Virion vs viroid & prions
- 2. Viron • A virion is a complete functional virus that has the capacity to infect living tissue. This means that it includes the genetic material, the capsid, the envelope and the membrane proteins that allow the virus to bind to its host and enter it. • Structural unit of the virus • It has two essential structures: DNA or RNA and capsid. • Sometimes, glycoprotein spicules can be added to these basic structures • VIRUSES can be found either inside a cell (intracellular) or outside of a cell (extracellular). If it is found extracellular, the virus is called a virion. A virion contains a protein coating called a capsid, which surrounds the core of the virus containing the nucleic acid (either DNA or RNA).
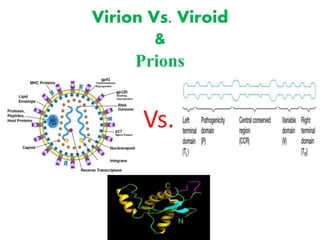
- 3. Bio-molecules found in virions • Genetic material, either DNA or RNA, single or double stranded, nucleoprotein capsid, maybe an envelope usually receptor proteins or enzymes that permit binding or entry into the host. • It is an extracellular virus consisting of a protein coat (capsid) surrounding a nucleic acid core, either DNA or RNA, together known as a nucleocapsid called an envelope. • A virus will not have an envelope within a cell. If the cell was burst artificially, then these virus particles cannot be called virion because they will lack certain proteins that will make them infectious even though the genetic material is present. • Although viruses lack cell membrane, some viruses have a viral membrane surrounding its capsid. These are called enveloped virion. One without an envelop is called a naked or non-enveloped virion.
- 4. • The virion shell or capsid protects the interior core that includes the genome and other proteins. After the virion binds to the surface of a specific host cell, its DNA or RNA is injected into the host cell and viral replication occurs, resulting in the spread of the infection to other host cells. • A virion is the infectious particle that is designed for transmitting the nucleic acid genome among hosts or host cells. Virions are produced in the cytoplasm of complex viral ‘factories,' the virus.
- 6. Viroids • Viroids are infectious, non-protein‐coding, highly structured small circular ribonucleic acids (RNAs) able to replicate autonomously and induce diseases in higher plants. • Infectious agents composed only of closed, circular ssRNAs • Do not encode gene products • Requires host cell DNA-dependent RNA polymerase to replicate • Cause plant diseases • Some found in infected host cell nucleolus, others found in chloroplast • May cause disease by triggering RNA silencing
- 8. • Viroids and viruses differ in structure, function and evolutionary origin • Viroids move intracellularly, cell‐to‐cell through plasmodesmata, and long distance through the phloem. • Viroids may infect their host plants latently or induce different pathogenic alterations including death. • Viroids, the smallest known pathogens, are naked, circular, singlestranded RNA molecules that do not encode protein yet replicate autonomously when introduced into host plants. • Symptoms of viroid infection in plants include stunting of growth, deformation of leaves and fruit, stem necrosis, and death. • E.g., Potato spindle Tuber Viroid, Coconut Cadang Cadang Viroid
- 11. Prions • Pronounced “pree-on” • Shortened term for: • Proteinaceous Infections Particle • Causes TSE (Transmissible Spongiform Disease) which attacks the central nervous system (the brain). • Discovered by Prusiner in 1982 in Scrapie(neurological disease of sheep) • Won Nobel prize in Physiology and medicine in 1997
- 12. Basic Structure • Normal prions contain about 200-250 amino acids twisted into three telephone chord-like coils known as helices, with tails of more amino acids. • The mutated, and infectious, form is built from the same amino acids but take a different shape. • 100 times smaller than the smallest known virus.
- 14. Differences From Bacteria & Viruses • Prions do not contain nucleic acid; they don’t have DNA or RNA. • They are extremely resistant to heat and chemicals. • Prions are very difficult to decompose biologically; they survive in soil for many years.
- 15. Controversy • DNA and RNA are the only substances now known to replicate in body tissues, so how do prions make copies of themselves without any nucleic acids? • Some believe TSEs are caused by an unidentified slow-acting virus. • Others believe a small virus accompanies a prion and they work together to cause disease.
