Nervous system word.docx
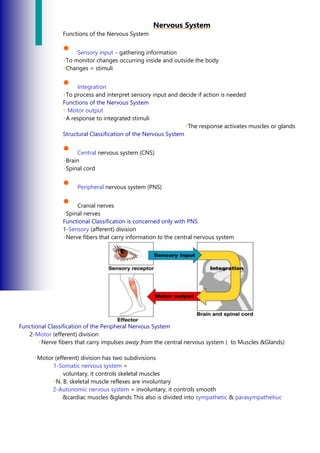
- 1. Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System • Sensory input – gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body Changes = stimuli • Integration To process and interpret sensory input and decide if action is needed Functions of the Nervous System Motor output A response to integrated stimuli The response activates muscles or glands Structural Classification of the Nervous System • Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Spinal cord • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) • Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Functional Classification is concerned only with PNS 1-Sensory (afferent) division Nerve fibers that carry information to the central nervous system Functional Classification of the Peripheral Nervous System 2-Motor (efferent) division Nerve fibers that carry impulses away from the central nervous system ( to Muscles &Glands) Motor (efferent) division has two subdivisions 1-Somatic nervous system = voluntary, it controls skeletal muscles N. B. skeletal muscle reflexes are involuntary 2-Autonomic nervous system = involuntary, it controls smooth &cardiac muscles &glands This also is divided into sympathetic & parasympathetiuc
- 2. Organization of Nervous System Histology of Nervous Tissue • Despite the complexity of the nervous system, there are only two functional cell types • Neurons - excitable nerve cells that transmit electrical signals • Neuroglia (glial) cells - supporting cells Histology of CNS Tissue - Neuroglia • Neuroglia - 4 types in the Central NS 1-Astrocytes • star shaped with many processes • connect to neurons; help anchor them to nearby blood capillaries • control the chemical environment of the neurons 2-Microglia • oval with thorny projections • monitor the health of neurons • if infection occurs, they change into macrophages (eating viruses, bacteria and damaged cells) Histology of CNS Tissue - Neuroglia • Neuroglia - 4 types in the Central NS Astrocytes
- 3. • star shaped with many processes • connect to neurons; help anchor them to nearby blood capillaries • control the chemical environment of the neurons Microglia • oval with thorny projections • monitor the health of neurons • if infection occurs, they change into macrophages (eating viruses, bacteria and damaged cells) Histology of CNS Tissue - Neuroglia • Neuroglia - 4 types in the CNS (continued) Ependymal cells • range in shape from squamous to columnar; many are ciliated • line the dorsal body cavity housing the brain and spinal cord • form a barrier between the neurons and the rest of the body Nervous Tissue: Neurons Oligodendrocytes • have few processes • line up along neurons and wrap themselves around axons • form the myelin sheath – an insulating membrane
- 4. Histology of PNS Tissue - Neuroglia • Neuroglia - 2 types in the Peripheral NS Satellite cells • surround neuron cell bodies in the periphery • maintain the extracellular environment Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes) • surround axons/dendrites and form the myelin sheath around larger nerve fibers in the periphery • similar to oligodendrocytes in function - insulators Neurons = nerve cells Cells specialized to transmit messages Major regions of neurons Cell body – nucleus and metabolic center of the cell Processes – fibers that extend from the cell body Neuron Anatomy Extension outside of the cell body Dendrites Conducts impulses towards the cell body Axon Conduct impulses away from the cell body Nerve Fiber Coverings Most long nerve fibers are covered with a whitish fatty material called myelin with waxy appearance. It insulates the fiber and increases transmission rate. -Axon outside CNS are wrapped by Schwann Cells. Axon and Nerve Impulses Axons end in axonal terminals
- 5. Axonal terminals contain vesicles with neurotransmitters Axonal terminals are separated from the next neuron(neuroneural junction) by a gap called Synaptic cleft (Synapse) Functional Classification of Neurons 1-Sensory (afferent) neurons Carry impulses from the sensory receptors Cutaneous sense organs Proprioceptors – detect stretch or tension in muscles and tendons and joints 2-Motor (efferent) neurons Carry impulses from the central nervous system to muscles and glands ,their cell bodies are always in CNS Functional Classification of Neurons 3-Interneurons (association neurons) Their cell bodies are always found in CNS Connect sensory and motor neurons in neural pathways Neuron Classification Structural Classification of Neurons Multipolar neurons – many extensions from the cell body
- 6. Structural Classification of Neurons Bipolar neurons – one axon and one dendrite Figure 7.8b Structural Classification of Neurons Unipolar neurons – have a short single process leaving the cell body which is very short ,divides almost immediatly Functional Properties of Neurons • Irritability – ability to respond to stimuli • Conductivity – ability to transmit an impulse Reflex Arc The plasma membrane at rest is polarized Fewer positive ions are inside the cell than outside the cell • Reflex – rapid, predictable, and involuntary responses to stimuli • Reflex arc – direct route from a sensory neuron, to an interneuron, to an effector • Ref. arch have a minimum 5 elements
- 7. Types of Reflexes and Regulation • Autonomic reflexes eg. Salivary gland secretion Heart and blood pressure regulation Changes in size of the pupil • Digestive system regulation • Somatic reflexes Activation of skeletal muscles REGIONS OF BRAIN Central Nervous System (CNS) • CNS develops from the embryonic neural tube By the fourth week the anterior end begins to expand and brain formation begins, The rest of the tube becomes the spinal cord
- 8. The central canal becomes enlarged in 4 regions of the brain to form ventricles the ventricles:-Four chambers within the brain -Filled with cerebrospinal fluid • Cerebral hemisphere • Diencephalon • Brain stem • Cerebellum
