Metabolism II enzyme
•Descargar como PPTX, PDF•
4 recomendaciones•590 vistas
Denunciar
Compartir
Denunciar
Compartir
Recomendados
Recomendados
This presentation was provided by William Mattingly of the Smithsonian Institution, during the third segment of the NISO training series "AI & Prompt Design." Session Three: Beginning Conversations, was held on April 18, 2024.Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: The Basics of Prompt Design"

Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: The Basics of Prompt Design"National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
Más contenido relacionado
Último
This presentation was provided by William Mattingly of the Smithsonian Institution, during the third segment of the NISO training series "AI & Prompt Design." Session Three: Beginning Conversations, was held on April 18, 2024.Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: The Basics of Prompt Design"

Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: The Basics of Prompt Design"National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
Último (20)
social pharmacy d-pharm 1st year by Pragati K. Mahajan

social pharmacy d-pharm 1st year by Pragati K. Mahajan
IGNOU MSCCFT and PGDCFT Exam Question Pattern: MCFT003 Counselling and Family...

IGNOU MSCCFT and PGDCFT Exam Question Pattern: MCFT003 Counselling and Family...
A Critique of the Proposed National Education Policy Reform

A Critique of the Proposed National Education Policy Reform
Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: The Basics of Prompt Design"

Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: The Basics of Prompt Design"
Call Girls in Dwarka Mor Delhi Contact Us 9654467111

Call Girls in Dwarka Mor Delhi Contact Us 9654467111
Disha NEET Physics Guide for classes 11 and 12.pdf

Disha NEET Physics Guide for classes 11 and 12.pdf
Interactive Powerpoint_How to Master effective communication

Interactive Powerpoint_How to Master effective communication
Destacado
Destacado (20)
Product Design Trends in 2024 | Teenage Engineerings

Product Design Trends in 2024 | Teenage Engineerings
How Race, Age and Gender Shape Attitudes Towards Mental Health

How Race, Age and Gender Shape Attitudes Towards Mental Health
AI Trends in Creative Operations 2024 by Artwork Flow.pdf

AI Trends in Creative Operations 2024 by Artwork Flow.pdf
Content Methodology: A Best Practices Report (Webinar)

Content Methodology: A Best Practices Report (Webinar)
How to Prepare For a Successful Job Search for 2024

How to Prepare For a Successful Job Search for 2024
Social Media Marketing Trends 2024 // The Global Indie Insights

Social Media Marketing Trends 2024 // The Global Indie Insights
Trends In Paid Search: Navigating The Digital Landscape In 2024

Trends In Paid Search: Navigating The Digital Landscape In 2024
5 Public speaking tips from TED - Visualized summary

5 Public speaking tips from TED - Visualized summary
Google's Just Not That Into You: Understanding Core Updates & Search Intent

Google's Just Not That Into You: Understanding Core Updates & Search Intent
The six step guide to practical project management

The six step guide to practical project management
Beginners Guide to TikTok for Search - Rachel Pearson - We are Tilt __ Bright...

Beginners Guide to TikTok for Search - Rachel Pearson - We are Tilt __ Bright...
Unlocking the Power of ChatGPT and AI in Testing - A Real-World Look, present...

