Ions and bonding
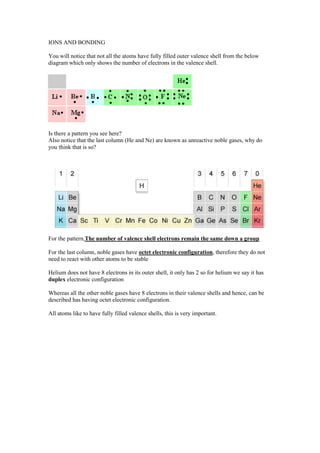
- 1. IONS AND BONDING You will notice that not all the atoms have fully filled outer valence shell from the below diagram which only shows the number of electrons in the valence shell. Is there a pattern you see here? Also notice that the last column (He and Ne) are known as unreactive noble gases, why do you think that is so? For the pattern,The number of valence shell electrons remain the same down a group For the last column, noble gases have octet electronic configuration, therefore they do not need to react with other atoms to be stable Helium does not have 8 electrons in its outer shell, it only has 2 so for helium we say it has duplex electronic configuration Whereas all the other noble gases have 8 electrons in their valence shells and hence, can be described has having octet electronic configuration. All atoms like to have fully filled valence shells, this is very important.
- 2. Notice that group 1-3 fall under metals While group 4 to 8 fall under non-metals Because metals have fewer valence electrons, they prefer to give away their valence electrons and enjoy the stability provided by an octet electronic configuration. What happens when an atom gives away electrons? Notice that a sodium atom has 11 protons and that number of protons will never change. But yet if it has given 1 electron away, how many electrons does it have left? _____ What happens is sodium has 1 more proton than electron, and we know that protons have a positive charge of +1 And that atom changes from being neutral to being an ion that has a charge of +1 As the diagram shows, a +1 ion produces an electrostatic field that can attract or repel other charged particles!
- 3. Solidify your understanding! 1) what is the ion formed by atoms of magnesium, boron, and lithium when they lose their electrons?_________________________ For non-metals, they can get a octet valence shell through 2 ways The first way is to gain electrons. Nitrogen needs to gain ____ more electrons to reach octet configuration. Oxygen needs to gain ____ more electrons to reach octet configuration. Similar to the example on sodium above, when a non-metal atom such as fluorine atom gains an electron, suddenly it has 10 electrons and only 9 protons and it has become an ______ with a charge of -1 Solidify your understanding! 1) what is the ion formed by atoms of chlorine and sulphur when they gain some electrons? ____________________ 2) what is the electronic configuration of sulphide (S2-) and oxygen ion? ____________________________________________ But in order to gain electrons, non-metal atoms need to come into contact with ___________ atoms. The transfer of electrons from metal to non-metal atoms results in ions of opposite charges being formed. Unlike charges cause them to be attracted strongly to each other.
- 4. Obtaining the formula for ionic compounds An ionic compound is always made up of _______ positively charged ions and _________________ negatively charged ions. The total charge of the ions always equal to zero, because the number of electrons given to form the positive ions is equal to the number of electrons gained to form the negative ions 3 simple steps to follow to get the formula of an ionic compound 1. Determine the charge of the metal positive ion using the periodic table 2. Determine the charge of the non-metal negative ion using the periodic table 3. Find the LCM of both charges to get the numbers of each ion in the compound Try to find out the formula of 1) Magnesium Chloride and 2) Lithium Oxide _______________________________________________________ Harder example: try to find the formula of Aluminium Oxide ______________________________________________________ There are also some ions which are not found in the periodic table such as ammonium ion which is NH4+, andsulphate ion which is SO42-, as well as nitrate NO3- and carbonate CO32-. Find out the chemical formula of ammonium sulphate ___________________ Take note that in your formula, the metal ion should always be first (such as NaCl) and big ions like sulphate or nitrate should be in brackets like in Mg(NO3)2. COVALENT BONDING A covalent bond is defined as the sharing of a pair of electrons between two atoms. And take note that covalent bonds only apply to non-metal atoms. Below are a few examples
- 5. This is CH4 Now you can try to form dot-and-cross diagrams of the following molecules, do not forget to include a legend, which is worth marks in exams! 1. F2 Some of the harder ones involve many atoms so you need to know which atoms are in the centre of the molecule. The more number of covalent bonds an atom need to get octet configuration, the more likely it is to be in the centre bonding to many other atoms. 1. N2 2. NH3 Atoms and molecules Molecules refer to two or more atoms covalently bonded together
- 6. IONS AND BONDING CHECKLIST 1) Identify the group that the following elements belong to Aluminium Group 3 Bromine Neon Lithium Magnesium Phosphorous Sulphur Beryllium Oxygen Helium Sodium Boron 2) Draw a dot and cross diagram of sodium fluoride showing all the electrons. 3) Draw a dot and cross diagram of HCl showing all the electrons
- 7. 4) Magnesium ion has a charge of +2 and oxide ion has a charge of +2, why is Magnesium Oxide’s formula not MgO2? 1) 1 Mg and 1 Oxide ion balance out with a net charge of +2. 2) 1 Mg and 1 oxide ion balance out with no net charge 3) 1 Mg and 2 oxide ion do not balance out, there is a net charge of +2 4) 1 and 3 are correct 5) 2 and 3 are correct 5) Draw a dot and cross diagram of H2O showing only the valence electrons