Finance
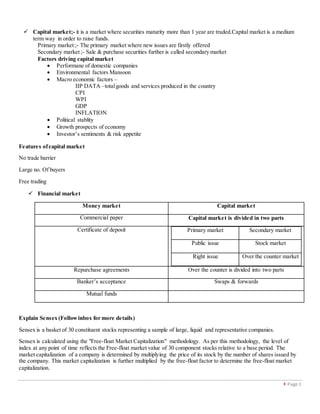
- 1. Page 1 Capital market;- it is a market where securities maturity more than 1 year are traded.Capital market is a medium term way in order to raise funds. Primary market ;- The primary market where new issues are firstly offered Secondary market ;- Sale & purchase securities further is called secondary market Factors driving capital market Performane of domestic companies Environmental factors Mansoon Macro economic factors – IIP DATA –totalgoods and services produced in the country CPI WPI GDP INFLATION Political stablity Growth prospects of economy Investor’s sentiments & risk appetite Features ofcapital market No trade barrier Large no. Of buyers Free trading Financial market Money market Capital market Commercial paper Capital market is divided in two parts Certificate of deposit Primary market Secondary market Public issue Stock market Right issue Over the counter market Repurchase agreements Over the counter is divided into two parts Banker’s acceptance Swaps & forwards Mutual funds Explain Sensex (Followinbox for more details) Sensex is a basket of 30 constituent stocks representing a sample of large, liquid and representative companies. Sensex is calculated using the "Free-float Market Capitalization" methodology. As per this methodology, the level of index at any point of time reflects the Free-float market value of 30 component stocks relative to a base period. The market capitalization of a company is determined by multiplying the price of its stock by the number of shares issued by the company. This market capitalization is further multiplied by the free-float factor to determine the free-float market capitalization.
- 2. Page 2 Understanding Free-float Methodology Free-float market capitalization is defined as that proportion of total shares issued by the company that are readily available for trading in the market. It generally excludes promoters' holding, government holding, strategic holding and other locked-in shares that will not come to the market for trading in the normal course Example Suppose the Index consists of only 2 stocks: Stock A and Stock B. Suppose company A has 1,000 shares in total, of which 200 are held by the promoters, so that only 800 shares are available for trading to the general public. These 800 shares are the so-called 'free-floating' shares. Similarly, company B has 2,000 shares in total, of which 1,000 are held by the promoters and the rest 1,000 are free- floating. Formula for calculating Sensex No. of shares *price of the stock*free float factors Market capitalization The total market value of a company‘s outstanding shares .Market capitalization is calculated by the following formula Total no. of outstanding shares * Market price per share Example = If there are 100 outstanding shares & each o/s share is worth of 350 Rs so the total capitalization would be 35000 Rs Risk of investing in equities Capital market It is the market where securities with a maturity of more than one year is traded Capital market six instruments are Equity shares Futures and options (Derivative instruments) Preference shares Debentures Bonds Swaps Forwards Features ofequity shares Claim on assets Claim on income
- 3. Page 3 Right to control Voting rights Limited liablity Introduction to futures A futures contract is an agreement between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a certain time in the future at a certain price. But unlike forward contracts,the futures contracts are standardized and exchange traded. To facilitate liquidity in the futures contracts,the exchange specifies certain standard features of the contract. It is a standardized contract with standard underlying instrument, a standard quantity and quality of the underlying instrument that can be delivered,(or which can be used for reference purposes in settlement) and a standard timing of such settlement. Futures in layman’s language ;- It is an agreement that say you lock the price at which you are willing to sell or buy the particular commodity orequity’sfutures at a particular day or before it. Example you buy a future of wheat ,you look a price of it at a future date suppose say 26 rs /per kg for100 kg & at the maturity the price of wheat may be 19 or 22 rs you have to buy it for rs 26 rs that is called futures. The buyer of the futures have to sell it on or before maturity date ,while sellerof a securtity has to buy it back. The standardized items in a futures contract are: � Quantity of the underlying � Quality of the underlying The date and the month of delivery � The units of price quotation and minimum price change � Location of settlement Options ;- options are contracts that grant the right, but not the obligation to buy or sell an underlying asset at a set price on or before a certain date.For options there is a premium has to be paid. The premiums are the price of buying the security or the derivative. Call option ;- Call holders & put