustainable agricultural products. • Ineffective organization and lack of coordination between institutions reduces local awareness of existing government programs, increases mis-trust in governance and reduces the capacity for basin-wide land-management implementation. COLOMBIA : Best Practices and Barriers to AdoptionIncentives for Ecosystem Services in Agriculture (IES)
- 6. COLOMBIA : IES Initiatives Program Financed by: Outcome and Activities: Fondo Conservacion Las Ceibas - FIDUCIA - Water users fees & public funds allocated for watershed protection i) Restore, reforest, conserve and manage the watershed forest protected area; ii) Implement bioengineering, applied to control erosion, water harvesting and improved cocoa production; iii) Contribute to basic sanitation infrastructure; iv) Strengthen institutional organization; and, v) Conduct environmental monitoring. ACA Asociacion Colombiana de Apicultores Conducts research, support and train bee keepers, and improve marketing of apiculture products and services. CIF Certificado de Incentivo Forestal - Forestry Incentive Certificate Financial incentive for private landowners, or municipal or decentralized bodies who provide public water and sewage services to offset externalities of reforestation. EDAT Incentivo para la elaboracion de estudios y disenos para proyectos asociativos de adecuacion de tierras Improve infrastructure and irrigation projects to stabilize soil in future construction, expansion or rehabilitation in Land Improvement Districts. FNC Federacion Nacional Café – Colombian Coffee Growers Federation Guarantees the purchase of coffee harvest at transparent prices, technical assistance to improve sustainability and productivity (such as reduced water use in post-harvest processes), and access to value-added markets to improve livelihoods. Monitors soil erosion, water ecosystem services and efficient use of agrochemicals. IAT Incentivo a la Asistencia Tecnica Technical assistance and technology transfer to improve competitiveness and productivity in agriculture, and also help reduce inequalities. ICR Incentivo a la Capitalizacion Rural Access to credit for new investments to modernize, increase competitiveness and sustainability of agricultural production, such as the use of production machinery and primary processing. PRONATTA Programa Nacional de Transferencia de Technologia Agropecuaria Technical assistance to build the capacity of farmers and implementing agencies in sustainable agricultural practices. These include reduced agricultural chemical use and improved soil management practices. ONU REDD UN-REDD Programme Compensation to reduce deforestation, improve governance of forest resources and reduce GHG through climate change mitigation. 6 Incentives for Ecosystem Services in Agriculture (IES)
- 7. Policy Recommendations [To improve coordination and integration of initiatives and incentives] • A conductive legal framework, supported by law to allocate public funds for watershed investments by regional development cooperations and municipalities. • Important prerequisite is the perceived need for ecosystem services (i.e. risk for water supply) by downstream stakeholders to engage in the process. It is important to use basic tools such as water balance models to illustrate the added value of ecosystem services conservation in terms of return of investment, reduced sediment loads and regulated flows, etc. • Efficiency is improved if stakeholder’s contributions are amalgamated into a single trust fund that is administered by one actor (in this case, CAR) and overseen by a catchment committee composed of all contributing actors. • Efficient delivery can be ensured by implementing the programme through an external agent, in this case FAO. Where there is a limited contract with the agent (in this case, six years), an exit strategy is needed to ensure that local capacity is built. This enables funds to continually be administrated during the implementation phase. • To enable sustainability of the IES scheme: • Strategic alliances should be sought with incentive programmes at national scale. (For example, certification schemes, Ministry of Agriculture) • It is crucial to seek further buy-in from the private sector not just as a social and environmental responsibility strategy, but as a core business cost to be included consistently in planning processes. To make this happen, it is important for the private sector to understand, with scientific tools, their risk exposure and the cost-benefit analysis of investing in conservation to reduce this risk. • Policy is crucial here. There is a good opportunity in Colombia now related to law (decreto 953) that states an obligation for municipalities to invest at least 1% of income (ingresos corrientes) in PES schemes and/ or buying strategic areas for water provision. Some policy suggestions from the Regional Dialogue: • CIF • Amend Law 139 94: “to promote the realization of direct investments in new protective forest plantations character-producer on land suitable for forestry,” to extend it to land agroforestry fitness. • ICR • Could be regulated through the National Agricultural Credit Commission, expanding the regions and explicitly investing in activities to achieve best practices • Could be regulated in Article 5 of Law 1133 (2007) in terms of support, in particular: “the incentive to productivity including allocation of resources aimed at promoting the culture of good agricultural and livestock practices, the partnership between producers, among others.” • Extending regions in which ICR is implemented. • REDD+ • Expansion of explicit activities to achieve REDD+ • Partnership projects through value chains, could be generated through Credit Line COLOMBIA : Policy Recommendations 7 Incentives Now Future Prohibition of use Taxes/ Charges Property use rights Mandatory farm set-asides Subsidies Conservation easements Permits and quotas Marketing labels – Certificates/ Standards Offsets Green Public Procurement Voluntary farm set-asides Conservation concessions Direct Payments for Ecosystem Services Corporate Social Responsibility Marketing labels (without certification/ standards) Rewards for Ecosystem Services (RES) Cultural and social norms Incentives for Ecosystem Services in Agriculture (IES)
