Dental problems
- 1. 1 DENTAL PROBLEMS IN OLD AGE JYOTI PACHISIA M.SC 1ST YEAR FOOD AND NUTRITION ROLL NO. 07 J D BIRLA INSTITUTE
- 2. 2 ABOUT THIS TOPIC As the first segment of the gastrointestinal system, the oral cavity provides the point of entry for nutrients. The condition of the oral cavity, therefore, can facilitate or undermine nutritional status. If dietary habits are unfavourably influenced by poor oral health, nutritional status can be compromised. However, nutritional status can also contribute to or exacerbate oral disease. General well‑being is related to health and disease states of the oral cavity as well as the rest of the body. An awareness of this interrelationship is essential when the clinician is working with the older patient because the incidence of major dental problems and the frequency of chronic illness and pharmacotherapy increase dramatically in older people.
- 3. 3 SERIAL NO. CONTENTS COVERED PAGE NO. 1 HEALTH STATUS OF INDIAN GERIATRIC POPULATION 4-5 2 ORAL HEALTH STATUS OF INDIAN GERIATRIC PEOPLE 6 3 COMMON DENTAL PROBLEMS SEEN IN OLD AGE 7-22 4 BASIC ORAL HYGIENE RULES TO BE FOLLOWED 23 5 NUTRITION AND ORAL HEALTH 24-25 6 ORAL HEALTH PROGRAMMES 26-27 7 CONCLUSION 28 8 REFERENCES 29 CONTENTS
- 4. 4 India is an aging society with the rate of growth of aging population exceeding the growth of general population. In India, it is estimated that the elderly in the age group 60 and above is expected to increase from 71 million in 2001 to 179 million in 2031 and in the case of those 70 year and older, the projected increase is from 27 million in 2001 to 132 million in 2051. Data available from India suggest that almost 50 per cent of the elderly suffer from chronic diseases with the prevalence of diseases increasing with age from 39% in 60-64 year to 55% in those older than 70 year. Cardiovascular diseases followed by respiratory diseases are two of the common causes of death among the elderly in India. Hearing and Visual impairments are two of the common causes of morbidity in the aged population. A National Survey noted that 5 per cent of the elderly have difficulty in physical morbidity with women (7%) experiencing more difficulty than men. Varying degrees of neuropsychiatric disorders being one out of three elders, with depression being the commonest disorder in the elderly. Among the elderly, the focus is not only on reducing disease related morbidity and mortality, but on promoting optimal health and ensuring disability-free years. In a population based study in a rural district from South India, authors using the International Classification of Impairments, Disabilities and Handicaps, noted that visual disability was the single most important cause of preventable disability (56%) among the elderly aged above 60 yr with only one third of them using assistive devices. In another study from northern India, a HEALTH STATUS OF INDIAN GERIATRIC POPULATION
- 5. 5 significant proportion of the elderly surveyed had multiple health-related morbidities (42.5%) and a higher number of morbidities were associated with greater disability and psychological distress. In a clinic based study from a tertiary health care centre in Delhi, of the 1586 subjects aged 60 yr and above, 6.9 per cent had impairment in daily activities. A study from Assam showed that utilization of health services was very low among the rural elderly compared to the urban elderly.
