Sulfonamides, Fluoroquinolones, Oxiquinolines, Nitrofurans,Quinoxalines, Oxazolidinones and Antifungal Drugs
- 1. SULFONAMIDES, FLUOROQUINOLONES, OXIQUINOLINES, NITROFURANS, QUINOXALINES, OXAZOLIDINONES and ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS 11
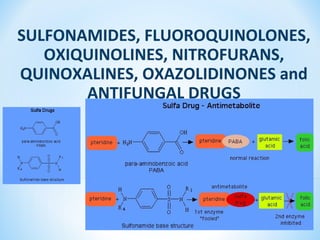
- 2. 22 Sulfonamides – the synthetic antimicrobial agents, containing a sulfonamido (–SO2–NH–) group. This group is present in other compounds like antidiabetic sulfonylureas, diuretics like thiazides, furosemide, and diacarb. The structure of the sulfonamides is similar to Para-Aminobenzoic Acid (PABA). Sulfonamides tend to be much more soluble at alkaline than at acid pH. Solubility may be decreased in acidic urine, resulting in precipitation of the drug or its acetylated metabolites.
- 3. 33 CLASSIFICATION of SULFONAMIDES I. Oral, Absorbable (Systemic Action): 1. Short-acting (6-9 hours): Sulfadimezine, Sulfazine, Ethazol, Urosulfane 2. Long-acting (24 hours) : Sulfapyridazine, Sulfadimethoxine 3. Ultra-long acting (72 hours): Sulfalen 4. Combined preparations with: - Trimethoprim: Co-trimoxazole [Biseptol] - Aminosalicylic acid: Salazopyridazine, Sulfasalasine Salazodimethoxine
- 4. II.II. Oral, NOral, Nonon-Absorbable-Absorbable ((acting the intestinal floraacting the intestinal flora):): PhthalazolPhthalazol SulginSulgin III.III. For Topical UseFor Topical Use:: Sulfacil-natriumSulfacil-natrium (Albucid)(Albucid)–– Silver SulfadiazineSilver Sulfadiazine (1%(1% ccream)ream) 44
- 5. 55
- 6. CLINICAL USES of SULFONAMIDESCLINICAL USES of SULFONAMIDES :: Respiratory infectionsRespiratory infections Acute urinary tract infection:Acute urinary tract infection: UrosulfanUrosulfan Combined withCombined with PyromethaminePyromethamine –– for drug-resistantfor drug-resistant MALARIAMALARIA, and for, and for TOXOPLASMOSISTOXOPLASMOSIS Inflammatory bowel disease, non-specific ulcerative colitis -Inflammatory bowel disease, non-specific ulcerative colitis - SulfasalazineSulfasalazine ((SulfapyridineSulfapyridine ++ AminosalicylateAminosalicylate)) Some sexually transmitted infections -Some sexually transmitted infections - TRACHOMATRACHOMA,, CHLAMYDIACHLAMYDIA 66
- 7. Co-trimoxazoleCo-trimoxazole: the combination of: the combination of SulfamethoxazoleSulfamethoxazole andand TrimethoprimTrimethoprim:: is generally bactericidalis generally bactericidal acts by sequential blockade ofacts by sequential blockade of FOLIC ACIDFOLIC ACID enzymesenzymes in the synthesis pathway:in the synthesis pathway: SulfamethoxazoleSulfamethoxazole inhibits formation ofinhibits formation of Dihydrofolic acidDihydrofolic acid fromfrom PABAPABA,, TrimethoprimTrimethoprim inhibitsinhibits Dihydrofolate reductaseDihydrofolate reductase responsible for formation ofresponsible for formation of Tetrahydrofolic acidTetrahydrofolic acid fromfrom Dihydrofolic acidDihydrofolic acid 77
- 8. Co-trimoxazoleCo-trimoxazole is effective against :is effective against : Escherihia coliEscherihia coli KlebsiellaKlebsiella EnterobacterEnterobacter Streptococcus pneumoniaeStreptococcus pneumoniae Staphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus aureus SalmonellaSalmonella ShigellaShigella Clinical useClinical use:: Chronic Bronchitis, Urinary tractChronic Bronchitis, Urinary tract infections,infections, Otitis media, Pneumocytis carini pneumonitis,Otitis media, Pneumocytis carini pneumonitis, Traveller’s Diarrhea, Pertussis, Cholera.Traveller’s Diarrhea, Pertussis, Cholera. 88
