Understanding LMC and bonus tolerances in GD&T
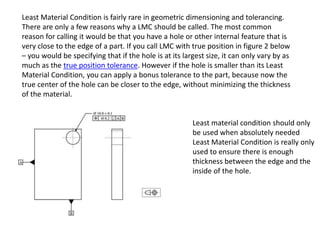
- 1. Least Material Condition is fairly rare in geometric dimensioning and tolerancing. There are only a few reasons why a LMC should be called. The most common reason for calling it would be that you have a hole or other internal feature that is very close to the edge of a part. If you call LMC with true position in figure 2 below – you would be specifying that if the hole is at its largest size, it can only vary by as much as the true position tolerance. However if the hole is smaller than its Least Material Condition, you can apply a bonus tolerance to the part, because now the true center of the hole can be closer to the edge, without minimizing the thickness of the material. Least material condition should only be used when absolutely needed Least Material Condition is really only used to ensure there is enough thickness between the edge and the inside of the hole.
- 3. Feature Size Position Tolerance Allowed 2.500 .010 2.501 .010 2.502 .010 2.503 .010 2.504 .010 2.505 .010 2.506 .010 2.507 .010 2.508 .010 2.509 .010 2.510 .010 Here we have a Ø2.500 +.010/-.000 hole and its position tolerance is Ø.010. Each of these conditions described above will have a different effect on the allowed position of this hole. RFS: When a tolerance is implied at RFS, the specified tolerance is independent of the feature's actual size. This means that no matter what the actual hole diameter ends up being, the applied tolerance is always the stated value. In this case .010. Here's a table to show what that means:
- 4. Feature Size Position Tolerance Allowed 2.500 .010 2.501 .011 2.502 .012 2.503 .013 2.504 .014 2.505 .015 2.506 .016 2.507 .017 2.508 .018 2.509 .019 2.510 .020 MMC: The stated tolerance applies at the MMC size of the feature, and additional tolerance is gained as the feature departs from the MMC size. This means that at the MMC (smallest diameter), the stated tolerance is applied. As the holes gets larger the position gains additional tolerance. Here's a table showing that:
- 5. Feature Size Position Tolerance Allowed 2.500 .000 2.501 .001 2.502 .002 2.503 .003 2.504 .004 2.505 .005 2.506 .006 2.507 .007 2.508 .008 2.509 .009 2.510 .010 Zero @ MMC: This is very similar to MMC, except that the stated tolerance is zero. At the MMC feature size, the allowed positional tolerance is zero. As the feature departs from the MMC, additional tolerance is gained. Here's a table showing the effect:
- 6. Feature Size Position Tolerance Allowed 2.510 .010 2.509 .011 2.508 .012 2.507 .013 2.506 .014 2.505 .015 2.504 .016 2.503 .017 2.502 .018 2.501 .019 2.500 .020 LMC: This is the exact opposite of MMC. The stated tolerance applies at the feature's LMC (largest diameter) and as the feature departs from the LMC more tolerance is allowed. Here's a table showing that effect:
- 7. Now that the effect of each modifier has been shown, how do you decide which one (if any) to use? RFS: Used when locating a press fit pin or shaft. MMC: When the hole is being used in a clearance application. Zero @ MMC: Can be used in place of MMC. LMC: Used in a locational application. Important note: LMC is not commonly used. RFS is usually the best option when using a feature to locate another.
- 8. When a geometric characteristic is specified with MMC, the geometric tolerance may have a bonus tolerance when its FOS is approaching to its Least Material Condition (LMC). From the table shown in this figure, if the diameter of a part is measured at 1.02, which is the MMC, there is no bonus tolerance and the Position Tolerance remains at 0.05. However, when the diameter is measured at 0.98, which is the LMC, the bonus tolerance is equal to 0.04. Therefore, the total Position Tolerance in this case increases to 0.09. Because of the bonus tolerances, application of MMC can be easily found in most GD&T design drawings.
- 9. When a geometric tolerance is specified with LMC, the geometric tolerance may have a bonus tolerance when its FOS is approaching to its MMC. From the table shown in this figure, when the diameter of a part is measured at 1.02, which is the MMC, there is a bonus tolerance and the total Position Tolerance increases to 0.09. However, when the diameter of a part is measured at 0.98, which is the LMC, there is no bonus tolerance. LMC is particularly applied to guarantee a larger minimum thickness in a thin part than MMC.
