Paleozoic era bb-Geomorhology Chapter
- 2. • Bangladesh is divided into two major tectonic units: i) Stable Pre-Cambrian Platform in the northwest, and ii) Geosynclinal basin in the southeast. A third unit, a narrow northeast-southwest trending zone called the hinge zone separates the above two units almost through the middle of the country. This hinge zone is currently known as palaeo continental slope. Stable Pre-Cambrian Platform in Bangladesh, refers to the stable shelf of the bengal basin. In Bangladesh, part of the Bengal Basin, the stable shelf can be divided into three major zones. They are Dinajpur slope (platform), Rangpur Saddle and Bogra slope. It is composed of continental crust overlain by Cretaceous (144 to 66 million years ago) to Recent sediment. However, in isolated basins on the stable shelf, there is Permo-Carboniferous (360 million years to 245 million years ago) sediments with considerable amount of coal. In Madhyapara area of Dinajpur the basement is only 130m deep from the ground surface.
- 4. • Shield, Platform and Basin • The Cambrian rocks form the basement of all geological formations and as a consequence they are referred to as Basement Complex or simply the Basement. • The regions occupied by the Precambrian rocks are known as Shields as they have virtually remained undisturbed and unaffected by changes except for vertical movement. • Literature on Plate Tectonics defines Shields as stable parts of the Earth composed of Precambrian rocks with little or no sedimentary cover. Metamorphic and plutonic rocks dominate in the constitution of the rocks. Shield areas show very little relief and tectonically remained stable for long periods of time. • Platforms also include the stable parts of the earth’s crust being composed of Precambrian Basement rocks which are overlain by typically 1 to 3 km of relatively underformed sediments. • From the definitions, it appears that the depth of the sediments on the Shield should be less than 1km. • The Basin applies to the regions where the Precambrian Basement lies 3km below msl.
- 5. • Geosynclinal Basin in the southeast is characterised by the huge thickness (maximum of about 20 km near the basin centre) of clastic sedimentary rocks, mostly sandstone and shale of Tertiary age. It occupies the greater Dhaka-Faridpur-Noakhali-Sylhet [Silet]-Comilla [Kumilla]-Chittagong areas. A geosyncline generally forms along continental edges, and is destroyed during periods of crustal deformation, which often produces folded mountain ranges. Bengal Geosyncline is one of the world's largest geosyncline that includes the bengal basin and the bay of bengal. The evolution of the Bengal Basin started in the Permo- Carboniferous with the sedimentation in the faulted Gondwana Basins. The break up of the Gondwanaland in the Cretaceous Period and the marine transgression led to the sedimentation in the Bengal Geosyncline.
- 7. For Bangladesh, the most important one is the Cenozoic era, because most of the sedimentary layers as well as the geological structures of the country were formed during this era. Bengal Basin, occupied mostly by Bangladesh, is the result of plate collision between the Indian plate and the Asian plate. Before Cretaceous time (125 mya), the Indian plate including part of Bangladesh (greater Rangpur and Dinajpur area) was joined together with Antarctica, Africa, Australia and South America, forming a super continent called Gondwanaland. The remaining part of Bangladesh did not exist at that time. It was only after the rifting, northward drifting of the Indian plate and the ultimate collision with the Asian plate that the Himalayas were formed and the deltaic plain of Bangladesh created.
- 8. • During the early Tertiary period (Mid-Palaeocene- 59mya) “soft collision” started between India and Southeast Asia. Most of Bangladesh was under open marine condition. The Tethys sea was disappeared. • During the late Tertiary period (44mya) (Middle Eocene) “hard collision” started between India and South Asia. The open sea retreated to the south in response to the uplift of the himalayas in the north and river systems built out a large deltaic land that formed the backbone of the present bengal delta.