- 9. ADVERSE EFFECTS of SULFONMIDESADVERSE EFFECTS of SULFONMIDES:: Hypersensitivity Reactions:Hypersensitivity Reactions: rashes, angioedema.rashes, angioedema. All sulfonamides and their derivatives, includingAll sulfonamides and their derivatives, including Diacarb, Thiazides, Furosemide, Butamide,Diacarb, Thiazides, Furosemide, Butamide, Glibenclamide, DiazoxideGlibenclamide, Diazoxide areare CROSS-ALLERGICCROSS-ALLERGIC Nephrotoxicity, Urinary tract disturbances:Nephrotoxicity, Urinary tract disturbances: SulfonamidesSulfonamides precipitate in urine, esp. at neutral orprecipitate in urine, esp. at neutral or acid pH, producingacid pH, producing CRYSTALLURIACRYSTALLURIA,, HAEMATURIAHAEMATURIA,, or evenor even OBSTRUCTIONOBSTRUCTION.. Adequate HYDRATION and ALKALINIZATION of urineAdequate HYDRATION and ALKALINIZATION of urine prevent the problemprevent the problem Haemopoietic disturbancesHaemopoietic disturbances:: hemolytic anemia,hemolytic anemia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, thrombocytopeniaagranulocytosis, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia Depression, aseptic meningitis, seizuresDepression, aseptic meningitis, seizures 99
- 10. Acute Poisoning/OverdoseAcute Poisoning/Overdose SULFONAMIDESSULFONAMIDES are able to formare able to form METHEMOGLOBINMETHEMOGLOBIN andand SULF-METHEMOGLOBINESULF-METHEMOGLOBINE, block the haemopoiesis and, block the haemopoiesis and produce hepato- and nephrotoxicity.produce hepato- and nephrotoxicity. ManifestationManifestation:: dizziness, drowsiness, unconsciousness, anorexia,dizziness, drowsiness, unconsciousness, anorexia, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, haemolytic anemia, acidosis,abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, haemolytic anemia, acidosis, agranulocytosis, sensitivity reactions, jaundice, hepatomegaliaagranulocytosis, sensitivity reactions, jaundice, hepatomegalia TreatmentTreatment:: gastric lavage, forced diuresisgastric lavage, forced diuresis ANTIDOTESANTIDOTES:: Nicotinic acidNicotinic acid IV 1% solution 2–5 mlIV 1% solution 2–5 ml oror NicotinamidNicotinamidee ChromosmonChromosmon (1%(1% Methylene BlueMethylene Blue solution in 25% glucose)solution in 25% glucose) IV 0.1 ml/kgIV 0.1 ml/kg Lipoic acidLipoic acid IV 0.5% solution 60-80 mlIV 0.5% solution 60-80 ml Folic acidFolic acid PO 1 mg tidPO 1 mg tid Transfusion of appropriate BLOOD PRODUCT:Transfusion of appropriate BLOOD PRODUCT: Fresh blood, Dry Plasma, Polyglucin , RheopolyglucinFresh blood, Dry Plasma, Polyglucin , Rheopolyglucin 1010
- 11. SulfasalazineSulfasalazine - Tab 0.5 g:- Tab 0.5 g: SulfapyridineSulfapyridine ++ Aminosalicylic AcidAminosalicylic Acid –– is split into its component parts by bacteria in the colon.is split into its component parts by bacteria in the colon. Clinical UsesClinical Uses:: Ulcerative Colitis, Enteritis, Inflammatory Bowel DiseasesUlcerative Colitis, Enteritis, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Rheumatoid diseases: acts by scavenging the toxicRheumatoid diseases: acts by scavenging the toxic oxygenoxygen metabolitesmetabolites produced by neutrophilsproduced by neutrophils IgAIgA andand IgMIgM Rheumatoid FactorRheumatoid Factor productionproduction Suppression ofSuppression of T cellT cell responsesresponses Inhibition ofInhibition of B cellB cell proliferationproliferation The absorption ofThe absorption of folic acidfolic acid is impaired –is impaired – this can be counteredthis can be countered by givingby giving Folic AcidFolic Acid supplementssupplements 1111
- 12. Sulfacyl-sodiumSulfacyl-sodium ((AlbucidAlbucid) –) – 10%, 15%, 30% ophthalmic solution or10%, 15%, 30% ophthalmic solution or ointment - effective for:ointment - effective for: Bacterial ConjunctivitisBacterial Conjunctivitis and as adjunctive therapy forand as adjunctive therapy for TrachomaTrachoma.. Ocular Gonorrheal infectionOcular Gonorrheal infection inin newbornsnewborns and adults.and adults. It acts byIt acts by inhibiting the uptake of PABAinhibiting the uptake of PABA, which is required in, which is required in the synthesis ofthe synthesis of Folic AcidFolic Acid needed for bacterial growth.needed for bacterial growth.
