Growth and Development Stages
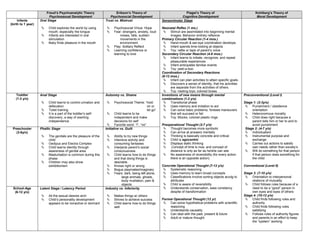
- 1. Freud’s Psychoanalytic Theory Erikson’s Theory of Piaget’s Theory of Kohlberg’s Theory of Psychosexual Development Psychosocial Development Cognitive Development Moral Development Infants Oral Stage Trust vs. Mistrust Sensorimotor Stage (birth to 1 year) Child explores the world by using Psychosocial Virtue: Hope Neonatal Reflex (1 mo.) mouth, especially the tongue Fear: strangers, anxiety, loud Stimuli are assimilated into beginning mental Infants are interested in oral noises, falls, sudden images. Behavior entirely reflexive stimulation movements in the Primary Circular Reaction (1-4 mos.) Baby finds pleasure in the mouth environment Hand-mouth & ear-eye coordination develops. Play: Solitary Reflect Infant spends time looking at objects Learning confidence or Toy: rattle or tape of parent’s voice learning to love Secondary Circular Reaction (4-8 mos.) Infant learns to initiate, recognize, and repeat pleasurable experiences Infant anticipates familiar events Toy: peel-a-boo Coordination of Secondary Reactions (8-12 mos.) Infant can plan activities to attain specific goals. Discovers a sense of identity, that his activities are separate from the activities of others. Toy: nesting toys; colored boxes Toddler Anal Stage Autonmy vs. Shame Inventions of new means through mental Preconventional (Level I) (1-3 y/o) combinations (1-2 y/o) Child learns to control urination and Psychosocial Theme: “hold Transitional phase Stage 1: (2-3y/o) defecation on or Uses memory and imitation to act Punishment / obedience Toilet training let go” Can solve basic problems, foresee maneuvers orientation It is a part of the toddler’s self- Child learns to be that will succeed or fail Heteronomous morality discovery, a way of exerting independent and make Toy: Blocks, colored plastic rings Child does right because a independence decisions for self parent tells him or her to and to Favorite word: “I”, “no” Preoperational Thought (2-7 y/o) avoid punishment Preschooler Phallic Stage Initiative vs. Guilt Thought becomes more symbolic Stage 2: (4-7 y/o) (3-6y/o) Can arrive at answers mentally Individualism The genitals are the pleasure of the Ability to try new things Thinking is basically concrete and critical Instrumental purpose and child Intensive activity and Child is egocentric exchange Oedipus and Electra Complex consuming fantasies Displays static thinking Carries out actions to satisfy Child learns identity through Interjects parent’s social .Concept of time is now, and concept of own needs rather than society’s awareness of genital area consciousness distance is only as far as he/she can see Will do something for that person Masturbation is common during this Child learns how to do things No awareness of reversibility (for every action if that person does something for phase and that doing things is there is an opposite action) the child Children may also show desirable exhibitionism Knows right or wrong Concrete Operational Thought (7-12 y/o) Conventional (Level II) Bogus playmates/imaginary Systematic reasoning Fears: dark, being left alone, Uses memory to learn broad concepts Stage 3: (7-10 y/o) large animals, ghosts, Classifications involve sorting objects accdg to Orientation to interpersonal body mutilation, pain & attributes relations of mutuality objects Child is aware of reversibility Child follows rules because of a School-Age Latent Stage / Latency Period Industry vs. Inferiority Understands conservation, sees constancy need to be a “good” person in (6-12 y/o) despite of transformation own eyes and eyes of others All the sexual desires arch Makes things w/ others Stage 4: (10-12 y/o) Child’s personality development Strives to achieve success Formal Operational Thought (12 yr) Child finds following rules and appears to be nonactive or dormant Child learns how to do things Can solve hypothetical problems with scientific authority well reasoning Child finds following rules Understands causality satisfying Can deal with the past, present & future Follows rules of authority figures Adult or mature thought and parents in an effort to keep the “system” working
- 2. Adolescent Genital Stage Identity vs. Role Confusion Operational Thought Postconventional (Level III) (13-20 y/o) Conflict: Setting Rules Determines own sense of self Stage 5: (Older than 12) Genitals become awakened Development of who, what & Capable of abstract thinking Social contract, utilitarian law- Adolescent develops sexual where they are going making persectives maturity and learns to establish Become focus (self-concept) Follows standards of society for satisfactory relationships w/ the Period of rebellion and the good of all people opposite sex uncertainty Stage 6: Adjusting to a new body and Universal ethical principle seeking emancipation from orientation parents, choosing a vocation Follows internalized standards of & determining