oral mucous membrane - II.pptx
- 1. An Overview of Oral Mucous Membrane-II
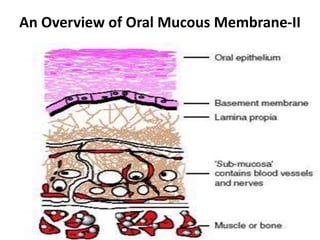
- 2. • Parts of oral mucous membrane – Covering epithelium – Underlying connective tissue – Submucosa – Periosteum, muscle • Three main types – Masticatory mucosa – Lining mucosa – Specialized mucosa courtesy :www.medscape.com/viewarticle/472915 •Two patterns of maturation a) Keratinized b) Non keratinized Richard B. Presland, Ph.D.; Richard J. Jurevic, D.D.S.. Making Sense of the Epithelial Barrier:What Molecular Biology and Genetics Tell Us About the Functions of Oral Mucosal and Epidermal Tissues. Journal of Dental Education April 2002.
- 3. Epithelial-Connective Tissue Interface Basement membrane /Basal lamina • Light microscope- 1-2µm thick is seen on the lamina propria side of the junction • Electron microscope- layer appears thinner
- 4. Basement membrane Richard B. Presland, Ph.D.; Richard J. Jurevic, D.D.S.. Making Sense of the Epithelial Barrier:What Molecular Biology and Genetics Tell Us About the Functions of Oral Mucosal and Epidermal Tissues. Journal of Dental Education April 2002.
- 5. • Using the electron microscope the following layers of the basement membrane can be distinguished: Lamina rara externa - 10 to 50nm thick Lamina densa -20 to 300nm, mostly 50 nm. Lamina rara interna is only about 10 nm thick Lamina fibroreticularis has a thickness of 200 - 500 nm. Rich in basotubules, 10 nm wide microfibrillike structures. Kimberley Brown. Epithelial Cells: Surface Domains & Junctions. Cell and Tissue Biology 2004
- 6. Structure of Hemidesmosome Courtesy: xtal.cicancer.org/research.html
- 7. Protein Alternate terms Site Keratin 5 Basal layer of stratified epithelia Keratin 14 Basal layer of stratified epithelia Plectin/HD1 Intracellular IFAP300 Intracellular P200 Intracellular BPAg1 BP230 or dystonin Intracellular BPAg2 BP180 or TYPE-XVII Transmembrane collagen a6b4 integrin Transmembrane Laminin 5 Epiligrin or nicein or kalinin BMZ Laminin 6 BMZ Ladinin LAD-1 BMZ Uncein BMZ Type-VII collagen BMZ Type-IV collagen BMZ Main hemidesmosome components J Bagan, LL Muzio, C Scully.Mucosal Diseases Series.Number III.Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid.Oral diseases 2005;11:197-218
- 8. • Basement membrane (basal lamina) is a tough elastic structure – Type IV and VII collagens – heparan sulphate (HS) (perlecan) – chondroitin sulphate (ChS) – proteoglycans (versican), and – glycoproteins laminin nidogen (entactin) thrombospondin tenascin fibronectin David F. Wilson et al. Oral cancer: Role of the basement membrane in invasion. Australian Dental Journal 1999;44:(2):93-97
- 9. Lamina lucida • Glycoprotein layer • It contains type IV collagen • It contains laminin and entactin. • Laminin and type IV collagen promote epithelial cell growth. Courtesy: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi
- 10. • Laminins – Laminin is a large, triple chain molecule. – α, β, γ subunits • Integrins – Family of transmembrane proteins consisting of 2 subunits- α and β. • Plectin and BP 230 – Members of the plakin family Courtesy: myworldatlarge.wordpress.com
- 11. Lamina densa • Layer of finely granular/filamentous material that run parallel to the basal cell membranes of the epithelial cells. • Inserted into the lamina densa are small loops of finely banded fibrils called anchoring fibrils.