- 13. 1313
- 14. 1414
- 15. CiprofloxacinCiprofloxacin ((TaTabb.. 0.0.5 g5 g; amp; amp.. 1%-10 ml)1%-10 ml) –– a synthetic, broad-spectrum, bactericidal antibiotic,a synthetic, broad-spectrum, bactericidal antibiotic, effective against both Gr(+) and Gr(-) bacteria.effective against both Gr(+) and Gr(-) bacteria. It has excellent activity against:It has excellent activity against: EnterobacteriaceaeEnterobacteriaceae Enteric coliform bacilliEnteric coliform bacilli, including resistant to, including resistant to Penicillins,Penicillins, CephalosporinsCephalosporins andand AminoglycosidesAminoglycosides Haemophilus influenzae,Haemophilus influenzae, Penicillinase-producingPenicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae,Neisseria gonorrhoeae, CampylobacterCampylobacter andand PseudomonadsPseudomonads.. Gr(+) organisms,Gr(+) organisms, streptococcistreptococci andand pneumococcipneumococci are only weaklyare only weakly inhibited and there is high incidence ofinhibited and there is high incidence of staphylococcal resistancestaphylococcal resistance.. 1515
- 16. Clinical usesClinical uses of the Fluoroquinolonesof the Fluoroquinolones Urinary tract infections:Urinary tract infections: Norfloxacin, OfloxacinNorfloxacin, Ofloxacin Complicated respiratory tract infections -Complicated respiratory tract infections - Gr(-) floraGr(-) flora Pseudomonas aeruginosaPseudomonas aeruginosa respiratoryrespiratory infectioninfection External otitis caused byExternal otitis caused by PP.. aeruginosaaeruginosa Chronic Gr(-) bacillaryChronic Gr(-) bacillary OSTEOMYELITISOSTEOMYELITIS Eradication ofEradication of Salmonella typhiSalmonella typhi in carriersin carriers Gonorrhoea:Gonorrhoea: Norfloxacin, OfloxacinNorfloxacin, Ofloxacin AnthraxAnthrax 1616
- 17. Chinoxydin (Quinoxydin – tab. 0.25 g) Dioxydin (amp. 1%-10 ml for topical use; amp. 0.5%-10 ml IV). They have broad-spectrum antibacterial effect including Proteus vulgaris, blue pus bacillus (Pseudomonas aeruginosa), pathogen anaerobes and others. These drugs are used in severe pyoinflammatory processes. They are toxic and adverse effects are not infrequent and include GIT upsets, headache, chill, seizures, allergic reactions.1717
- 18. NitroxolineNitroxoline ((5-NOK, Nitrox)5-NOK, Nitrox) –– Tab. 0.05 gTab. 0.05 g a urinary antiseptic -a urinary antiseptic - a broad-spectrum, bacteriostatic agent. blocks replication of nucleonic acids, forming chelate complexes with microelements (Fe, Cu) of microbes => enzyme systems inhibition. is quickly absorbed from GIT, eliminates in unmodified mode with urine, where it is accumulated in bacteriostatic concentrations. Clinical uses: urinary tract infections (Cystitis, Pyelonephritis, Urethritis, Prostatitis), prophylaxis of infections after kidney and urinary tract surgery. Unwanted effects: GIT upsets. Urine is discolored brightly yellow during administration of drug. 1818
- 19. 1919
- 20. FuracilinFuracilin ((NitrofurazoneNitrofurazone,, Furacin)Furacin) 0.02% solution, Tab. 0.02 and 0.1 g -0.02% solution, Tab. 0.02 and 0.1 g - is a synthetic, broad-spectrum antibacterialis a synthetic, broad-spectrum antibacterial NITROFURANNITROFURAN derivative used mainly for topic application as ANTISEPTIC:derivative used mainly for topic application as ANTISEPTIC: Externally for the treatment and prevention ofExternally for the treatment and prevention of pyoinflammatory processes, major burnspyoinflammatory processes, major burns (esp. when resistance to other antibacterial agents occurs)(esp. when resistance to other antibacterial agents occurs);; PreventionPrevention of skin graft infections.of skin graft infections. 0.02%0.02% FuracilinFuracilin SolutionSolution is applied directly to lesion or tois applied directly to lesion or to dressing used to cover the affected area daily ordressing used to cover the affected area daily or as indicated,as indicated, depending on severity ofdepending on severity of burn or injury.burn or injury. 2020