- 10. Unlike MMC and LMC, Regardless of Feature Size gives no additional geometric tolerance. The concept of RFS has been used prior to the introduction of MMC and LMC principles. Figure 4 shows a design drawing using an RFS Position Tolerance. Since there is no modifier added to the Position Tolerance, according to Rule 26, the Position Tolerance is an RFS. From the table shown in this figure, the Position Tolerance remains the same regardless the variations on the FOS.
- 11. According to ASME14.5M1,6,7, Rule 1 states: “Where only a tolerance of size is specified, the limits of size of an individual feature prescribe the extent to which variations in its form – as well as in its size- are allowed.” This definition includes two main components: (1) the envelope-size principle and (2) the Form Tolerance allowed when a FOS departs from MMC. For example, Figure 1 shows the diameter of a shaft in an engineering drawing. Figure 2 shows the envelope-size principle, which states that the FOS is applicable not only to the size at each cross section, but also to the whole length of the feature. Figure 3 shows that, when the FOS departs from its MMC, a Form Tolerance will be allowed. Therefore, when the FOS is at its MMC, the part must have a perfect form. Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3 The envelope-size principle An allowable Form Tolerance for a part when its diameter departs from MMC
- 12. According to ASME14.5M, Rule 2 states: “For all applicable geometric tolerances, Regardless of Feature of Size (RFS) applies with respect to the individual tolerance, datum reference, or both, where no modifying symbol is specified. Maximum Material Condition M, or Least Material Condition L, must be specified on drawing where it is required.” The rule can be applied to the design drawing shown in Figure. Due to the nature of the control, RFS can be applicable at most of geometric characteristics except at three Form Tolerances: Flatness, Circularity, and Cylindricity. While Rule 2 seems clear and simple, several geometric characteristics without m or l are still non RFS. These exceptions cause confusions to the students when taking this class.
- 13. Cases in Which Rule 2 Applies There are two cases in which Rule 2 is applicable. The first case is when a geometric characteristic is applied with an FOS, and the second case is when a geometric characteristic is applied with a feature. RFS when Geometric Characteristics applied with FOS Geometric characteristics which are allowed to specify with FOS are Straightness, Perpendicularity, Parallelism, Angularity, Position, Circular Runout, Total Runout, Concentricity, and Symmetry, are RFS. RFS with Straightness Figure shows that a Straightness Tolerance is specified with an FOS. The Straightness is used to control the central axis of the shaft. As shown from the table, the Straightness Tolerance remains the same regardless the change on the FOS of the diameter. Therefore, this is an RFS. In the Form Tolerances, RFS is only applicable to Straightness. Fig : RFS Straightness control on the central axis of a shaft
- 14. RFS with Orientation Tolerances Figure shows that a Perpendicularity Tolerance is specified with an FOS. Similar to the RFS with Straightness, the Perpendicularity is used to control the central axis of the hole. As shown from the table, the Perpendicularity Tolerance remains the same regardless the change on the FOS of the diameter. Therefore, this is an RFS. The same situation can be applied to other Orientation Tolerances. RFS with Perpendicularity
- 15. RFS with Position Tolerances As given in Table 1, Location Tolerances includes Position, Concentricity, and Symmetry Tolerances. Figure shows a Position Tolerance with RFS. The Position Tolerance zone of φ0.015 is used to control the central location of the hole. The boxed dimensions in this drawing are called basic dimensions, which can be described as the theoretically exact dimensions. As shown from the table, the Position Tolerance remains the same regardless the variations on the FOS of the diameter. The same rule can be applied to other Position Tolerances, such as Concentricity and Symmetry. From the examples shown above, when a geometric characteristic is specified with an FOS, the tolerance will be an RFS
- 16. RFS with Runout - FOS Figure shows a Runout Tolerance with RFS. The tolerance zone of 0.015” is used to control the Total Runout on the outer surface of φ4.500”. Therefore, when compared to tolerance zone in Figure 10, there is no φ in front of 0.015”. The datum axis is at the center axis of φ2.000”. As shown from the table, the Total Runout remains the same regardless the variations on the FOS of the diameter.
- 17. RFS with Runout when applied with a feature Apart from the examples given, there is only one RFS example when the geometric characteristic is applied with a feature. The geometric characteristic is a Runout control, which is shown in Figure 12. The circular runout of 0.06 is to control the wobble of the Surface B, and is measured when the surface is rotated around the datum axis A. Based on the nature of the runout measurement, the Circular Runout remains the same regardless the variations on the FOS (2.25”). Therefore, this is also an RFS.