Folds and foldings
•
40 recomendaciones•15,927 vistas
What are folds? •Parts of the folds •Classification of folds •Classification on the basis of axial planes •Classification on the basis of curvature(by Ramsay) •Classification on the basis of plunge •Engineering considerations
Denunciar
Compartir
Denunciar
Compartir
Descargar para leer sin conexión
Recomendados
Importance of geological considerations while choosing tunnel sites and alignments of the tunnel
Importance of geological considerations while choosing tunnel sites and align...

Importance of geological considerations while choosing tunnel sites and align...Buddharatna godboley
Más contenido relacionado
La actualidad más candente
Importance of geological considerations while choosing tunnel sites and alignments of the tunnel
Importance of geological considerations while choosing tunnel sites and align...

Importance of geological considerations while choosing tunnel sites and align...Buddharatna godboley
La actualidad más candente (20)
Importance of geological considerations while choosing tunnel sites and align...

Importance of geological considerations while choosing tunnel sites and align...
Destacado
Destacado (6)
Joukowski's airfoils, introduction to conformal mapping

Joukowski's airfoils, introduction to conformal mapping
Similar a Folds and foldings
Similar a Folds and foldings (20)
Más de RAHUL SINHA
Más de RAHUL SINHA (20)
Último
From customer value engagements to hands-on production support, our Services span across every stage of our customers digital transformation journey, to help ensure that every customer is successful in their adoption of our solutions.
• Implementation, Upgrade, Migration, and Maintenance Services
• On-Premises and On-Cloud
• COTS Training Services; On-Site and Virtual
• Software Support Services; Legacy and 3DEXPERIENCE
• Value Engagement & Blueprinting
• Specialized Consulting and Support Services
• Customized Training Services
• Automation and Configuration Services
• Technical Resource Augmentation Services
• Project Management
• Know-how Training (mentoring) and Resource AugmentationNavigating Complexity: The Role of Trusted Partners and VIAS3D in Dassault Sy...

Navigating Complexity: The Role of Trusted Partners and VIAS3D in Dassault Sy...Arindam Chakraborty, Ph.D., P.E. (CA, TX)
Último (20)
Cara Menggugurkan Sperma Yang Masuk Rahim Biyar Tidak Hamil

Cara Menggugurkan Sperma Yang Masuk Rahim Biyar Tidak Hamil
Kuwait City MTP kit ((+919101817206)) Buy Abortion Pills Kuwait

Kuwait City MTP kit ((+919101817206)) Buy Abortion Pills Kuwait
Orlando’s Arnold Palmer Hospital Layout Strategy-1.pptx

Orlando’s Arnold Palmer Hospital Layout Strategy-1.pptx
Navigating Complexity: The Role of Trusted Partners and VIAS3D in Dassault Sy...

Navigating Complexity: The Role of Trusted Partners and VIAS3D in Dassault Sy...
"Lesotho Leaps Forward: A Chronicle of Transformative Developments"

"Lesotho Leaps Forward: A Chronicle of Transformative Developments"
Tamil Call Girls Bhayandar WhatsApp +91-9930687706, Best Service

Tamil Call Girls Bhayandar WhatsApp +91-9930687706, Best Service
A CASE STUDY ON CERAMIC INDUSTRY OF BANGLADESH.pptx

A CASE STUDY ON CERAMIC INDUSTRY OF BANGLADESH.pptx
NO1 Top No1 Amil Baba In Azad Kashmir, Kashmir Black Magic Specialist Expert ...

NO1 Top No1 Amil Baba In Azad Kashmir, Kashmir Black Magic Specialist Expert ...
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX

XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Folds and foldings
- 2. TOPICS •What are folds? •Parts of the folds •Classification of folds •Classification on the basis of axial planes •Classification on the basis of curvature(by Ramsay) •Classification on the basis of plunge •Engineering considerations
- 3. What are folds? •Folds may be defined as undulations or bends or curvatures developed in the rocks of the crusts as a result of stresses on these rocks. •The process of development of in the rocks is called is called folding.
- 4. Parts of the folds
- 5. Parts of the folds Terms used to describe the shape of the folds are: •Limbs: these are side or flanks of the folds. •Hinge: in a folded layer, a point can be found where curvature is maximum and one limb ends and the other starts at this point. This point is called hinge point. •Hinge line: when the rocks occur in the sequence and all the hinge points are joined ;the resultant line us called hinge line. •Axial planes: it is the imaginary plane that passes through all points of maximum curvature in folded sequence. It may be vertical, horizontal or horizontal in nature.
- 6. •Axis of the fold: it may be defined as a line parallel to the hinge line of a fold. Or it may be defined as line of intersection of a axial plane of a fold and with any bed of the fold. •Plunge of the fold: the axis of the fold may be horizontal, vertical or inclined with respect to other parts of the fold. The angle of inclination of the fold axis with the horizontal as measured in a vertical plane. In other words fold axis is a line and plunge is the angle which this line makes with horizontal. •Crest and trough: the line running through the highest points in a uparched fold is called crest. Similarly line running through the lowest point in a downarched fold is called trough.
- 8. Classification of folds •Two basic types of folds Anticlines Synclines •Anticlines are defined as the folds in which the strata is uparched The geographically older rocks occupy a position at the core of the fold and the youngest forming the outermost flank. The limbs dip away from each other at the crest in the simplest form. •Synclines are defined as the folds in which The strata is downarched The geographical younger rocks occupy a position in core of the fold and older rocks form the outer flanks. The limbs dip towards a common center.
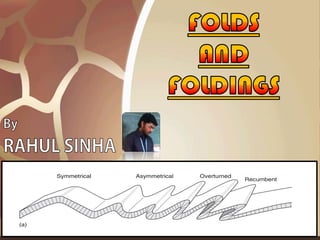
- 10. Classification on the basis of axial planes •Symmetrical folds: the axial plane is essentially vertical. The limbs are equal in length and dip equally in opposite direction. In short, two limbs are essentially mirror images of each other. It may be anticline or syncline. •Asymmetrical folds: all those folds, anticlines or synclines, in which the limbs are unequal in length and dips unequal on either side from the hinge line. •Overturned folds: fold with the inclined axial planes in which both the limbs are dipping essentially in the same direction. In some cases, due to extreme compression from opposite sides reverse the general dip conditions – anticline limbs dip towards each other and the synclinal limbs dip away from each other. Such type of fold is called fan fold. •Isoclinal folds: may be defined as groups of folds in which all the axial planes are essentially parallel i.e. all the component limbs are dipping at equal amount. They may be made up of series of anticlines and synclines.
- 13. Arch: zone of curvature corresponding to crest and trough Shell: outer zone made up of sedimentary formation. Core: innermost part of the fold and mostly formed of crystalline igneous or metamorphic rocks. Root zone: basal part of the fold. It is not easily traceable; once traced can show whether the fold was anticline or syncline that has suffered further inversion. Recumbent folds: may be defined as extreme type of overturned folds in which the axial plane acquire almost an horizontal attitude. Parts of this types of folds are:
- 15. Classification on the basis of curvature(by Ramsay) Class 1 folds: folds in which the degree of curvature in the outer arch of the fold is less than the curvature of inner arch. Class 2 folds: folds in which the degree of curvature in the outer arch of the fold is equal to the curvature of inner arch. Class 3 folds: folds in which the degree of curvature in the outer arch of the fold is more than the curvature of inner arch.
- 16. Classification on the basis of plunge •Plunging fold: any fold in which fold axis is NOT HORIZONTAL i.e. it makes an angle with the horizontal, may be termed as plunging folds. •Non-plunging fold: any fold in which fold axis is essentially HORIZONTAL i.e. it doesn’t makes an angle with the horizontal, may be termed as plunging folds.
- 17. Engineering considerations Effect of folding on civil engineering projects: •Change in altitude: folding of any type would cause the change in attitude (dip and strike) of the same strata in the aerial extent and also in depth. Hence same layers may be repeated in alignment. If it happens so and encountered layers are of undesirable nature, the project cost and time will be affected.
- 18. •Strained nature: all the stresses that act on the rocks during the folding are generally absorbed by the rocks undergoing strain and hence stores some strain energy. So these rocks may respond to any disturbance caused by nature or by engineering. General example is rock bursts (falling of huge blocks of rocks due to release of strain energy) during excavation of a tunnel through folded region. •Shattering of rocks: folding is a result of stress. These stresses are maximum in the axial zones which are enough to break the rocks. Hence axial regions are likely to be the areas of fractured zones which are weak in strength and porous in character. Such areas of folded rocks cannot be trusted as roofs and floors of tunnels or foundation sites for dam.
- 19. Please visit (for more presentations) www.slideshare.net/RAHULSINHA1993