- 21. FurazolidoneFurazolidone (Tab 0.05 g) is a(Tab 0.05 g) is a NITROFURANNITROFURAN compound active against manycompound active against many Gr(–) bacilliGr(–) bacilli includingincluding Salmonella, ShigellaSalmonella, Shigella,, Giardia lambliaGiardia lamblia andand TrichomonasTrichomonas.. Clinical Uses:Clinical Uses: ForFor GIARDIASISGIARDIASIS 100 mg tid for 5–7 days is inferior to100 mg tid for 5–7 days is inferior to metronidazolemetronidazole oror tinidazoletinidazole.. Intestinal infections: Bacterial EnteritisIntestinal infections: Bacterial Enteritis Food poisoning diarrhoeas, Bacillary DysenteryFood poisoning diarrhoeas, Bacillary Dysentery Trichomonad colpitisTrichomonad colpitis FurazolidoneFurazolidone is partly absorbed from intestines and excreted in urineis partly absorbed from intestines and excreted in urine which turns orange – patients should be told about it.which turns orange – patients should be told about it. It is used orally, intravaginally and rectally.It is used orally, intravaginally and rectally. Adverse effectsAdverse effects are mild and infrequent – nausea, headache, dizziness.are mild and infrequent – nausea, headache, dizziness.2121
- 22. FuradoninFuradonin (Nitrofurantoin(Nitrofurantoin – Tab. 0.05 g, Caps. 0.1 g) is– Tab. 0.05 g, Caps. 0.1 g) is an effectivean effective urinary antisepticurinary antiseptic.. Is a bacteriostatic compound, but may be cidal at higherIs a bacteriostatic compound, but may be cidal at higher concentrations and inconcentrations and in acidic urineacidic urine: its activity: its activity is enhanced at loweris enhanced at lower pH 5.5pH 5.5 or below.or below. Ihibits many Gr(+) and Gr(–) bacteria.Ihibits many Gr(+) and Gr(–) bacteria. It antagonizes the action ofIt antagonizes the action of Nalidixic acidNalidixic acid.. Mechanism of actionMechanism of action. Susceptible bacteria appear to enzymetically. Susceptible bacteria appear to enzymetically reducereduce furadoninfuradonin to generate the active form:to generate the active form: it is highly reactive and damages DNA.it is highly reactive and damages DNA. Clinical usesClinical uses:: urinary tract infection.urinary tract infection. Adverse reactionsAdverse reactions:: Interstitial changes in the lung, bronchoobstructiveInterstitial changes in the lung, bronchoobstructive syndrome, cough; neuropathies and hemolytic anaemia occur insyndrome, cough; neuropathies and hemolytic anaemia occur in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Rashes, pulmonary infiltration and other hypersensitivity reactionsRashes, pulmonary infiltration and other hypersensitivity reactions (chills, fever, anaphylaxis); nausea, epigastric pain, diarrhoea.(chills, fever, anaphylaxis); nausea, epigastric pain, diarrhoea. 2222