- 6. 6 Indian geriatric population has poor oral health and prosthetic status with high unmet needs. Indiscriminate studies and paucity of data on residents depicts the proportionate degree of negligence towards the oral health conditions in residents. By and large, there is a hike in the incidence of root caries, edentulousness (tooth loss), periodontal problems and oral mucosal disorders. Dental Council conducted National Oral health Surveys in 65 to 74 year old elderly in urban and rural households in each state in 2002-2003 as per the WHO recommendations. The data collected shown a prevalence of 85% and 80% among 65-74 years old for dental caries and periodontal diseases respectively. According to cross-sectional study, Dental caries (43.2%) and periodontal diseases (34.8%) were the most common dental disorders in urban residents of Nagpur, Maharashtra. Only 4.2% had complete dentures and 22% are completely edentulous in geriatric homes of Mangalore. Moreover, in Delhi, 44.9% of the elderly had decayed teeth, 39.2% were edentulous. 57.9% had deep periodontal pockets. ORAL HEALTH STATUS OF INDIAN GERIATRIC POPULATION
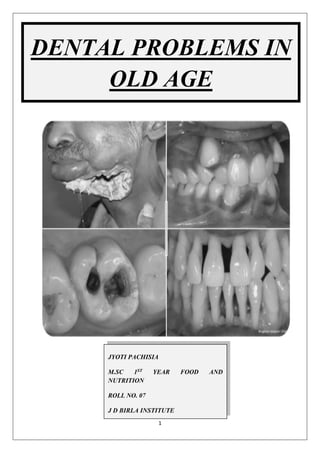
- 7. 7 COMMON DENTAL PROBLEMS TOOTH LOSS/ EDENTULISM DENTURE STOMATITIS DENTAL CARIES PERIODONTA L DISEASE XEROSTOMI A/ DRY MOUTH ORAL CANCER ORAL ULCER GINGIVITIS SENSITIVITY CANDIDIASIS ANGULAR CHELITIS
- 8. 8 1. TOOTH LOSS/ EDENTULISM: Edentulism is the state of having lost all of one’s natural teeth. Monitoring the occurrence of an oral “end state” such as edentulism is important because it is an indicator of both population health and the functioning and adequacy of a country’s oral health care system. It is a debilitating and irreversible condition and is described as the “final marker of disease burden for oral health.” Edentulism remains a major disease worldwide, especially among older adults. Factors associated with edentulism include socioeconomic factors such as increasing age, gender, lower education, lower economic status, lower social class, health security and rural residence; chronic conditions such as asthma, diabetes, arthritis, angina pectoris, stroke, hypertension and obesity; health risk behaviour including smoking, inadequate consumption of fruit and vegetables, infrequent dental visits; and other health-risk factors including functional disability, lower scores on cognitive testing, poorer self- rated level of general health, social cohesion and self- esteem and quality of life. Edentulism leads to reduced food intake specially fruits and vegetables thereby increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases and obesity, gastrointestinal disorders, ulcers, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, decreased daily function & physical activity which ultimately leading to poorer quality of life. Also association between edentulism and sleep- disordered breathing, including obstructive sleep apnea is seen. Edentulism is also associated with tardive dyskinesia, a type of dyskinesia occurring among between patients chronically treated with antipsychotic drugs. Edentulism
- 9. 9 can be accompanied by functional and sensory deficiencies of the oral mucosa, oral musculature, and the salivary glands. Edentulism has a series of deleterious consequences for oral and general health. Oral consequences vary from the well known residual ridge resorption to an impaired masticatory function, an unhealthy diet, social disability, and poor oral health quality of life. Edentulous individuals are also in greater risk for different systemic diseases and an increase in mortality rate. Therefore, oral health care providers should prevent tooth loss with proper dental education, oral health promotion, and a high level of dental care in an attempt to assure the existence of a physiologic dentition. People during senior years, dental cavities, gum disease and tooth loss may make it difficult to chew and swallow food and because changes in texture and temperature of foods, they get deprived of nutritional requirements. Eating soft or minced foods that are appetizing and dense in protein, vitamins and minerals may help in weight loss and nutritional deficiencies. 2. DENTURE STOMATITIS: Denture stomatitis (DS), also known as denture-induced stomatitis, denture induced stomatitis or chronic erythematous candidosis, is an oral condition that presents clinically as erythemateous and inflamed areas of mucosa exclusively limited to those sites covered by denture. 67% of denture wearers suffer from some degree of Dental stomatitis. Denture stomatitis is usually aymptomatic, although some patients may complain of itching, burning, discomfort and occasional bleeding. In its mildest form, Denture stomatitis may arise from a poor fit of the denture. However, the aetiology of Denture stomatitis is likely to be complex in more clinically severe cases. In addition to physical irritation, potential precipitating factors include, poor denture hygiene, continuous wearing of dentures, poor denture quality, undiagnosed or poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, reduced salivary gland function, tobacco use, hypersensitivity reactions to denture materials, immune-suppression or immune- compromised states, and Candida infection. With regards to the latter, Denture stomatitis is considered to be most prevalent form of oral candidosis.