a value system conduct. Young Adult Intimacy vs. Isolation Person makes commitments to one another Isolation and self absorption if unsuccessful Independent from parents, possible marriage / partnership Major goals to accomplish in career and family Marrying age Fulfillment of career Middle Adult Generativity vs. Stagnation Middle Adulthood: Physical Changes: graying hair, wrinkling skin, pain & Settling down muscle aches, menopausal Find jobs period Start a family Psychosocial Virtue: Care Mature adult is concerned w/ establishing & guiding the new generation or else feels Late Adulthood personal impoverishment Relates to older & younger Satisfaction w/ career generations Become “Pillars of the Community” Older Adult Integrity vs. Despair Accomplishment of goals Achieves sense of acceptance of own life Adapts to triumphs & disappointment w/ a certain ego integrity Accepts the inevitability of death or else falls into despair Appraisal of life & changing social roles Self-concerned & withdrawn
- 3. Havighurst’s Age Periods and Sullivan’s Theory of PHYSICAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT Developmental Task Interpersonal Relationships Mo. Gross Fine Motor Development Play Yr. Motor Development Infants Largely reflex The eyes is fixated on (birth to 1 the person SOLITARY Infancy Weight: 7 to 8 lbs year) 0-1 Keeps hands fisted PLAY Infancy and Early Childhood Maternal anxiety Length: 19 to 21 in Able to follow object to midline Learning to walk Vital Signs: Holds head up when Development of social prone smile Learning to take solid food Childhood 2 Responds to familiar Learning to talk As the child grows he T – 37.5 C voices Learning to control the elimination of learns to interact P – 120 – 140 bpm Holds head & chest The baby knows how to body wastes Use one specific R – 30 – 60 /min up when prone cry Laughs aloud Learning sexual differences & sexual language at a time BP – 80/40 mmHg 3 Babbles and “coos” modesty (language shock) Follows object past midline Achieving psychologic stability forming simple concepts of social and physical Grasp Can raise head and Stepping chest reality Juvenile Tonic neck Teething Learning to relate emotionally to The child slowly 4 Reflexes are fading Reach out to object parents, siblings & other people learning accepts authority from to distinguish right from wrong & his subordinates developing a conscience More concept of self, Turns front to back Roll over Has head lag when Hold blocks at each status, & role pulled upright hand 5 Bears partial weight on feet when pulled Middle Childhood upright Learning physical skills necessary for ordinary games Turns both ways Doubles birth weight Moro reflex fading Eruption of 1st tooth Building wholesome attitudes toward Sits w/ minimal support oneself as a growing organism 6 Uses palmar grasp Learning to get along w/ age mates Reaches out in “dada”, “mama” Learning an appropriate masculine and anticipation of being Sleeps on prone feminine social role picked up position 7 Sits unsteadily Uses fingers to hold Developing fundamental skills in objects reading, writing & calculating Transfers objects hand to hand Developing concept necessary for everyday living Sits securely w/o Sits alone steadily for support an indefinite period Developing conscience, morality & 8 Recognizes strangers scale of values Peek-a-boo (to test memory)
- 4. Achieving personal independence Creeps or crawls Can hold own bottle Starts to crawl Developing attitudes toward social 9 Understands simple groups & institutions gestures Pulls self to standing From crawling to standing 10 Responds when called by his/her name From crawling to Walks with assistance 11 standing Stands alone Triples birth weight 12 Some infants take 1st Can say 2 syllable step words Can walk w/ help Toddler A child gains about 5 Walks alone well Puts small pellets into (1-3 y/o) to 6 lb and 5 in a 15 Can seat self in chair small bottles PARALLEL year during the Can creep upstairs Scribbles voluntarily w/ PLAY toddler stage a pencil / crayon Head circumference Holds a spoon increases only about 2cm Can run and jump in No longer rotates a Prominent abdomen place spoon to bring it to – pouchy belly 18 Can walk up and mouth Respirations slow down stairs w/ slightly assistance HR: 90 – 110 bpm BP: 99/64 mmHg Walks up stairs Can open doors by The brain develops 24 alone turning doorknobs to about 90% of its Unscrew lids adult size Control of the urinary Can jump down from Makes simple lines or and anal sphincters 30 chairs strokes or crosses w/ a becomes possible pencil 8 new teeth (canines and molars) erupt Preschooler Ectomorphic (slim Alternates feet Undresses self (3-6 y/o) body built) or 3 Runs Stacks tower of blocks A endomorphic (large y/o Rides tricycle Draws a cross S body built) becomes Stands on one foot S apparent O PR: 85 bpm C BP: 100/60 mmHg Constantly in motion Can do simple buttons I Voiding is frequent 4 Jumps A (about 9 to 10 times y/o Skips T a day) I The average child V gains only about 4.5 E lb a year. Height gain is also Throws overhand Draws a 6-part man & minimal: 2 to 3.5 Can lace shoes inches 5 Imaginative Generally have all 20 y/o PLAY deciduous teeth by age 3