- 23. OXAZOLIDINONES Linezolid (Zyvox) – tab. 0.6 g, amp. 15% - 2 ml ● a synthetic antibiotic for the treatment of resistant Gr(+) coccal (aerobic and anaerobic) and bacillary infections. Gr(–) bacteria ARE NOT INHIBITED! It is active against methicillin resistant and vancomycin resistant Staph. Aureus (VRSA), vancomycin resistant enterococci (VRE), penicillin resistant Strep. pyogenes, Str. viridans and Str. pneumoniae, Corynebacterium, Listeria, Clostridia and Bact. fragilis. Linezolid is primarily bacteriostatic, but cidal against some streptococci, pneumococci and Bact. Fragilis. MOA: It binds to the 23S fraction of the 50S ribosomes and interferes with formation of the ternary tRNA–ribosome–mRNA complex and stops protein synthesis before it starts. There is no cross resistance with any other class of antibiotics. 2323
- 24. ANTIFUNGAL DRUGSANTIFUNGAL DRUGS I. For the treatment of mycoses causedI. For the treatment of mycoses caused byby PATHOGENICPATHOGENIC FUNGIFUNGI:: 1.1. ForFor subcutaneoussubcutaneous andand systemicsystemic mycosesmycoses:: AntibioticsAntibiotics:: Amphotericin BAmphotericin B MycoheptinMycoheptin Azole derivatives:Azole derivatives: •• ImidazolesImidazoles:: Ketoconazole,Ketoconazole, MiconazoleMiconazole •• TriazolesTriazoles:: Itraconazole, FluconazoleItraconazole, Fluconazole 2424
- 25. 2.Drugs for2.Drugs for Superficial FungalSuperficial Fungal InfectionsInfections:: AntibioticsAntibiotics:: GriseofulvinGriseofulvin Methylnaftaline derivativeMethylnaftaline derivative:: TerbinafineTerbinafine ((LamizylLamizyl – Tab 0.25 g– Tab 0.25 g;; 1% cream)1% cream) Imidazole derivativesImidazole derivatives:: MiconazoleMiconazole ClotrimazoleClotrimazole (1% cream, lotion(1% cream, lotion;; Tab. vaginal 0.1 g)Tab. vaginal 0.1 g) Nitrophenol derivativesNitrophenol derivatives:: NitrofunginNitrofungin Iodine preparationsIodine preparations:: Iodide alcohol solutionIodide alcohol solution Potassium iodide solutionPotassium iodide solution 2525
- 26. II. Drugs for the treatment of mycoses caused byII. Drugs for the treatment of mycoses caused by Conditional Pathogenic FungiConditional Pathogenic Fungi:: AntibioticsAntibiotics:: NystatinNystatin Amphotericin BAmphotericin B LevorinLevorin Imidazole derivativesImidazole derivatives:: MiconazoleMiconazole ClotrimazoleClotrimazole 2626
- 27. Amphotericin BAmphotericin B is a macrolide antibiotic, producedis a macrolide antibiotic, produced byby Streptomyces nodosumStreptomyces nodosum.. the drug of choice in the treatment of thethe drug of choice in the treatment of the Systemic MycosesSystemic Mycoses.. MOAMOA: Several polyene molecules bind to: Several polyene molecules bind to ERGOSTEROLERGOSTEROL in cellin cell membrane of fungal cells to form pores disrupting membranemembrane of fungal cells to form pores disrupting membrane permeabilitypermeability andand transport functions,transport functions, allowing electrolytesallowing electrolytes (esp.(esp. K+K+) and small molecules to leak from the cell, leading to cell death.) and small molecules to leak from the cell, leading to cell death. 2727
- 28. Synthetic Antifungal AgentsSynthetic Antifungal Agents –– AAzoleszoles:: Miconazole, KetoconazoleMiconazole, Ketoconazole TTriazolesriazoles:: Fluconazole, ItraconazoleFluconazole, Itraconazole MOAMOA: produce: produce inhibitinhibition ofion of the fungalthe fungal CYCYPP--450 enzyme450 enzyme,, LLanosine 14anosine 14αα-demethylase-demethylase which is responswhich is responsiible forble for convertingconverting LLANOSTEROLANOSTEROL toto EERGOSTEROLRGOSTEROL,, the main sterol in the fungal cell membrane.the main sterol in the fungal cell membrane. The depletion ofThe depletion of ERGOSTEROLERGOSTEROL alters the fluidity of thealters the fluidity of the membrane and interferes with the action of themembrane and interferes with the action of the Membrane-Membrane-AAssociated Enzymesssociated Enzymes.. =>=> InhibitionInhibition oof Replicationf Replication.. 2828