- 10. 10 Importantly, it has been shown that the visible mucosal inflammatory changes associated with Denture stomatitis actually reduce following treatment with either topical or systemic antifungal therapy. This response provides strong evidence for the role of Candida in the aetiology of Candida in the aetiology of Denture stomatitis. However, inflammation usually rapidly recurs following cessation of such antifungal treatment, an observation that, in part, probably reflects the failure to eradicate the presence of Candida, on the denture surface. Therefore to control this, it is likely to be necessary to simultaneously reduce mucosal inflammation and the microbial colonisation of the denture. As a consequence, dentures should be removed during sleep, since this will reduce any physical irritation and permit access of saliva to the mucosa. It is also important to keep the dentures in a clean storage container so that denture is not re-colonised. In addition, adequate denture hygiene should be regularly maintained such as through the regular soaking and brushing of dentures using a denture cleanser in an attempt to eliminate the infection. Since stomatitis could be a result of the collection of toxins in the body, for long term relief from this condition, it is important for people to follow a diet that is high in healthy stomatitis foods. However, in the beginning, a stomatitis diet requires the patient to consume nothing but water and orange juice for around 3 to 4 days. For best results, the orange juice should be diluted in an equal part of warm water, before it is consumed. This mixture should be consumed every two hours or so, so that the body does not suffer from a lack of nutrition. For those people who do not like orange juice, carrot juice diluted in water should be used instead. However, people may need to take a warm water enema to cleanse the bowels during this phase. After the duration of 3 to 4 days, people can switch over to a diet, comprising healthy stomatitis foods to eat, such as fresh fruits like peach, pear, grapefruit, apple, papaya, pineapples, oranges and grapes. After that, the patient needs to follow a stomatitis diet that mainly comprises fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts and seeds. Special emphasis should be laid
- 11. 11 on whole grains, cereals, fruits and vegetables that are either raw or cooked lightly. Sprouted seeds like green gram beans and alfalfa are also healthy stomatitis foods to eat. There are certain stomatitis foods that should be strictly avoided too, such as candies, processed food, pickles, ice cream, soft drinks, refined foods, meat, coffee, tea, white flour, sugar and condiments. However, before adding any foods to a regular diet, or eliminating any, it is absolutely essential to consult a doctor and get an approval. 3. DENTAL CARIES: Caries is the demineralization of the inorganic part of the tooth with the dissolution of the organic substance due to multifactorial etiology. The demineralization of the enamel and of organic acids that form in the dental plaque is because of bacterial activity, through the anaerobic metabolism of sugars from the diet. Tooth decay is the process that results in the gradual destruction of a tooth and is caused by the combination of bacteria (dental plaque) and sugar (diet). Decay often occurs rapidly at that time of a life crisis such as chronic diseases or loss of partner. In older people this process can be painless.
- 12. 12 Decay/ Dental caries may occur in the enamel cap, around and under fillings and (especially in older people) in the softer root dentine exposed as guns recede. This root decay may only be spotted by X- ray examination in its early stages, and is a serious problem for older people with natural teeth. The types of sugar ingested through diet also influence the onset of illness. In fact, studies on the pH of the dental plaque have shown that lactose produces less acidity in comparison to other sugars. The main causes of dental caries/ decay are: Poor or lack of tooth brushing with fluoride toothpaste Lack of cleaning between teeth Snacking of foods high in sugar Frequent intake of sweetened drinks, including fruit juices and fizzy drinks Dry mouth The warning signs are: Tooth covered in debris and food Holes in teeth Broken teeth Brown or discoloured teeth Brown or discoloured teeth Tooth sensitivity to hot or cold foods Difficulty with eating or chewing Toothache Bad breath Swelling in the face and jaw area Dental caries can be prevented by brushing daily with fluoride toothpaste, reduction of sweetened foods and drinks, especially in between meals Diet can be a good ally in the prevention of caries: .(i)Increase in the consumption of fibres: diminution of the absorption of sugars contained in other food.
