Analysis of pharmaceuticals by mani
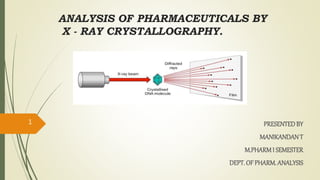
- 1. ANALYSIS OF PHARMACEUTICALS BY X - RAY CRYSTALLOGRAPHY. PRESENTEDBY MANIKANDANT M.PHARMI SEMESTER DEPT. OF PHARM. ANALYSIS 1
- 2. INTRODUCTION: Method to determine the arrangement of atoms within a crystal. A beam of x ray strikes a crystal and causes the beam of light to spread into many specific directions. X-ray beam hit the crystallized molecule & diffract as the X- rays. This forms a pattern --X-ray diffraction pattern. 2
- 3. From the angle and intensities , three-dimensional picture can be obtained from the density of electrons within the crystal. It is a tool to identify the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal. 3
- 4. Instrumentation Three main fields of x-ray spectroscopy are X-ray absorption Diffraction Fluorescence Optical system varies in each case. Component parts of the equipment are same. The main components are 1. Production of X-rays 2. Collimator 3. Monochromator 4. Detectors 4
- 5. 1.Production of x-rays X-rays are produced inside the x-ray tube by the interaction of high energy electrons with the atoms of the anode. Conditions necessary: Source of electrons Target (anode) High potential difference Cooling facility Coolidge X-ray Tube 5
- 6. Cathode is a filament of tungsten metal heated by a battery to emit the electrons. This beam of electrons moves towards anode and attain the kinetic energy 99% of energy is converted into heat by collision Remaining 0.5- 1% is converted to X-rays by strong coulomb interactions ( Bremsstrahlung process). Generally the target gets very hot in use. This problem has been solved by cooling the tube with water. 6
- 7. 2.Collimator. The X-rays produced by the target material forms a hemisphere at the centre. To get a narrow beam of X-rays, the X-rays generated are allowed to pass through a collimator. The collimator absorbs all the X-Ray except the narrow beam that Passes between the gaps. 7
- 8. 3.Monochromator They are two types; A. Filter monochromator: A filter absorbs undesirable radiation but allows the radiation of required wavelength to pass. Example: zirconium filter --used for molybdenum radiation When X-rays emitted from molybdenum are passed through a Zirconium filter. Zr strongly absorbs the radiation of molybdenum at short wavelengths. It weakly absorbs the K alpha lines of molybdenum and allows the K beta lines to pass. 8
- 9. B.CRYSTAL MONOCHROMATOR. A crystal monochromator is made up of a suitable crystalline material (sodium chloride, lithium fluoride, quartz). The beam is split up by the crystalline material into the component wavelengths --same way as a prism splits up the white light into rainbow Such a crystalline substance is called an analysing crystal. 9
- 10. Crystal monochromator are of two types Flat crystal Curved crystal 10
- 11. 4.Detector X-ray intensities can be measured and recorded by A. Photographic methods B. Counter methods 1) Geiger muller counter 2)Proportional counter 3) Scintillation counter 4) solid state semi conductor 11
- 12. A. Photographic methods: A plane or cylindrical film is used to record the position and intensity of X-ray beam. The blackening of the developed film is expressed in terms of density- units D given by D = log I˳/I Where, I˳ and I refer to the incident and transmittance intensities of X-rays respectively. The value of D is measured by densitometer. This is used in diffraction studies 12
- 13. B. Counter methods 1) Geiger Muller Counter The Geiger tube is filled with an inert gas (argon) Central wire anode is maintained at a positive potential (800 to 2500V). When an X-ray is entering the Geiger tube, This ray undergoes collision with the filling gas, resulting in the production of an ion pair. 13
- 14. The electron produced moves towards the central anode. Positive ions moves towards outer electrode. The electron is accelerated by the potential gradient (causes the ionisation of large no. of argon atoms) Resulting production of electrons --travel towards the central anode This results in an output pulse of 1 to 10v. 14
- 15. Advantages : - The Geiger tube is inexpensive and is a trouble-free detector. Disadvantages : - Geiger tube-- falls rapidly at wavelength below 1 Aº. A Geiger tube cannot be used to measure the energy of ionising radiation. 15
- 16. B) Proportional counter: Its construction is similar to a Geiger tube counter. A proportional counter is filled with a heavier gas (xenon or krypton). The heavier gas is preferred because it is easily ionised. It is operated at the voltage below the Geiger plateau. C)Scintillation detector: The scintillation detector ---useful for measuring x-rays of short wavelengths When X- ray is incident upon the crystal, the emitted pulses of visible light are detected by the photomultiplier tube. Crystal used sodium iodide( activated by thallium) , anthracene, naphthalene. 16
- 17. DIFFERENT X- RAY METHODS X ray absorption method X ray diffraction method X ray fluorescence method Auger emission spectroscopy 17
- 18. X -ray Absorption method A beam of x-ray is allowed to pass through the sample. Wavelength at which a sudden change in absorption occurs is used to identify an element (sample). Magnitude of the change determines the amount of particular element present. Used in elemental analysis of barium and iodine in body. It is helpful in certain cases like elemental analysis and thickness measurement. 18
- 19. X-ray Fluorescence methods. X-ray is generated within the sample and by measuring the wavelength and intensity of the generated x rays. One can perform qualitative and quantitative analysis. The primary X-ray ejects electron from inner energy levels where the wavelength is equal to absorption edge. But when the wavelength is shorter than absorption edge it emits secondary X-ray when electrons fall into inner vacant levels. 19
- 20. Auger Emission spectroscopy. AES measure electrons emitted from the surface, induced by electron bombardment. The primary X-rays eject electrons from inner energy levels. Once the atom is ionized, it must relax by either emitting a photon or an electron 20