holders are not obligated to buy or sell respectively.they have a choice to exercise their right if they choose.this limits the risk of buyers of options, so that the most they can ever lose is the premium of their options. Put option ;-- Call writers &put writers (seller) however are obligated to buy or sell.This means that a seller may be required to make good on a promise to buy or sell.It also implies that option sellers have unlimited risk,meaning they can lose much more than the price of the options premium. At the money ;- for call option & put option=> cost Strike price = Excersize Call option 8600=8600 Put option 8600=8600 cost to cost excluding transaction In the money ;- when it is advisible or profitable to excersise the contract ,for call option Strike price > Excersize price 8600 :8650 For Put option 8700:8600 Out of the money ;- when it is not advisible or profitable to excercise the contract ,for call option Strike price <Excersize 8600 :8550,
- 4. Page 4 For Put option 8800:8700 Difference between call option & put option Call option Put option It gives the right to buy but not obligation to buy the option contracts It gives right to sell but not obligation to sell the contract Limited risk(premium will be lost) Unlimited risk (more then premium can be lost) Value of an option will increase as the prices of the underlying increases. Value of an option decreases as the underlying security prices increases. Factors affecting option prices/Characterstics ofOption’s prices Stock price Excercize price Time to expiry Volatility in the stock price Risk free interest rate Dividends if any expected during life of an option HEDGE FUNDS A hedge fund uses a wide range of investment techniques & invest in a wide array of assets to generate higher returns for a given level of risk than what’s expected of normal investments , In many cases Hedge funds are managed to generate a consistent level of return regardless of what market does A hedge fund has ways to reduce the risk without cutting into investment income, Hedge funds Why you want to go for hedge fund( You don’t like to confined by stricter rules that MF have to follow & would appreciate the ability to look for short positions & or use derivatives Difference between Hedge funds & Mutual funds Hedge funds Mutual funds Managers have more freedom in their use of investment tools Managers must adhere to the strategy described There is no limit on fees charged a hedge fund can charge its investors Mfs fees & expenses are disclosed are disclosed in detail Hedge funds unlike mfs are not required to register with SEC MF has to be registered under SEC They can run highly concentrated portfolio The objective is to protect investors investment & hence diversification is the key principal Fee charged is 2% Of AUM & 20 % OF PROFIT Annual expenses vary from 2.25 % to 2.5 % Difference between futures & Forwards Futures Forwards They are highly standardized They are privately negotiated Futures are traded on an exchange They are traded in over the counter market Futures contracts have clearing houses which guarantee the transactions Because forwards contracts are private agreements, there is always a chance that a party may default They are settled daily which means that daily changes are settled day, until the end of the contract Forwards contracts are settled at the end of the contract
- 5. Page 5 Say up front that I want to learn more about financial market related things asyou can see most of the things are related to investment only When asked about technical analysis,Tell themabout hammer,support & resistance How do you predict the stock short term Will check forthe sectors in which it is trading ( Any good or bad news about the sector) put to call ratio Mid term Its fundamentalslike Cipla ( A company which is there more into indian markets will not be affected based on other countries policies) Charts;- It’s chartssupport & resistance, Long term P E Ratio Products it is dealing in Earnings per share Profit margins PEG Ratio ROCE Other ways Company name & its introduction Sector- Sector ,commodities prices in the market Fundamental rationale Technical view(for mid termforcasting)3 months Key risks (Commodities prices in the market) Other ways Peer comparision, News about the stocks Any dividend history,splits etc as it affectsits share prices Fundamentals-> which include Dividends,Splits,Results,Pe Ratio,Roce,Debt-To- Equity Ratio,EPS,CAGR,Shareholding Pattern,Acquisition,Mergers,Takeovers Etc,Net Profits