- 13. 13 (ii)Diets characterized by a ratio of many amides/little sugar have very low levels of caries. (iii)Cheese has cariostatic properties. (iv)Calcium, phosphorus and casein contained in cow milk inhibit caries. (v)Wholemeal foods have protective properties: they require more mastication, thus stimulating salivary secretion. (vi)Peanuts, hard cheeses, and chewing gum are good gustative/mechanical stimulators of salivary secretion. (vii)Black tea extract increases the concentration of fluorine in the plaque and reduces the cariogenicity of a diet rich in sugars. (viii) Fluorine remains a milestone in the prevention and in the control of dental caries. It has a pre-eruptive mechanism of action (incorporation in the enamel during amelogenesis) and a post-eruptive mechanism (topical action). 4. PERIODONTAL DISEASE/ PERIODONTITIS: Periodontitis is the destructive form of gum disease. Untreated gingivitis can advance to periodontitis as, with time, plaque can spread and grow below the gum line. The pathogenesis of periodontal disease involves bacteria and the host response to these bacterial by products (toxins and enzymes). Toxins produced by the plaque bacteria cause an inflammatory response which destroys the periodontal fibres and bone supporting the teeth. As the disease progresses, more gum tissue and bone are destroyed. Eventually, the tooth becomes loose and falls out or may have to be removed. In short, periodontal disease range from mild forms, such as gingivitis, to severe forms of periodontitis that results in the destruction of periodontal supportive tissue and ultimately tooth loss. Periodontitis is characterized by red swollen or tender gums, receding gums, or gums that pull away from the teeth, loose teeth, pus formation between the gum and the tooth, bad breath, change in the way teeth fit together when biting, or even during wearing dentures. The following are the preventive measures to be taken: Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- 14. 14 Regular cleaning between teeth if part of care plan Reduction of sweetened foods and drinks, especially in between meals- and replacing with “tooth safe” alternatives such as water rather than fruit juices or fizzy drinks. Regular professional check-ups and cleaning Health professionals should consider certain factors and develop a comprehensive inter- professional approach when addressing nutritional care and diet counselling from screening to assessment to intervention to monitoring to referral, as appropriate to maximize patient/ client care outcomes. 5. DRY MOUTH/ XEROSTOMIA: Dry mouth or xerostomia is a condition where the mouth becomes very dry due to reduced saliva flow. It is caused by certain medical conditions and is also a side effect of medications such as antihistamines, painkillers, high blood pressure medications, diuretics, antidepressants and others. People suffering from dry mouth are more susceptible to tooth decay, gum disease and bad breath. The soft tissues in the mouth are more prone to irritation for those who wear dentures. The most common causes are: Certain medications Radiation and chemotherapy
- 15. 15 Conditions such as Sjogren’s syndrome and Alzhemier’s disease Warning/ Alarming signs for dry mouth/ xerostomia are: Difficulty in swallowing and speaking Dryness in mouth Burning sensation or sore feeling in the mouth Bad breath Preventive measures to be taken to combat the problem: Follow strict daily oral hygiene routine using soft brush with fluoride toothpaste and cleaning between teeth (if this is part of Oral Care plan). Salt and bicarbonates (baking soda) rinses can be used as often as required during the day to remove any mucus or debris in the mouth. Discuss the medications with the doctor to find suitable alternatives (if that is possible) that are less likely to cause dry mouth. Drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration
- 16. 16 Avoid drinking sweetened drinks, especially in between meals Special products are available in the market to restore moisture in the mouth. Therefore, a product is recommended in the Oral Care plan. 6. ORAL CANCER: Oral cancer includes cancer of lip, tongue, cheeks and other sides of the mouth. Ulcers lasting for more than two weeks must be screened for oral cancer. The association between diet and oral cancer is extremely serious. It is a pathology that is diagnosed in three hundred thousand new cases in the world every year and presents the greatest incidence in people who smoke, chew tobacco and consume alcohol. The use of tobacco can alter the distribution of nutrients such as antioxidants, which develop a protective action toward the cells: smokers present levels of carotenoids and vitamin E in the blood that are superior to those in the oral mucous and, in addition, have a different distribution in comparison to the norm; the levels of folates in the blood and in the cells of the oral tissues of smokers are inferior to those of nonsmokers; the inside of the cheeks of smokers presents numerous micronuclei (modifications typical of pre- and neoplastic lesions). The study of the incidence of this illness has underlined the possibility that diet can represent an important etiological factor for oral carcinogenesis. Vitamins A, E, C, and Beta Carotene have antioxidant properties. (i)They neutralize metabolic products.(ii)They interfere with the activation of procarcinogens.(iii)They inhibit chromosomal aberration.(iv)They potentially inhibit the growth of malignant lesions (leukoplakia). The mechanism that connects smoke to this disease has not been discovered but some progress has been made: smoke modifies the distribution of protective substances such as