- 9. Figure 7.1 GRAY MATTER -Outer layer composed mostly of neuron BASAL NUCLEI -Internal islands of gray matter WHITE MATTER -fiber tracts inside the gray matter -ex: corpus callosum connects hemispheres The surface is made of ridges (gyri) and grooves (sulci) Specialized Area of the Cerebrum Cerebral areas involved in special senses Gustatory area (taste) Visual area Auditory area Olfactory area Specialized Area of the Cerebrum Interpretation areas of the cerebrum Speech/language region Language comprehension region General interpretation area Cerebral Hemispheres (Cerebrum) Paired (left and right) superior parts of the brain Include more than half of the brain mass
- 10. Diencephalon • Sits on top of the brain stem Enclosed by the cerebral heispheres Made of three parts Thalamus Hypothalamus Epithalamus Thalamus • Surrounds the third ventricle The relay station for sensory impulses (except olfaction) Transfers impulses to the correct part of the cortex for localization and interpretation Hypothalamus • Under the thalamus Important autonomic nervous system center Helps regulate body temperature Controls water balance Regulates metabolism Hypothalamus • An important part of the limbic system (emotions) The pituitary gland is attached to the hypothalamus Epithalamus • Forms the roof of the third ventricle Houses the pineal body (an endocrine gland) Includes the choroid plexus – forms cerebrospinal fluid Brain Stem • Attaches to the spinal cord Parts of the brain stem Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata
- 11. Midbrain • Mostly composed of tracts of nerve fibers Has two bulging fiber tracts – cerebral peduncles Has four rounded protrusions – corpora quadrigemina Reflex centers for vision and hearing The bulging center part of the brain stem Mostly composed of fiber tracts Includes nuclei involved in the control of breathing Medulla Oblongata • The lowest part of the brain stem Merges into the spinal cord Includes important fiber tracts Contains important control centers Heart rate control Blood pressure regulation Breathing Swallowing Vomiting Reticular Formation • Diffuse mass of gray matter along the brain stem Involved in motor control of visceral organs Reticular activating system plays a role in awake/sleep cycles and consciousness Cerebellum • Two hemispheres with convoluted surfaces Provides involuntary coordination of body movements BLOOD BRAIN BARRIER • Includes the least permeable capillaries of the body Excludes many potentially harmful substances • Useless against some substances Fats and fat soluble molecules Respiratory gases Alcohol Nicotine
- 12. Anesthesia Slight brain injury No permanent brain damage TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURIES • Concussion Slight brain injury No permanent brain damage • Contusion Nervous tissue destruction occurs Nervous tissue does not regenerate • Cerebral edema Swelling from the inflammatory response May compress and kill brain tissue Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) • Commonly called a stroke The result of a ruptured blood vessel supplying a region of the brain Brain tissue supplied with oxygen from that blood source dies Loss of some functions or death may result Alzheimer’s Disease • Progressive degenerative brain disease Mostly seen in the elderly, but may begin in middle age Structural changes in the brain include abnormal protein deposits and twisted fibers within neurons Victims experience memory loss, irritability, confusion and ultimately, hallucinations and death Mixed nerves – both sensory and motor fibers Afferent (sensory) nerves – carry impulses toward the CNS Efferent (motor) nerves – carry impulses away from the CNS CLASSIFICATION OF NERVES • 12 pairs of nerves that mostly serve the head and neck Numbered in order, front to back Most are mixed nerves, but three are sensory only
- 13. CRANIAL NERVES I Olfactory nerve – sensory for smell II Optic nerve – sensory for vision III Oculomotor nerve – motor fibers to eye muscles IV Trochlear – motor fiber to eye muscles nerve – sensory for the face; motor fibers to chewing muscles VI Abduces nerve – motor fibers to eye muscles VII Facial nerve – sensory for taste; motor fibers to the face VIII Vestibulocochlear nerve – sensory for balance and hearing IX-fibers to the pharynx X Vagus nerves – sensory and motor fibers for pharynx, larynx, and abdominal viscera XI Accessory nerve – motor fibers to neck and upper back XII Hypoglossal nerve – motor fibers to tongue Spinal Nerves • There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each vertebrae for a total of 31 pairs Spinal nerves are formed by the combination of the ventral and dorsal roots of the spinal cord Spinal nerves are named for the region from which they arise AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM • The involuntary part of the peripheral nervous system Consists of motor nerves only • • • •
- 14. • • • • Divided into two divisions Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division • The involuntary part of the peripheral nervous system Consists of motor nerves only • Divided into two divisions Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Differences Between Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems • Nerves Somatic – one motor neuron Autonomic – preganglionic and postganglionic nerves • Effector organs Somatic – skeletal muscle Autonomic – smooth muscle, cardiac muscle,and glands Differences Between Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems • Nerurotransmitters Somatic – always use acetylcholine Autominic – use acetylcholine, epinephrine, or norepinephrine
- 15. Sympathetic – “fight-or-flight” Response to unusual stimulus Takes over to increase activities Remember as the “E” division = exercise, excitement, emergency, and embarrassment Parasympathetic – housekeeping activities
- 16. Conserves energy Maintains daily necessary body functions Remember as the “D” division - digestion, defecation, and diuresis Development Aspects of the Nervous System • The nervous system is formed during the first month of embryonic development • Any maternal infection can have extremely harmful effects • The hypothalamus is one of the last areas of the brain to develop Development Aspects of the Nervous System • No more neurons are formed after birth, but growth and maturation continues for several years • The brain reaches maximum weight in Young adults