MEASUREMENTS AND CONVERSIONS OF UNITS.pdf
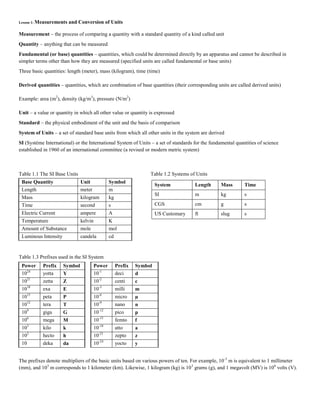
- 1. Lesson 1: Measurements and Conversion of Units Measurement – the process of comparing a quantity with a standard quantity of a kind called unit Quantity – anything that can be measured Fundamental (or base) quantities – quantities, which could be determined directly by an apparatus and cannot be described in simpler terms other than how they are measured (specified units are called fundamental or base units) Three basic quantities: length (meter), mass (kilogram), time (time) Derived quantities – quantities, which are combination of base quantities (their corresponding units are called derived units) Example: area (m2 ), density (kg/m3 ), pressure (N/m2 ) Unit – a value or quantity in which all other value or quantity is expressed Standard – the physical embodiment of the unit and the basis of comparison System of Units – a set of standard base units from which all other units in the system are derived SI (Système International) or the International System of Units – a set of standards for the fundamental quantities of science established in 1960 of an international committee (a revised or modern metric system) Table 1.1 The SI Base Units Table 1.2 Systems of Units Table 1.3 Prefixes used in the SI System The prefixes denote multipliers of the basic units based on various powers of ten. For example, 10-3 m is equivalent to 1 millimeter (mm), and 103 m corresponds to 1 kilometer (km). Likewise, 1 kilogram (kg) is 103 grams (g), and 1 megavolt (MV) is 106 volts (V). Base Quantity Unit Symbol Length meter m Mass kilogram kg Time second s Electric Current ampere A Temperature kelvin K Amount of Substance mole mol Luminous Intensity candela cd System Length Mass Time SI m kg s CGS cm g s US Customary ft slug s Power Prefix Symbol Power Prefix Symbol 1024 yotta Y 10-1 deci d 1021 zetta Z 10-2 centi c 1018 exa E 10-3 milli m 1015 peta P 10-6 micro µ 1012 tera T 10-9 nano n 109 giga G 10-12 pico p 106 mega M 10-15 femto f 103 kilo k 10-18 atto a 102 hecto h 10-21 zepto z 10 deka da 10-24 yocto y
- 2. Length In October 1983, the meter (m) was redefined as the distance traveled by light in vacuum during a time of 1/299 792 458 second. Mass The SI unit of mass, the kilogram (kg), is defined as the mass of a specific platinum–iridium alloy cylinder kept at the International Bureau of Weights and Measures at Sèvres, France. Time In 1967, the second was redefined to take advantage of the high precision attainable in a device known as an atomic clock, which uses the characteristic frequency of the cesium-133 atom as the “reference clock.” The second (s) is now defined as 9 192 631 770 times the period of vibration of radiation from the cesium atom. Conversion of Units Dimensional analysis (also known as factor-label method) – treats dimensions as algebraic quantities Dimension – the physical nature of a quantity (Whether a distance is measured in units of feet or meters or fathoms, it is still a distance and we say its dimension is length.) 