- 17. 17 folates and some antioxidants. A rebalancing of nutrients obtained through diet can modify the altered distribution caused by the consumption of tobacco. In an imbalanced diet there is a depletion of antioxidant nutrients. Fruit and vegetables have, vice versa, important antioxidant properties. Many micronutrients (vitamins in particular) are used in chemoprevention programs formulated by the US National Cancer Institute. The National Cancer Institute and the American Cancer Society have established some prudential dietary recommendations for the choice of food: (1)maintain a desirable body weight, (2)eat a varied diet, (3)include a new variety of fruits and vegetables in the daily diet, (4)consume a greater quantity of foods rich in fibre, (5)decrease the total intake of fats (30% less than the total calories), (6)limit the consumption of alcohol, (7)limit the consumption of salted food or food preserved with nitrates. In patients with an advanced tumour disease, protein-caloric malnutrition is a recurrent problem due to factors such as a form of anorexia that is established, maldigestion, malabsorption, and to a difficulty in mastication and deglutition. Foods should be provided that aim to correct nutritional deficits and ponderal reduction when consumed in a large enough quantity to cover protein and caloric requirements. Malnutrition also interferes negatively with humoral and cellular immunocompetence and with tissue and reparative functions. In addition, the alteration of the liver function can change the way drugs are metabolized. Therefore, malnutrition can interfere with oncological therapy and increase the severity of the collateral effects. Some studies show a small effect of dietary supplementation on cancer incidence, while others show that supplementation with antioxidant vitamins may have an adverse effect on the incidence of cancer and cardiovascular diseases or no effect. Increasing attention has been given to the potential protective roles of specific antioxidant nutrients found in fruits and vegetables.
- 18. 18 In a recent research El-Rouby showed that lycopene can exert protective effects against 4- nitroquinoline-1-oxide induced tongue carcinogenesis through reduction in cell proliferation and enhanced cellular adhesion, suggesting a new mechanism for the anti-invasive effect of lycopene. In a recent report Edefonti et al. showed that diets rich in animal origin and animal fats are positively, and those rich in fruit and vegetables and vegetable fats inversely related to oral and pharyngeal cancer risk 7. ORAL ULCER: Oral ulcers are painful areas that appear inside the mouth. They are usually red or yellowish in colour. Ulcers can be caused by trauma due to biting the cheek or tongue, poorly fitted dentures, sharp broken teeth or dental fillings. ORAL ULCER
- 19. 19 These areas heal spontaneously or when the cause of the ulcer is removed. If the ulcer does not heal within two weeks it is important to consult a dentist. Use of topical analgesics like gels, Replacement of old broken fillings, adjustment of poorly fitting dentures, rinsing the mouth to keep clean are common treatments to be kept in mind 8. GINGIVITIS: Gingivitis is a common form of gum disease and is often left unnoticed as it is not painful. Gingivitis can be treated and reversed but if left untreated can develop into periodontal disease which can lead to premature tooth loss. Inadequate or lack of tooth brushing and lack of cleaning between teeth are the common causes of gingivitis. Gingivitis is characterised by red, swollen or tender gums, bleeding while brushing or flossing and bad breath. General oral health care practices are to be followed. 9. SENSITIVITY/ TOOTH WEAR: Enamel is the outer surface of the tooth crown, and it protects the sensitive dentine underneath. Young and middle-aged people can complain of tooth sensitivity during brushing and while eating very hot or cold foods. This is usually due to some exposed dentine being stimulated. This is rare in older people because the nerves of teeth are protected by insulating tissues, which have formed in earlier years. There is therefore, little value in using toothpastes designed for sensitive teeth for older people. If an older person has sensitive teeth it is usually because of decay, and so they should be seen by a dental professional.