- 29. KetoconazoleKetoconazole ((NizoralNizoral) –) – Tab. 0.2 g, 2% cream, 1% Shampoo -Tab. 0.2 g, 2% cream, 1% Shampoo - is distinguished fromis distinguished from FluconazoleFluconazole andand ItraconazoleItraconazole by its greater propensity toby its greater propensity to inhibitinhibit humanhuman CYP-450CYP-450 enzymesenzymes Inhibition of human CYP-450 enzymes:Inhibition of human CYP-450 enzymes: ◊◊ Interferes with biosynthesis ofInterferes with biosynthesis of ADRENALADRENAL andand GONADAL STEROIDGONADAL STEROID HORMONESHORMONES, producing significant endocrine effects such as, producing significant endocrine effects such as GYNECOMASTIA, INFERTILITYGYNECOMASTIA, INFERTILITY, and, and MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES.MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES. ◊◊ CYCYPP 450 enzymes450 enzymes inhibition =>inhibition => MMetabolismetabolism of other drugs,of other drugs, leadingleading toto enhancedenhanced toxicitytoxicity 2929
- 30. CLOTRIMAZOLECLOTRIMAZOLE – only for local administration– only for local administration 1% cream, lotion1% cream, lotion;; Tab. vaginal 0.1 g –Tab. vaginal 0.1 g – a synthetic imidazole derivative for dermatophytic infections,a synthetic imidazole derivative for dermatophytic infections, IncludingIncluding Tinea corporis, Tinea pedis, Tinea crurisTinea corporis, Tinea pedis, Tinea cruris;; VVulvovaginalulvovaginal andand Oropharyngeal CandidiasisOropharyngeal Candidiasis,, KKeratitiseratitis.. MOAMOA: by binding with: by binding with PHOSPHOLIPIDSPHOSPHOLIPIDS in the fungal cell membrane,in the fungal cell membrane, alters cellalters cell MEMBRANE PERMEABILITYMEMBRANE PERMEABILITY It inhibits or kills many fungi, including yeast and dermatophytes, andIt inhibits or kills many fungi, including yeast and dermatophytes, and also is acting against some Gr(+) bacteria.also is acting against some Gr(+) bacteria. Pharmacokinetics:Pharmacokinetics: Absorption is negligible and adverse effects are rare.Absorption is negligible and adverse effects are rare. 3030
- 31. TerbinafineTerbinafine ((LamizilLamizil – Tab 0.25 g– Tab 0.25 g;; 1% cream) -1% cream) - Methylnaftaline derivative forMethylnaftaline derivative for Superficial FungalSuperficial Fungal Infections –Infections – a highly lipophilic keratophilic fungicidal compounda highly lipophilic keratophilic fungicidal compound Inhibits the enzymeInhibits the enzyme Squalene EpoxidaseSqualene Epoxidase, which is involved in the, which is involved in the synthesis ofsynthesis of ERGOSTEROLERGOSTEROL fromfrom SQUALENESQUALENE in the fungal cell wall.in the fungal cell wall. The accumulation of squalene within the cell is toxic to the organism.The accumulation of squalene within the cell is toxic to the organism. Given orally, it is rapidly absorbed and is taken up by skin, nails andGiven orally, it is rapidly absorbed and is taken up by skin, nails and adipose tissue.adipose tissue. Given topically, it penetrates skin and mucous membranes.Given topically, it penetrates skin and mucous membranes. 1 tab. PO for 12 weeks achieves a cure rate of up to1 tab. PO for 12 weeks achieves a cure rate of up to 90%90% forfor onychomycosisonychomycosis (ringworm of nails)(ringworm of nails) Unwanted effectsUnwanted effects :: GGIT upsets, rashes, pruritus, joint and muscle pains, hepatitis.IT upsets, rashes, pruritus, joint and muscle pains, hepatitis. 3131
- 32. 3232