- 5. School-Age Average weight gain 6 A year of constant motion (6-12 y/o) is 3 to lb y/o Skipping is a new skill Increase in height is First molars erupt 1 to 2 inches By age 10 brain 7 Central incisors erupt A growth is complete y/o Difference b/w sexes become apparent in play S Posture becomes Spends time in quiet play S more erect O PR: 70 – 80 bpm 8 Coordination definitely improved C BP: 112/60 mmHg y/o Playing with gang becomes important I Development of Eyes become fully developed A Secondary Sex T 9 Characteristics I y/o All activities done w/ gang Sexual Maturation: V 10 Girls (12 – 18 y/o); E y/o Coordination improves boys (14 - 20 y/o) Deciduous teeth are 11 PLAY lost and permanent y/o Active, but awkward and ungainly teeth erupt 12 y/o Coordination improves Adolescent Developing intellectual skills and Onset of puberty SEXUAL MATURATION (13-20 y/o) Cessation of body Yr BOYS GIRLS concepts necessary for civic growth Growth spurt Pubic hair thick & curly, competence Most girls are 1 to 2 continuing triangular in distribution Desiring and achieving socially inches taller than Pubic hair Breasts, areola & papilla boys abundant & curly form secondary mound responsible behavior Boys grow about 4 to 13 Testes, penis, & Menstruation is ovulatory, 12 inches in ht and to scrotum enlarging making pregnancy Acquiring a set of values & an ethical gain 15 to 65 lb 15 further possible system as a guide to behavior Girls grow 2 to 8 Axillary hair inches and gain 15 present Achieving emotional independence from to 55 lb Facial hair fine & parents & other adults achieving PR: 70 bpm downy RR: 20 breaths/min Voice changes assurance of economic independence BP: 120/70 mmHg happening w/ Selecting and preparing for an Gain 2nd molars by annoying freq. age 13 and 3rd Genitalia adult Pubic hair curly & occupation molars b/w 18 and Pubic hair abundant (adult); may Preparing for marriage and family life 21 y/o abundant & curly extend onto medial aspect Achieving a new and more mature 15 Scrotum dark & of thighs to heavily rugated Breast tissue adult & relations w/ age mates of both sexes 16 Facial and body nipples protrude Achieving masculine or feminine social hair present Areolas no longer project Sperm production as separate ridges from role mature breasts Accepting ones physique & using the May have some degree of facial acne body effectively Pubic hair curly & abundant (adult); END OF SKELETAL may extend along GROWTH 16 medial aspect of to thighs 17 Testes, scrotum & penis adult in size May have some degree of facial acne Gynecomastia
- 6. 17 to END OF SKELETAL 18 GROWTH Selecting a mate Young Adult / Learning to live w/ a partner Early Starting a family Adulthood Rearing children Managing a home Getting started in an occupation Taking on civic responsibility Finding a congenital social group Middle Adult Achieving adult civic and social responsibility Establishing and maintaining economic standard of living Assisting teenage children to become responsible and happy adult Developing adult-leisure time activities Relating oneself to one’s spouse as a person Older Adult / Adjusting to decreasing physical Late strength & health Adulthood Adjusting to retirement & reduced income Adjusting to death of a spouse Establishing an explicit affiliation w/ one age group Terms: INFANCY Extrusion Reflex – food placed on an infant’s tongue is thrust forward and out of the mouth. Natal Teeth – teeth in newborns Neonatal Teeth – teeth erupted in the first 4 weeks of life Deciduous Teeth – temporary baby teeth Gross Motor Devt – ability to accomplish large body movements Fine Motor Devt – measured by observing or testing the prehensile ability (ability to coordinate hand movements) Ventral Suspension – refers to an infant’s appearance when held in midair on a horizontal plane, supported by a hand under the abdomen Landau Reflex – develops at 3 mos. When held in ventral suspension, an infant’s head, legs, and spine extend. When the head is depressed, the hips, knees and elbows flex Parachute Reaction – when infants are suddenly lowered toward an examining table from ventral suspension, the arms extend as if to protect themselves from falling. Neck-righting reflex – this reflex causes the baby to lose balance and roll sideways when lifting the head up Thumb opposition – ability to bring the thumb and fingers together (4 mos) Pincer Grasp – ability to bring the thumb and 1st finger together. This enables the baby to pick up small objects (10 mos) Binocular vision – ability to fuse two images into one Hand Regard – hold hands in front of face and study their fingers for long periods of time Eight-Month Anxiety – the height of fear of strangers
