structure of atom crash course .pptx
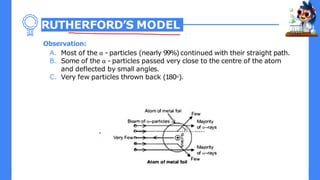
- 1. RUTHERFORD’S MODEL Observation: A. Most of the α - particles (nearly 99%)continued with their straight path. B. Some of the α - particles passed very close to the centre of the atom and deflected by small angles. C. Very few particles thrown back (180о).
- 2. Conclusion A. Most of the α- particles were continued their straight path that means most of the space inside the atom is empty. B. The centre of an atom has a positively charged body called nucleus which repel positively charged α - particles and thus explained the scattering phenomenon. C. Almost all mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus. D. The size and volume of the nucleus is very small as compared to the total size and volume of atom.
- 3. Planck’s Quantum Theory According to this theory atoms or molecules could emit or absorb energy only in discrete quantities (small packets) and not in any arbitrary amount. Planck gave the name quantum to the smallest quantity of energy that can be emitted in the form of E.M. radiation. Quantum of light is known as PHOTON
- 4. Planck’s Quantum Theory The energy of Quantum 𝖺 ν of wave E =hν or The energy of a photon is proportional to its frequency and is given by E =hν where h =6.626 x 10-34Jsec,
- 5. Planck’s Quantum Theory A body can emit or absorb energy only in terms of the integral multiples of quantum, i.e. E=n.hν, where n =1, 2, 3, ....... i.e. a body can emit or absorb energy as hν, 2hν ...... but it can not emit or absorb energy in fractional values of hν such as 1.5 hν, 2.5 hν. The energy absorbed/released by a substance =n.hν =n.hc/λ n =number of Quantum
- 6. Planck’s Quantum Theory The energy of a single quantum is really small thus a new unit is used (eV) 1eV =1.6x10-19 C.V =1.6x10-19J ⇒ 1eV =1.6 x 10-19J
- 7. Planck’s Quantum Theory E(ev) =1240/λ(nm) or 12400/λ(Å)
- 8. Photoelectric Effect Emission of electrons from a metal surface when exposed to light radiations of appropriate wavelength is called photoelectric effect. The emitted electrons are called photoelectrons.
- 9. Photoelectric Effect Emission of electrons from a metal surface when exposed to light radiations of appropriate wavelength is called photoelectric effect. The emitted electrons are called photoelectrons.
- 10. Intensity I =energy of Radiation/Time x surface area I =nhν/t.A A ⟶ Fixed ν ⟶ Fixed High intensity =More number of protons
- 11. Threshold Energy Work function or threshold energy may be defined as the minimum amount of energy required to eject electrons from a metal surface. According to Einstein, Maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electron=absorbed energy-work function where, ν0, and λ0, are threshold frequency and threshold wavelength respectively
- 12. Bohr’s Atomic Model Applicable only for mono electric system H, He+, Li2+, Be3+ ● The atom has a central massive core nucleus where all the protons and neutrons are present. The size of the nucleus is' cry small. ● The electron in an atom revolve around the nucleus in certain discrete orbits. Such orbits are known as stable orbits or non - radiating or stationary orbits.
- 13. Bohr’s Atomic Model An electron can move only in those permissive orbits in which the angular momentum (mvr) of the electron is an integral multiple of h/2π Thus, where, m =mass of the electron, r =radius of the electronic orbit, v = velocity of the electron in its orbit.
- 14. rn =0.529 n2 Å Z v =2.188 x 106 x Z m/sec n Bohr’s Atomic Model
- 15. Thus, TE of e- =KE +PE n =E =-13.6 Z2 n2 eV/atom n =E =-21.8 x 10-19 Z2 n2 J /atom
- 16. KE =-TE & PE =2TE or TE =-KE =PE/2
- 17. For Hydrogen, n E =-13.6 Z2 n2 eV/atom E1 =-13.6eV E2 =-3.4eV E3 =-1.51eV E4=-0.85eV
- 18. (En) any atom =(En)H x Z2
- 19. n =4 (3rd excited state) n =3 (2nd excited state) n =2 (1st excited state) n =1(ground state)
- 20. Wavelength of Photon Eph =Eho - Elo RH =Rydberg’s constant =109677 cm-1
- 22. Ionization of monoelectric species. The minimum energy required to remove the ground state e- out of the atom nlo= 1⟶ nho =∞ Epn =Eho - Elo =E∞- E1 =0-E1 =IE =-(E1) For H, IE= 13.6ev
- 24. ● When mono electric mono atomic H(g) is heated, all gas and state e-s will get excited to higher state ● Thus, after some time, these es will be to come back to ground state IN EVERY POSSIBLE WAY ● Because of this, so many photons of diff. λ will be emitted. Line spectrum of Hydrogen
- 25. Electron transitions for the Hydrogen atom
- 26. 1. It could not explain the line spectra of atoms containing more than one electron. 2. This theory could not explain the presence of multiple spectral lines. 3. This theory could not explain the splitting of spectral lines in magnetic field (Zeeman effect) and in electric field (Stark effect). The intensity of these spectral lines was also not explained by the Bohr atomic model. 4. This theory could not explain uncertainty principle. Failure of Bohr Model
- 27. It suggests wave-like nature of particle. In 1924, de Broglie proposed that an electron, like light, behaves both as material particle and as a wave. The electrons, protons and even atoms, when in motion, possess wave properties. This proposal gave a new theory, known as wave mechanical theory of matter. De Broglie Hypothesis
- 30. If a charged particle present at rest is accelerated by V volts, then, λ = Inc. in KE =q.v =(KE)particle =0 +qv =qv h √2m q.v q= charge particle (c) only mag. V=voltage (v)
- 32. Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle For a MOVING MICROSCOPIC particle, it is impossible to determine exact value of both potion & momentum SIMULTANEOUSLY. While treating e- as a wave it is not possible to ascertain simultaneously the exact position and velocity of the e- more precisely at a given instant
- 33. Δx =error in position (m) Δp =error in momentum (kg m/s) Δx. Δp ≥h/4π ⇒ (Δx)min .(Δp)min =h/4π
- 35. Wave mechanical model Quantum mechanical model - Proposed by heisenberg and schrodinger. - Exact pos. of e- can’t be determined inside the atom also - Only the probability of finding the e- can be determined.