- 21. X-ray Diffraction Method. It is based on constructive interference of monochromatic x ray and a crystalline sample. x-rays are generated by a cathode ray tube, filtered to produce monochromatic radiation and directed towards the sample. The interaction of incident rays with the sample produces constructive interference (condition satisfy Braggs laws). These methods are based on the scattering of x rays by crystal. By this ,the crystal structure of various solid compounds can be identified. These methods are extremely important as compared with x- ray absorption and x-ray fluorescence methods. nλ= 2dsinθ 21
- 22. X-RAY DIFFRACTION METHODS. 1)Laue photographic method. 2)Bragg x-ray spectrometer method 3)Rotating crystal method 4)Powder crystal method. 22
- 23. 1)Laue photographic method. There are two methods Transmission method Back reflection method TRANSMISSION METHOD A - source of X-rays. B - pinhole collimator. C - crystal to investigate structure D – film on a rigid base 23
- 24. This film is provided with beam stop to prevent direct beam from causing excessive fogging of the film. The x-rays are recorded on photographic plate is used to study the diffraction patterns which gives the structure of crystal. 24
- 25. Back-Reflection Method It is similar to Transmission method The film is placed between the x-ray source and the crystal. The beams which are diffracted in a backward direction are recorded. Method for the study of large and thick Specimens. 25
- 26. Braggs X-ray Spectrometer Method. A beam of x-ray is passed through a crystals The emitted x-ray are obtained on a photo graphic plate in a form of pattern (laues photograph) Using photographs, Braggs analysed the structure of crystals of NaCl, KCl and ZnS. Braggs devised a spectrometer -- measure the intensity of x-ray beam. When x-rays are scattered from a crystal lattice, peaks of scattered intensity are observed to the following conditions: 1. The angle of incidence = angle of scattering. 2. The path length difference is equal to an integer number of wavelengths. 26
- 27. The Braggs equation nλ= 2dsinθ where n is a positive integer λ is the wavelength of incident wave d is the path length θ is the incident angle 27
- 28. Rotating Crystal Method X rays are generated in the x-ray tube --the beam is made monochromatic by a filter. From the filter, the beam is passed through collimating system which permits a fine pencil of parallel x-ray From the collimator, the x-ray beam is made to fall on a crystal mounted on the shaft which can be rotated at a uniform angular rate by the small motor. 28
- 29. Now the shaft is moved to put the crystal into slow rotation This causes the sets of planes into their reflecting positions. Each plane will produce a spot on photographic plate. Photographs can be taken in two ways: Complete rotation method Oscillation method 29
- 30. Powder Crystal Method In this method, sample can be taken as little as 1mg of the material. X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) is a rapid analytical technique primarily used for phase identification of a crystalline material. The analysed material is finely ground and homogenized. A- source of X-rays. 30
- 31. X-ray beam is allowed to fall on the powdered specimen P through the slits S1 and S2. Fine powder, p is struck on a hair by means of gum and is suspended vertically in the axis of a cylindrical camera. This enables sharp lines to be obtained on the photographic film which is surrounding the powder crystal in the form of a circular arc. After falling on the powder , it passes out of the camera through a cut in the film. It is observed on the photographic plate. 31
- 32. Application To determine structural properties and atomic arrangement. Identification of fine-grained minerals --clays and mixed layer clays that are difficult to determine optically. Determination of Cis- trans isomerism. Differentiation of sugar. X-ray analysis of milk powder. It is used for the identification of unknown crystalline materials (e.g. minerals, inorganic compounds). Determination of unknown solids --studies in geology, environmental science, material science, engineering and biology. 32
- 33. Example Determination of minor and trace elements in kidney stone 1)Experimental setup for XRF studies on kidney stone. XRF spectrometry on different kidney stones Exposure of kidney stone XRF measurement by the detector Background subtraction from XRF spectrum Spectrum analysis by PyMCA 33
- 34. Optimisation of PyMCA parameters Information of identified peak elements Determination of elements and their concentration. The elements which were identified from this techniques are silver, arsenic, bromine, chromium, copper, gallium, selenium, germanium , etc 34
- 35. XRF SPECTRUM OF THE APATITE KIDNEY STONE 35
- 36. XRF SPECTRUM OF THE CYSTINE KIDNEY STONE 36
- 37. RESULT AND DISCUSSION The results from XRF analysis can serve as a reliable method for accurate determination of elements and its composition in the kidney stones. The result from such analysis can be utilised to develop more effective methods for the new medicines for kidney stones. PyMCA program is used to identify elemental composition and their concentrations of the kidney stones with high degree of accuracy. 37
- 38. REFERENCE 1)Instrumental method of analysis-Willard’s, 7th edition, CBS Publishers page no:320-345 2)Instrumental method of chemical analysis- Chatwal, Himalayan Publishing House page no:2.303-2.339. 3) Alvarez, M. and Mazo-Gray, V, “Determination of trace elements in organic specimens by energy dispersive x-ray fluorescence using a fundamental parameters method,” X-Ray Spectrom., doi:(2005). 4) Hirokawa, Y., Shibata, Y., Konya, T., Koike, Y. and Nakamura, T., “X-ray fluorescence analysis of Co, Ni, Pd, Ag, and Au in the scrapped printed-circuit-board ash,” X-Ray Spectrom., doi (2013). 38
- 39. 39
Notas del editor
- Is the voltage range in which the GM tube operates in correct mode where the ionization occurs along the length of anode