Unlocking the Power of ChatGPT and AI in Testing - A Real-World Look, present...
Metabolism II enzyme
- 1. METABOLISM IIENZYME Suggestion: senior high school/general lessons-today.blogspot.com
- 2. introduction what is enzyme? have you ever heard the word of catalyst? enzymes also include catalysts, but called biocatalyzer. A catalyst is a substance that can accelerate the chemical reaction, but does not change in the reaction. Accelerate the reaction is also lower activation energy, called activation energy is the minimum energy required the particles to grind to react to other particles. Usually, you will find catalyst lessons in the chemical, besides the catalyst, in the metabolism of this chapter, we will also find lessons related to the chemical, is redox, what is a redox? you should have to learn it first so you really understand this chapter, metabolism.
- 3. Substrate, Product, and Component Before we learn enzyme, we should know what is substrate and product in this chapter. Substrate are molecules that react in a reaction catalyzed by enzyme, whereas product is molecules produced in that reaction The component of enzyme: Apoenzyme: enzyme composed of proteins Cofactor: the non-protein component in the enzyme. Coenzyme: the cofactor that is in the form of inorganic ion. Holoenzyme: enzyme bound to the cofactor
- 4. Kinds of cofactor and enzyme Kinds of enzyme: Intracellular enzyme: enzyme that works inside the cell. Exp: catalase. Extracellular enzyme: work outside the cell. Exp: amylase. Kinds of cofactor: Inorganic ions, exp: chloride and calcium ions that will bind to the enzyme amylase Prosthetic group: prosthetic group consisting of organic molecules that bind the enzyme strongly. Exp: heme. coenzyme: it uses to transfer chemical group, atoms, or electrons from one enzyme to the other. Exp: NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide)
- 5. Characteristics and Factors Characteristics: enzyme is protein that have big molecules. function as catalyze. Enzyme works specifically. needed in small amounts. enzyme is reversible. Factors: temperature pH concentration of enzyme activator inhibitor concentration of substrate
- 6. Temperature Temperature can affect the work of the enzyme, the enzyme works optimally at temperatures not too high nor too low (typically, min: 40 ° C), if the enzyme is at very high temperatures, it will be damaged, as a result can not bind with the substrate again. This destruction of enzymes is called denaturation. However, there are enzymes that can be returned in their original states, for example RNAase. This event is called renaturation.
- 7. Activator and Inhibitor Activator: molecules that make enzyme easy to bind substrate. Inhibitor: molecules that make enzyme difficult to bind substrate. There are two kinds of inhibitor, those are: competitive inhibitor: molecule inhibitor that works to compete with the substrate for getting side of enzyme active. These inhibitors can be overcome by adding the concentration of substrate. non-competitive inhibitor: molecule inhibitor that works to attach themselves to the outer side of enzyme active. So, the shape of enzyme changes, and make it inactive. These inhibitor can’t be overcome by adding the concentration of substrate.
- 8. Lock and key Theory In this theory, form of the enzyme is very specific, so that only certain molecules that can be substrate for the enzyme. The enzyme has a side of that is used for the binding of substrate, this side is called side of active enzyme, this side contains amino acids.In this theory, the enzyme and substrate will be joined to form a complex such as locks and padlocks are united, substrate who have joined with the enzyme can react quickly, after the substrate reaction is complete, then the product will be released from the enzyme, and enzyme-free again and will be binding other substrate.
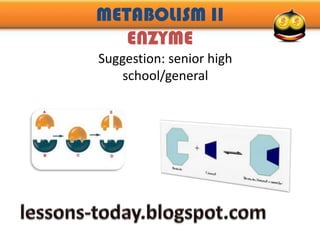
- 9. Induced Fit Theory In this theory, the enzyme is considered flexible, can change as their substrate, when the substrate come and join, the enzyme will adjust the form, then substrate react quickly and result in products that will be released enzymes, and enzyme-free again and ready to join the other substrate.Look at the picture, an enzyme that has an active side of square can join and adjust as substrate shape (trapezoid)
- 10. Catabolism and Anabolism Metabolism is a series of chemical reactions initiated by the initial substrate and end the final product, which occurs in cells. Metabolism is divided into two types based on the destination, those are: catabolism: decomposition reaction of complex compounds into simpler compounds, and this process is exergonic / can produce energy. anabolism: forming reaction of simple compounds into complex compounds. This reaction is needed energy. ……………………………………………………….to be continued….
- 11. Thank You Follow this lessons, find the next lessons on lessons-today.blogspot.com. We will post the next lessons, name of metabolism III Please, follow us on twitter: lessonstoday