- 12. REGIONAL VARIATIONS OF ORAL MUCOSA
- 13. Lip • Skin on its outer surface • Labial mucosa on its inner surface • Vermilion zone/ Red zone/ Transitional zone • Striated muscles in their core- muscles of facial expression • Minor mucous salivary glands • Skin – Keratinized layer of epidermis on a bed of connective tissue – Sweat glands, sebaceous glands and bases of hair follicles Section of skin of lip. A=keratinized epidermis, B=shaft of hair, C=sebaceous gland, D=dermis. Masson’s trichrome;x30 Fig.14.31 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 14. Vermilion • Lacks the appendages of skin • Angles of the mouth- sebaceous glands • Constant moistening by the tongue- lacks mucous glands • Vermilion zone – Epithelium is keratinized, thin and translucent – Connective tissue papilla are long and narrow • Intermediate zone- lacks a granular layer and has a thick parakeratinized layer Section of red zone of lip. Keratinized epithelium & lamina propria H&E x80 Fig: 14.32 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 15. Labial Mucosa • Thick, non keratinized epithelium • Lamina propria is wide with short and irregular papillae • Sub mucosa- Minor salivary glands Section of labial mucosa. A=non-keratinized oral epithellium, B=lamina propria, C=minor salivary gland in submucosa, D=fibres of orbicularis oris H&E; x15 Fig: 14.33 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 16. Cheek • Epithelium- non keratinized • Lamina propria- dense with short, irregular papillae • Submucosa- minor mucous salivary glands • Linea alba- keratinized, white line coincident with the occlusal plane • Fordyce’s spots- Sebaceous glands appear as small yellow patches Section of buccal mucosa. B=non keratinized oral epithelium, C=lamina propria, D=minor salivary glands in submucosa, A=fibres of buccinator muscle. H&E;X15 Fig: 14.34 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 17. Alveolar Mucosa • Thin, non keratinized epithelium • Lamina propria shows poorly developed dermal papillae • Sub mucosa houses many minor mucous salivary glands Section of lining oral epithelium from the alveolar mucosa. Absence of keratin in the superficial layer H&E;x80 Fig: 14.13 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 18. Gingiva • Two recognized regions – Attached gingiva – Free gingiva – Gingival margin – Gingival sulcus • Mucogingival junction Free gingival groove courtesy :www.medscape.com/viewarticle/1893
- 19. Attached Gingiva • Keratinized • No sub mucosa • Lamina propria-bound directly to the bone Crevicular(sulcular) epithelium • Epithelium on the inner surface of the gingiva • Non keratinized Section of parakeratinized oral epithelium from the gingiva. The superficial layer stain more heavily for keratin but nuclei are retained H&E; x100 Fig: 14.12 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 20. Junctional epithelium • Epithelial collar that surrounds the tooth and extends from the region of the cementum-enamel junction to the bottom of the gingival crevice • Two zones: – A single layer of cuboidal cells- stratum germinativum – Several layers of flattened cells- stratum spinosum • Features of the junctional epithelium – Hemidesmosomes and basal lamina- Attachment apparatus/ Epithelial attachment – Internal basal lamina – External basal lamina Demineralized section showing the dentogingival junction .A=region of attached gingiva covered by masticatory epithelium, B=region of free gingiva covered externally by masticatory epithelium,C=non-keratinized crevicular epithelium, D=non-keratinized junctional epithelium H&E; x30 Fig: 14.42 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 21. Cont… Internal basal lamina- 2 zones • Electron lucent zone adjacent to the cell • Electron dense layer adjacent to the tooth surface • Lacks type IV collagen and anchoring fibrils • Lamina propria – Rich blood supply • Turnover is rapid
- 22. Cont… Enamel cuticle • Non-mineralized structure interposed between the junctional epithelium and the underlying hard tissue • Ultrastructurally – Amorphous and biochemically distinct – Proteinaceous and may be derived from serum