- 10. About 22 Ma, Early Miocene, a time of major collision between India and South Tibet in the north and India and Burma in the east. • In response to the eastwards directed subduction of the Indian Plate, the molasses sediment (The term "molasse" refers to the sandstones, shales and conglomerates formed as terrestrial or shallow marine deposits in front of rising mountain chains) of this zone were folded into a series of elongated asymmetric folds arranged in en-echelon form. The alignment of the folds follows NNW-SSE in the Chittagong hill tracts. During this time the direction of the Indian plate convergence changed from north to north-east with increasing collision with Southeast Asia. • In the mean-time subduction of the Indian plate beneath the Asian plate created a sutured zone of plate zone in the northern Himalayas while in the east the Indo-Burman range marks the zone of plate and the Asian plate continues and this is evidenced from the release of stress in the form of earthquakes in the vicinity of the plate boundary from time to time
- 12. Since the Oligocene time (35 mya), plate collision continued and major SEDIMENTS were shed by the rising Himalayas as large river systems started filling up the proto-Bengal basin to the south. • From Miocene onward (from 25 mya), rapid rise in the Himalayas accompanied by rapid SUBSIDENCE in the basin resulted huge in deposition of a huge sedimentary pile with the simultaneous development of a mega-delta. This delta building continues at present as the Ganges- Brahmaputra delta. • Dauki Fault zone: The fault zone has divided the former Northern Foreland shelf with the rising shillong Massif; the southern has been down-faulted and concealed beneath a thick clastic sequence of plio-pleistocene age. • The Dauki fault has continued to be active as evedenced by the continued sinking of the Surma Basin to its south
- 15. • Neotectonic Activity: “The study of geologically recent motions of the Earth's crust, particularly those produced by earthquakes,. • …."recent tectonic movements occurred in the upper part of Tertiary. • Geological investigation, gravity, seismic, magnetic data have indicated hat the late Pliocene-Pleistocene Himalayan orogenic movement has continued to be active upto the present time. • Since the Bengal Basin is a part of the Himalayan orogen, it is included in the intensive tectonic processes of most recent and contemporary geological history. • There are clear indications that Bengal Basin have been uplifted and subsided as a result of neotectonic activity beginning from the Pliocene age.
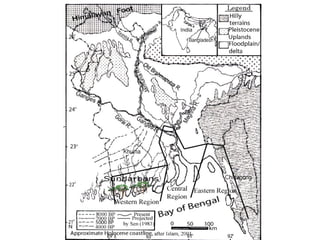
- 16. The Shillong Plateau in the northeast India gives an excellent example of neotectonic activity. The plateau occurs as an east-west trending horst block rising to an elevation of nearly 2000m flanked by the surma basin to its south which is known to have subsided 4-5 km during the past 2-3 mys. • The Dauki fault has continued to be active as evedenced by the continued sinking of the Surma Basin to its south. • The deltaic region of the Bengal basin is constantly subsiding owing mainly to compaction of rcent sediments and also to structural downwarping. Other areas of subsidence in the basin include the Chalan Beel, the Dhaka Depression, and the Faridpur Beel ( related to the Faridpur trough).
- 17. • Regional structural feature: • Zone of folded and faulted Neogene deposits on the western side of the Indo-Burman ranges • The present day Bengal foredeep, which is divided into two sub basins with a sedimentary fill ranging from Cretaceous to Recent in age, with a progading delta sequence since middle Miocene. • The continental slope as zone of facies transition between the foreland shelf and deeper portion of the basin in upper Cretaceous and Paleogene times. • Western foreland shelf: consisting of Precambrian crystalline rocks with remnants of Gondwana halfgraben and an upper Creteaous to Paleogene shelf succession, which is overlain by a Neogene prograding delta sequence. • E-W striking Dauki Fault zone: with block faulted shelf and block faulted piedmont deposits of Plio-Pleistocene age in the susang hills.
- 18. • Foreland basin systems: • The wedge-top sits on top of the moving thrust sheets and contains all the sediments charging from the active tectonic thrust wedge. • The foredeep is the thickest sedimentary zone and thickens toward the orogen. Sediments are deposited via distal fluvial, lacustrine, deltaic, and marine depositional systems. • The forebulge and backbulge are the thinnest and most distal zones and are not always present. When present, they are defined by regional unconformities as well as aeolian and shallow- marine deposits.