- 36. Principal quantum number (n): - It was proposed by Bohr and denoted by ‘n’ - It determines the average distance between electron and nucleus, - It determine the energy of the electron in an orbit where electron is present. - It gives the information of orbit K, L, M, N,.... - The value of energy increases with the increasing value of n. - It represents the major energy shell from which the electron belongs.
- 37. Azimuthal quantum number or angular quantum number (l): - It was proposed by sommerfield and denoted by ‘l’. - It determines the number of subshells or sublevels to which the electron belongs. - The value of l is integral values upto (n - 1), starting from zero where ‘n’ is the number of principle shell. - It tells about the shape of subshells.
- 38. Magnetic quantum number (m) :
- 39. Magnetic quantum number (m) : - It was proposed by linde and denoted by ‘m’ - It gives the number of permitted orientation of subshells. - The value of m varies from -l to +l through zero.
- 40. n = 1 l = 0 m = 0 1 s n = 2 l = 0 m = 0 l = 1 m = -1, 0, 1 n = 3 l = 0 l = 1 m = 0 m = -1 , 0, 1 l = 2 m = -2 , -1, 0, 1, 2
- 41. Spin quantum number (s): It was proposed by goldschmidt and uhlenbeck and denoted by the symbol of ‘s’ The value of ‘s’ is +½or - ½,which is signified as the spin or rotation or direction of electron on it’s axis during the movement.
- 42. The spin may be clockwise or anticlockwise. It represents the value of spin angular momentum is equal to h/2π √s(s+1). Maximum spin of an atom =½x number of unpaired electron.
- 43. Nodes Radial Or spherical Nodes n - l - 1 Angular nodes or nodal planes or cones (l)
- 44. Nodes Radial Or spherical Nodes n - l - 1 Angular nodes or nodal planes or cones (l)
- 45. Atomic Structure - Radial modes =n - l - 1 - Angular nodes =l - Total nodes =n - 1
- 46. Rules for R2(r)v/sr graph - At origin, nucleus is present. - For s orbitals, the curve starts from a max value - For p, d, f orbitals, the curve starts from origin. - The pt. Where the curve cuts x - axis represents radial nodes.
- 47. Rules for 4πr2 R2(r)dr v/sgraph - Nucleus is present at origin - For every orbital , the curve starts from origin - ∵ if r =o P(r) =O - All curves are in 1st quadrant only [for all orbitals] - Each touch on x - axis is a radial node
- 48. Rules to write e.conf. 1. Aufbau’s Rule For mono electronic system, Energy is dependent on value of n only 1s <2s =2p <3s =3p =3d <4s =4p =4d =4f
- 49. Rules to write e.conf 1. Aufbau’s Rule for multi electronic system, Energy is dependent on value of n+l - Subshell having small (n+l) has lesser energy - If for 2 subshells, n+l is same Subshell with smaller n is of less energy ⇒ 1S α 2S <2p <3S <3p <4S <3d <
- 51. Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity - The subshells are first filled with the e-s of some spin and then the pairing occurs. - maximum multiplicity conf is the most stable.
- 52. Exchange energy In a subshell with degenerate orbitals, the e-s having same spin can exchange their pos, ⇒ energy is released ⇒ exchange energy Since energy is released ⇒ stability inc.
- 53. Pauli’s exclusion principle No two e-s in an atom can have same value of all the 4 Q.No. or In an- orbital, e-s must be present with opp. spin
- 54. Periodic Classification Sc Ti V G Mn Fe Co Ni Cu 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 4S23d1 4S23d2 4S23d3 4S23d5 4S23d6 4S23d7 4S23d8
- 55. d - Block exceptions
- 56. Periodic Classification 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au
- 57. JEE Main July 2021 A. B. C. D.
- 59. A. B. C. D.
- 60. Periodic Classification Magnetic Moment: μ =√n(n +2) B.M Measure of paramagnetic Nature n = 1 μ = 1.73 BM n = 2 μ = 2 BM n = 3 μ = 3 BM
- 61. JEE Main Mar 2021
- 62. Time Table Crash Course Monday to Saturday Nishant Sir Namrata Maam 2:00 - 4:00 PM Sakshi Maam Paaras Sir 4:30 - 6:30 PM Abhilash Sir Ajit Sir 7:00 - 9:00 PM Maths Chemistry Physics
- 66. Join with us in Telegram ● t.me/unacademyatoms TELEG R A MC H ANNEL C O MPLETEN O T E sA N DLEC T UREs ● livedaily.me/atoms
- 67. India’s BEST Educators Unacademy Subscription If you want to be the BEST “Learn” from the BEST
- 68. SAKSHI SAKSHI
- 69. Unlimite d Access Structured Courses Personal Guidance Get one on one guidance from top exam experts Test Analysis Get one on one guidance from top exam experts Study Material Specialised Notes & Practice Sets Study Planner Customized study plan with bi-weekly reviews Experts' Guidelines Study booster workshops by exam experts ICONIC Live Classes Weekly Tests PLUS
- 73. SAKSHI