- 20. 20 Along with decay the other causes of loss of tooth structure in older people is “fair wear and tear”. This usually occurs in the form of pieces of tooth breaking away from fillings, and teeth chipping and becoming sharp to the tongue. These conditions should be referred to and managed by a dental professional as worn teeth that are functional and supported by healthy gums are superior in all respects to dentures. Regular dental check-ups are important to spot and treat the causes of sensitive teeth such as decay, broken teeth or fillings. 10. ORAL THRUSH/ CANDIDIASIS: This is a fungal infection of the mouth. This is seen as patches of white film or red dots that can be painful. It can also a sign of Vitamin B12, folate or iron deficiency. A significant correlation has been evinced with a lack of iron. This causes alterations in the epithelium with consequent atrophy and alteration in cellular turn-over, an alteration in the iron-dependent SENSITIVITY
- 21. 21 enzymatic system depression in cell-mediated immunity, phagocytosis, and in the production of antibodies. The correlation between candidiasis and the lack of folic acid, vitamins A, B1, B2, vitamins C, K, zinc, and a diet rich in carbohydrates is also significant. Weak immune system, dry mouth, leaving dentures in the mouth for a long time without adequate cleaning, long- term administration of antibiotics are the common causes of oral thrush. Candidiasis is characterised by white patches that cannot be wiped away, small red inflamed dots on the tongue and inflammation or redness of palate (in front of the mouth). Eating a well balanced diet, allowing the gum tissues to rest from wearing dentures and use of anti- fungal medications are some preventive measures. 12. ANGULAR CHEILITIS: CANDIDIASIS
- 22. 22 Angular cheilitis is a bacterial or fungal infection that usually appears as red inflamed sores and cracks at the corners of the mouth, is associated with 0.7- 3.8% in elderly people. Poorly fitting dentures, dentures not cleaned properly or sometimes underline immune or nutritional deficiency are the common causes. It can begin as a small fissure without much inflammation and may eventuate into deep inflamed fistures. The problem may be a symptom of Riboflavin deficiency or may be resultant of other chronic diseases. Angular cheilitis often represents an opportunistic infection of fungi and/or bacteria, with multiple local and systemic predisposing factors involved in the initiation and persistence of the lesion. It is important to appreciate that most of the cases of this problem are infectious and should be treated The treatment is highly dependent on the cause. For idiopathic causes, the treatment could be as simple as applying petroleum jelly to the affected areas. Denture replacement for those without teeth has been found to treat angular cheilitis effectively and for people with dentures, it is important that oral prostheses be of appropriate size and shape. It can be also important to consider other factors such as avoiding contact irritants, ensuring proper salivation and treating structural abnormalities, if present
- 23. 23 If people start following these steps themselves or with assistant help, they will be able to fight against the various problems discussed above. BASIC ORAL HYGIENE RULES TO BE FOLLOWED
- 24. 24 An unhealthy diet has been implicated as risk factors for several chronic diseases that are known to be associated with oral diseases. Studies investigating the relationship between oral diseases and diet are limited. Therefore, this study was conducted to describe the relationship between healthy eating habits and oral health status. The dentistry has an important role in the diagnosis of oral diseases correlated with diet. Consistent nutrition guidelines are essential to improve health. A poor diet was significantly associated with increased odds of oral disease. Dietary advice for the prevention of oral diseases has to be a part of routine patient education practices. Inconsistencies in dietary advice may be linked to inadequate training of professionals. Literature suggests that the nutrition training of dentists and oral health training of dietitians and nutritionists is limited. The concept of oral health correlated to quality of life stems from the definition of health that the WHO gave in 1946. Health is understood to be “a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity”. The programs for the prevention of oral diseases concern teaching about oral hygiene and healthy eating, fluoride prophylaxis, periodic check-ups, sessions of professional oral hygiene, and secondary prevention programs. The term “bionutrition” refers to the important interactions which exist between diet, use of nutrients, genetics, and development. This term emphasizes the role of nutrients in maintaining health and preventing pathologies at an organic, cellular, and subcellular level. There exists a biunique relationship between diet and oral health: a balanced diet is correlated to a state of oral health (periodontal tissue, dental elements, quality, and quantity of saliva). Vice versa an incorrect nutritional intake correlates to a state of oral disease. Diet influences the development of the oral cavity: depending on whether there is an early or late nutritional imbalance, the consequences are certainly different. In fact, an early nutritional imbalance influences malformations most. Moreover, the different components of the stomatognathic NUTRITION AND ORAL HEALTH
- 25. 25 apparatus undergo periods of intense growth alternated with periods of relative quiescence: it is clear that a nutritional imbalance in a very active period of growth will produce greater damage. A shortage of vitamins and minerals in the phase before conception influences the development of the future embryo, influencing dental organogenesis, the growth of the maxilla, and skull/facial development An insufficient supply of proteins can lead to the following: (i)atrophy of the lingual papillae, (ii)connective degeneration, (iii)alteration in dentinogenesis, (iv)alteration in cementogenesis, (v)altered development of the maxilla, (vi)malocclusion, (vii)linear hypoplasia of the enamel. An insufficient supply of lipids can lead to the following: (i)inflammatory and degenerative pathologies, (ii)parotid swelling—hyposalivation, (iii)degeneration of glandular parenchyma, (iv)altered mucosal trophism. An insufficient supply of carbohydrates can lead to the following: (i)altered organogenesis, (ii)influence of the metabolism on the dental plaque, (iii)caries, (iv)periodontal disease. Diet influences the health of the oral cavity, conditioning the onset of caries, the development of the enamel, the onset of dental erosion, the state of periodontal health, and of the oral mucous in general.
