cell_communication cheat sheet
•
8 recomendaciones•2,601 vistas
cell communication cheat sheet
Denunciar
Compartir
Denunciar
Compartir
Descargar para leer sin conexión
Recomendados
Recomendados
Más contenido relacionado
La actualidad más candente
La actualidad más candente (20)
Destacado
Destacado (20)
Similar a cell_communication cheat sheet
Similar a cell_communication cheat sheet (20)
BCH422 signal transduction.pptx and cell comunication

BCH422 signal transduction.pptx and cell comunication
1 the progress of cell signaling.pdf Understanding cell signaling

1 the progress of cell signaling.pdf Understanding cell signaling
Cell Signaling | Steps Involved | Types | Receptors | Signal Transduction | ...

Cell Signaling | Steps Involved | Types | Receptors | Signal Transduction | ...
Más de Timothy Welsh
Más de Timothy Welsh (20)
Último
This presentation was provided by William Mattingly of the Smithsonian Institution, during the fourth segment of the NISO training series "AI & Prompt Design." Session Four: Structured Data and Assistants, was held on April 25, 2024.Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: Structured Data, Assistants, & RAG"

Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: Structured Data, Assistants, & RAG"National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
This presentation was provided by William Mattingly of the Smithsonian Institution, during the third segment of the NISO training series "AI & Prompt Design." Session Three: Beginning Conversations, was held on April 18, 2024.Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: The Basics of Prompt Design"

Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: The Basics of Prompt Design"National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
APM Welcome
Tuesday 30 April 2024
APM North West Network Conference, Synergies Across Sectors
Presented by:
Professor Adam Boddison OBE, Chief Executive Officer, APM
Conference overview:
https://www.apm.org.uk/community/apm-north-west-branch-conference/
Content description:
APM welcome from CEO
The main conference objective was to promote the Project Management profession with interaction between project practitioners, APM Corporate members, current project management students, academia and all who have an interest in projects.APM Welcome, APM North West Network Conference, Synergies Across Sectors

APM Welcome, APM North West Network Conference, Synergies Across SectorsAssociation for Project Management
Último (20)
IGNOU MSCCFT and PGDCFT Exam Question Pattern: MCFT003 Counselling and Family...

IGNOU MSCCFT and PGDCFT Exam Question Pattern: MCFT003 Counselling and Family...
Measures of Dispersion and Variability: Range, QD, AD and SD

Measures of Dispersion and Variability: Range, QD, AD and SD
Disha NEET Physics Guide for classes 11 and 12.pdf

Disha NEET Physics Guide for classes 11 and 12.pdf
Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: Structured Data, Assistants, & RAG"

Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: Structured Data, Assistants, & RAG"
Presentation by Andreas Schleicher Tackling the School Absenteeism Crisis 30 ...

Presentation by Andreas Schleicher Tackling the School Absenteeism Crisis 30 ...
Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: The Basics of Prompt Design"

Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: The Basics of Prompt Design"
APM Welcome, APM North West Network Conference, Synergies Across Sectors

APM Welcome, APM North West Network Conference, Synergies Across Sectors
cell_communication cheat sheet
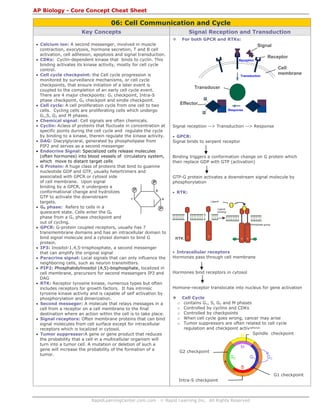
- 1. RapidLearningCenter.com.com © Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved AP Biology - Core Concept Cheat Sheet 06: Cell Communication and Cycle Key Concepts • Calcium ion: A second messenger, involved in muscle contraction, exocytosis, hormone secretion, T and B cell activation, cell adhesion, apoptosis and signal transduction. • CDKs: Cyclin-dependent kinase that binds to cyclin. This binding activates its kinase activity, mostly for cell cycle control. • Cell cycle checkpoint: the Cell cycle progression is monitored by surveillance mechanisms, or cell cycle checkpoints, that ensure initiation of a later event is coupled to the completion of an early cell cycle event. There are 4 major checkpoints: G1 checkpoint, Intra-S phase checkpoint, G2 checkpoit and sindle checkpoint. • Cell cycle: A cell proliferation cycle from one cell to two cells. Cycling cells are proliferating cells which undergo G1,S, G2 and M phases. • Chemical signal: Cell signals are often chemicals. • Cyclin: Aclass of proteins that fluctuate in concentration at specific points during the cell cycle and regulate the cycle by binding to a kinase, therein regulate the kinase activity. • DAG: Diacylglyceral, generated by phospholipase from PIP2 and serves as a second messenger • Endocrine Signal: Specialized cells release molecules (often hormones) into blood vessels of circulatory system, which move to distant target cells • G Protein: A huge class of proteins that bind to guanine nucleotide GDP and GTP, usually hetertrimers and associated with GPCR or cytosol side of cell membrane. Upon signal binding by a GPCR, it undergoes a conformational change and hydrolizes GTP to activate the downstream targets. • G0 phase: Refers to cells in a quiescent state. Cells enter the G0 phase from a G1 phase checkpoint and out of cycling. • GPCR: G-protein coupled receptors, usually has 7 transmembrane domains and has an intracellular domain to bind signal molecule and a cytosol domain to bind G protein. • IP3: Inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate, a second messenger that can amplify the original signal • Paracrine signal: Local signals that can only influence the neighboring cells, such as neuron transmitters. • PIP2: Phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate, localized in cell membrane, precursors for second messengers IP3 and DAG • RTK: Receptor tyrosine kinase, numerous types but often includes receptors for growth factors. It has intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity and is capable of self activation by phosphorylation and dimerization. • Second messeger: A molecule that relays messages in a cell from a receptor on a cell membrane to the final destination where an action within the cell is to take place. • Signal receptors: Often membrane proteins that can bind signal molecules from cell surface except for intracellular receptors which is localized in cytosol. • Tumor suppressor:A gene or gene product that reduces the probability that a cell in a multicellular organism will turn into a tumor cell. A mutation or deletion of such a gene will increase the probability of the formation of a tumor. Signal Reception and Transduction For both GPCR and RTKs: Signal reception --> Transduction --> Response • GPCR: Signal binds to serpent receptor Binding triggers a conformation change on G protein which then replace GDP with GTP (activation) GTP-G protein activates a downstream signal molecule by phosphorylation • RTK: • Intracellular receptors Hormones pass through cell membrane Hormones bind receptors in cytosol Homone-receptor translocate into nucleus for gene activation Cell Cycle o contains G1, S, G2 and M phases o Controlled by cyclins and CDKs o Controlled by checkpoints o When cell cycle goes wrong, cancer may arise o Tumor suppressors are often related to cell cycle regulation and checkpoint activation. Phosphate group Ligand Ligand binding Signal Receptor Reception Transduction Transducer Response Cell membrane Effector G1 checkpoint Intra-S checkpoint G2 checkpoint Spindle checkpoint