- 23. Gingival crevicular fluid • Tissue fluid and cells passing through the epithelium from the connective tissue- GCF • Can be collected by capillary tubing, gingival washing or absorbent paper strips • Composition of GCF – Immunoglobulins – Complement – Polymorphonucleocytes – Epithelial squames
- 24. Interdental Gingiva • Part of the gingiva between adjacent teeth • Wedge shaped appearance • Interdental col- curved depression between the buccal and lingual peaks • Epithelium- non keratinized and derived from the reduced enamel epithelium Demineralized section of the interdental papillae cut in the buccolingual plane between two cheek teeth showing the ‘interdental col’. H&E; x4 Fig: 14.53 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 25. Collagen fibres • Type I collagen • Functions – Support of the free gingiva – Binding of the attached gingiva to the alveolar bone and tooth – Linkage of one teeth to another
- 26. Types of Gingival Fibers Diagram showing arrangement of principal collagen fibre groups in the lamina propria of the gingiva. a.buccolingual section, b.mesiodistal section, c.horizontal section, d.buccolingual section along the interdental col. A= DENTOGINGIVAL FIBRES B= LONGITUDINAL FIBRES C= CIRCULAR FIBRES D= ALVEOLO GINGIVAL FIBRES E= DENTOPERIOSTEAL FIBRES F= TRANSSEPTAL FIBRES G= SEMICIRCULAR FIBRES H= TRANSGINGIVAL FIBRES I= INTERDENTAL FIBRES J= VERTICAL FIBRES Fig: 14.55 a c b d B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 27. Cont… Lamina propria of gingiva • Fibroblasts lack alkaline phosphatase • Less contractile proteins • Releases more prostaglandins • Less ground substance and Type III collagen
- 28. Palate Hard palate • Keratinized and Para keratinized epithelium • Central region- no sub mucosa • Palate joins the alveolus- sub mucosa contains main neurovascular bundles and minor mucous salivary glands(posteriorly) and adipose tissue(anteriorly) Demineralised section of the hard palate showing the oral surface. A=lined by masticatory epithelium and the nasal epithelium, B=lined by a respiratory epithelium, C=bone of hard palate, D=duct from mucous gland opening onto surface H&E;x110 Fig: 14.61 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 29. Cont… • Nasal surface- respiratory epithelium – Ciliated columnar epithelial cells and goblet cells – Vascular sub mucosa- minor glands of both mucous and serous types Section of nasal surface of hard palate. A=cilitated columnar epithelium, B=goblet cell, C=minor gland H&E;x500 Fig: 14.62 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 30. Soft Palate • Non keratinized lining mucosa • Lamina propria – Papilla are short and broad – Elastic fibers and collagen bundles are thin • Sub mucosa – Small mucous glands – Attached to the palatal muscles • Nasal surface- respiratory epithelium Section of soft palate showing the oral surface being covered by a non keratinized lining mucosa, numerous minor salivary glands, palatal musculature and nasal epithelium H&E;x20 Fig: 14.63 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 31. Tongue and Floor of the Mouth • Epithelium- thin, non keratinized and shows short papillae • Sulcus terminalis – Palatal surface – Pharyngeal surface • Anterior 2/3rd of tongue- numerous papillae – Filiform – Fungiform – Foliate – Circumvallate • Posterior 1/3rd of tongue – Small lymphatic nodules/follicles Section showing the ventral surface of the tongue(A), and floor of mouth(B) being lined by non-keratinized lining epithelium H&E;x20, fig: 14.64 Section of fungiform papillae on dorsal surface of anterior part of tongue showing taste buds H&E;x120, Fig: 14.68 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 32. • Anterior tongue – Keratinized/ Para keratinized epithelium – Hair like tufts • Filiform papillae – Central core of lamina propria with smaller, secondary papillae branching from it • Fungiform papillae – Isolated, elevated mushroom-shaped papillae scattered between the filiform papillae – 150-400µm in