- 26. 26 The proportion of older people continues to grow worldwide, especially in developing countries. Non-communicable diseases are fast becoming the leading causes of disability and mortality, and in coming decades health and social policy-makers will face tremendous challenges posed by the rapidly changing burden of chronic diseases in old age. Chronic disease and most oral diseases share common risk factors. Globally, poor oral health amongst older people has been particularly evident in high levels of tooth loss, dental caries experience, and the prevalence rates of periodontal disease, xerostomia and oral precancer/cancer. The negative impact of poor oral conditions on the quality of life of older adults is an important public health issue, which must be addressed by policy-makers. The means for strengthening oral health programme implementation are available; the major challenge is therefore to translate knowledge into action programmes for the oral health of older people. The World Health Organization recommends that countries adopt certain strategies for improving the oral health of the elderly. National health authorities should develop policies and measurable goals and targets for oral health. National public health programmes should incorporate oral health promotion and disease prevention based on the common risk factors approach. Control of oral disease and illness in older adults should be strengthened through organization of affordable oral health services, which meet their needs. The needs for care are highest among disadvantaged, vulnerable groups in both developed and developing countries. In developing countries the challenges to provision of primary oral health care are particularly high because of a shortage of dental manpower. In developed countries reorientation of oral health services towards prevention should consider oral care needs of older people. Education and continuous training must ensure that oral health care providers have skills in and a profound understanding of the biomedical and psychosocial aspects of care for older people. Research for better oral health should not just focus on the biomedical and clinical ORAL HEALTHCARE SERVICES
- 27. 27 aspects of oral health care; public health research needs to be strengthened particularly in developing countries. Operational research and efforts to translate science into practice are to be encouraged. WHO supports national capacity building in the oral health of older people through intercountry and interregional exchange of experiences.
- 28. 28 • The proportion of older people continues to grow worldwide. • Non-communicable diseases are fast becoming the leading causes of disability and mortality, and in coming decades health and social policy-markers will face tremendous challenges posed by the rapidly changing burden of chronic diseases in old age. • Globally, poor oral health amongst older people has been particularly evident in high levels of tooth loss, dental caries experience, and the prevalence rates of periodontal disease, xerostomia and oral pre-cancer/cancer. • Education and continuous training must ensure that oral health care providers have skills in and a profound understanding of the biochemical and psychosocial aspects of care for older people. • National public health programmes should incorporate oral health promotion and disease prevention based on the common risk factors approach. • Also, control of oral disease and illness in older adults should be strengthened through organization of affordable oral health services, which meet their needs. CONCLUSION
- 29. 29 1. Healthy Mouth, Healthy Aging: Oral Health Guide for Caregivers of Older people, 2010 cited by New Zealand Dental Association, Auckland 2. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1741- 2358.2011.00518.x/pdf 3. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1949217/ 4. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3664508/ 5. http://www.omicsonline.org/immune-response-and-candidal- colonisation-in-denture-associated-stomatitis-2155-9899.1000178.pdf 6. Naik Amit, Pai Ranjana, “A study of factors contributing to Denture Stomatitis in a North Indian Community”, International Journal of Dentistry, 2011;1-4 7. Panchbhai Arati, “ Oral Health Care needs in the dependent Elderly in India”, Indian Journal of Palliative Care, 2012;18(1): 19-26 8. Peltzer K, Hewlett S, et al., “ Prevalence of loss of All Teeth (edentulism) and associated factors in Older adults in China, Ghana, India, Mexico, Russia and South Africa”, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2014(11): 11308-11324 9. Petersen P.E, Kandelman D, et.al, “ Global oral health of older people- for public health action”, Community Dental Health 27(2),2010:257-Call 268 10.Scardina G.A. and Messina P, “Good oral health and diet”, Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology;2012:(1-8) REFERENCES