𝑮𝒊𝒗𝒆𝒏 𝑼𝒏𝒊𝒕 𝒙 𝑫𝒆𝒔𝒊𝒓𝒆𝒅 𝑼𝒏𝒊𝒕 𝑮𝒊𝒗𝒆𝒏 𝑼𝒏𝒊𝒕 = 𝑫𝒆𝒔𝒊𝒓𝒆𝒅 𝑼𝒏𝒊𝒕 Conversion Factor – a fraction whose numerator and denominator are the same quantity expressed in different units Equalities between SI and U.S. customary units are listed in the Table 4. For example, 2.54 cm and 1 in. are the same length, 2.54cm = 1in. This relationship allows us to write two conversion factors: 2.54 𝑐𝑚 1 𝑖𝑛. and 1 𝑖𝑛. 2.54 𝑐𝑚 We use the first factor to convert inches to centimeters. For example, the length in centimeters of an object that is 8.50 in. long is (8.50 in.) 2.54 𝑐𝑚 1 𝑖𝑛. = 21.6 cm The unit inches in the denominator of the conversion factor cancels the unit inches in the given data (8.50 inches). The unit centimeter in the numerator of the conversion factor becomes the unit of the final answer. Sample Problem 1.1 Converting Units Using Two or More Conversion Factors: The average speed of a nitrogen molecule in air at 25 °C is 515 m/s. Convert this speed in miles per hour. Sample Problem 1.2 Conversions Involving Volume (based on unit length conversion factor): Determine the mass in grams of 2 cubic inches (2.00 in.3 ) of gold, which has a density of 19.3 g/cm3 . Significant Figures – used to indicate the amount of information that is reliable when discussing a measurement (digits believed to be correct by the person who makes the measurement). In reporting measurements (Figure 1.1), one estimated digit (or uncertain one) is declared and no more. Rules: 1. Nonzero digits are always significant. 2. Zeroes are sometimes significant and sometimes they are not. a. Zeroes at the beginning of number that is used to position the decimal point are not significant. b. Zeroes between nonzero digits are significant. c. Zeroes at the end of a number that contains decimal point are always significant. d. Zeroes at the end of a number that does not contain decimal may or may not be significant unless otherwise written in scientific notation.
- 3. 3. Exact numbers can be considered as having an unlimited numbers of significant figures. (Applies to the defined quantities.) 4. Multiplication and Division: the number of significant figures in a result must be the same as the number of significant figures in the factor with the fewest significant figures. 5. Addition and Subtraction: the result must have the same number of digits to the right of the decimal point as in the measurement that has the fewest digits to the right of the decimal point. Note: A technique for avoiding error accumulation is to delay the rounding of numbers in a long calculation until you have the final result. Figure 1.1 References: Serway and Jewett. 2019. Physics for Scientists and Engineers. Cengage Young and Freedman. 2020. University Physics with Modern Physics. Person Schaums Outline for College Physics. 9th Edition Brown, et al. 2018. Chemistry: The Central Science. Pearson. Table 1.4 Common Conversion Factors Length 1 in. = 2.54 cm (exact) 1 m = 39.37 in. = 3.281 ft 1 ft = 12 in. = 0.304 8 m 1 yd = 3 ft = 0.914 4 m 1 mi = 1.609 km = 5280 ft 1 km = 1000 m 1 m = 100 cm = 1000 mm 1 lightyear = 9.461 X 1015 m Volume 1 m3 = 1000 L 1 m3 = 1,000,000 cm3 1 L = 1000 cm3 1 m3 = 35.31 ft3 1 ft3 = 1728 in3 1 ft3 = 7.481 gal 1 gal = 3.786 L 1 gal = 231 in3 1 drum = 55 gal Area 1 hectare (ha) = 10,000 m2 1 m2 = 10,000 cm2 1 m2 = 10.76 ft2 1 ft2 = 144 in2 Mass 1 ton = 1000 kg 1 kg = 1000 g 1 slug = 14.59 kg Useful equivalence 1 kg = 2.205 lb 1 lb = 16 oz Pressure 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mmHg = 14.7 psi = 101325 Pa = 1.01325 bar 1 bar = 100 000 Pa 1 Pa = 1 N/ m2 Time 1 mo = 30 days 1 day = 24 h 1 h = 60 min 1 h = 3600 s 1 min = 60 s Work and Energy 1 J = 1000 erg = 0.788 ft-lb 1 cal = 4.186 J 1 BTU = 252 cal Force 1 lb = 4.448 N Power 1 hp = 746 W = 550 ft-lb/s 1 BTU/h = 0.293 W Figure 1.1