diameter – Thin epithelium which is non- keratinized – Vascular core of lamina propria – Taste buds may be found on the surface Section showing dorsum of anterior 2/3rd of the tongue H&E;x35 Fig: 14.66 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 33. • Foliate papillae – One/ two longitudinal clefts at the side of the tongue – Non keratinized epithelium • Circumvallate papillae – Large and rounded – Surrounded by trench-like feature – Non keratinized epithelium – Taste buds-internal wall of the trench – Small serous glands of von Ebner Section of circumvallate papillae, A=serous glands B= of von Ebner empty via the ducts into the base of the trench C= surrounding the papillae, which is not raised above the surface of the tongue, D= muscle of tongue H&E; x35 Fig: 14.72 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 34. Taste Buds • Chemoreceptive organs- Taste • Located within the epithelium – Walls of the circumvallate papillae – Upper surface of fungiform papillae – Lateral walls of foliate papillae – Mucosa of the soft palate and in the epiglottis • 2 types of cells – Supporting cell – Taste cell Section of wall of circumvallate papillae showing two barrel-shaped areas representing two taste buds. Masson’s trichrome; x300 Fig: 14.74 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 35. Cont… • Taste cell- 4 distinct cell types – Undifferentiated type IV cells – Type I cells- dark appearance – Type II and III cells- lighter • Type I and III cells – Form synapses with intragemmal nerves
- 36. Posterior tongue • Collection of lymphoid follicles- Lingual tonsil • This forms a component of Waldeyer’s ring- protects the opening into the pharynx • Follicles are deep crypts lined with epithelium and containing a mass of lymphoid material • Follicles open onto the surface of the tongue • Contains small mucous glands Section of dorsal surface of posterior 1/3rd of tongue containing a lymphoid follicle. This part of the tongue is covered by a non keratinized lining epithelium H&E; x40, Fig: 14.76 Section of foliate papilla showing taste buds. H&E; x200 Fig: 14.70 B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 37. Functions of the oral mucosa • It is protective mechanically against both compressive and shearing forces • It provides a barrier to microorganisms, toxins and various antigens • It has a role in immunological defense, both humoral and cell mediated • Minor glands within oral mucosa provide lubrication and buffering as well as secretion of some antibodies. The viscoelastic mucous film also acts as a barrier, helping to retain water and electrolytes • The mucosa is richly innervated, providing input for touch, proprioception, pain and taste
- 38. • Keratinized epithelium – Masticatory mucosa • Gingiva • Hard palate – Vermilion border of the lip • Non keratinized epithelium – Lining mucosa • Lip and cheek • Vestibular fornix and alveolar mucosa • Inferior surface of tongue and floor of oral cavity • Soft palate – Specialized mucosa • Dorsal lingual mucosa • Taste buds B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252.
- 39. References • ANTONIO NANCI.TENCATE’S ORAL HISTOLOGY DEVELOPMENT, STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION.SIXTH EDITION:ELSEVIER;2005.CHAP.12;329-375. • B.K.B.BERKOVITZ.ORAL ANTOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY. FOURTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2009.CHAP.14;223-252. • G S KUMAR.ORBAN’S ORAL HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY.TWELFTH EDITION:MOSBY ELSEVIER;2008. CHAP.9;210-257. • David F. Wilson. Oral cancer: Role of the basement membrane in invasion. Australian Dental Journal 1999;44:(2):93-97. • Kimberley Brown. Epithelial Cells: Surface Domains & Junctions. Cell and Tissue Biology 2004. • J Bagan, LL Muzio, C Scully.Mucosal Diseases Series.Number III.Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid.Oral diseases 2005;11:197-218. • Geoffrey M.Cooper, Robert E.Hausman,editors.The Cell.A Molecular Approach.Fourth Edition:ASM Press Washington D.C.;2007.Chap.14;569-575.