- 6. Page 6 Technical view->Historical performantceby charts,volume in last three months,average trading price 200 days moving average,.CMP,Market capitalization What is intrinsic value? The intrinsic value of a company or an asset based on an underlying perception of its true value including all the aspects of business in terms of business in terms of both tangible & intangible factors.Additionally ,Intrinsic value is primarily used in options pricing to indicate the amount an option is in the money. Intrinsic value ofan option The intrinsic value for call option is the difference between the underlying stock price & strike price.conversely the intrinsic value for put option is the difference between the strike price & the underlying stock price Example ;- If a call option’s strike price is 15 $ & underlying stock’s market price is at 25 $ then the intrinsic value of the option is 10 $. Extrinsic value Extrinsic value measures the difference between market price of an option & its intrinsic value Example ;- 8600 strike price – intrinsic value 50 What is time value The portion of an option’s premium that is attributable to the amount of time remaining untill the expiration of the option contract. Any premium that is in excess of the options intrinsic value is referred as time value For equities time value is calculated thru theta Fixed income security A fixed income security ,commonly reffered to as a bond or money market security,is a loan made by an investor to a government or corporate borrower,or issuer,promises to pay a set amount of interest called the coupon ,on a predetermined basis untill a set date ,the issuer returns the principal amount also called the face value or par value to the investor on the maturity date The most common fixed income securities are treasury bonds Treasury bonds Corporate bonds Certificate of deposits Preferred stocks Certificate ofdeposit The CD is a document of title similar to a fixed deposit receipt issued by banks there is no prescribed interest rate on such CDs it is based on the prevailing market conditions. Certificate of deposit is a saving certificte with a fixed maturity date ,specified fixed interest rate & can be iissued in denomination aside from minimum investment requirements.A CDS restricts access to the funds untill the maturity date of the investment.
- 7. Page 7 Preferred stock;- Preferred stock derives its name from the fact that it has certain preferences over the junior common stock—preferred stock is paid cash dividends before any can be distributed to the common stockholders , and in the event of liqidating the business,preferred stock is redeemed before any money is returned to the common stockholders but after the bondholders, It is a Hybrid security because it has features of ordinary shares & debentures It has following features Fixed dividends ;- Preference shares are also called fixed income security because it provides constant income to investors Participation features;-In some cases they have participation features Convertibility – they can be converted into common shares. Priority;- They have priority over bondholders Voting rights ;- It does not have any voting rights Difference between Preference shares & Equity shares PREFERNCE SHARE Equity shares Preference shares are paid dividend before the equity shareholders Equity shareholders are paid dividend after the dividend paid to the pref shareholders Rate of dividend is fixed Rate of dividend is decided be board of directors Preference shares can be converted into equity shares Equity share can’t be converted Preference shares don’t have right to participate in mgt of company Equity shares have this right At the time of winding up of the company pref. shareholders are paid first On winding up equity share capital is repaid after pref share capital is paid up Bond A bond is a debt instrument in which an investor gives money to an entity (Typically corporate or government ) which borrows the funds for a defined period of time at availiable or fixed rate of interest rate.onds are used by companies ,muncipalities,states,governments to raise money & finance a variety of projects & activities. Owners of bonds are debt holders or creditors of the issuer bonds are commonly referred to as fixed income securities Howdoes bond work The issuer issues a bond that contractually states that the interest rates that will be paid & the time at which the loan principle amount will be repaid or paid back Why Bonds ussually come at par value at the end ofmaturity ? If interest rates drop to 4 % ,the bond will continue paying out 5 % ,Making it more attractive option.On the other hand,If interest rates rises upto 6 % ,the coupon rate 5 % is no longer attractive the bond prices will decrease ,selling at a discount will make profit for him untill its effective rate is 6 %. Because of this mechnism ,bonds prices will move inversely with interest rates. Characterstics ofa bond Coupon rate Fixed or floating rate of interest is paid for bonds which will be predefined Face value;- It is the money amount the fund will be worth at its maturity Coupon date;- It is the date the bond holder will makr interest payments Maturity date ;- It is the date on which bond will mature
- 8. Page 8 Types ofbonds Corporate Bonds A company can issue bonds just as it can issue stock Large corporations have a lot of flexibility as to how much debt they can issue: the limit is whatever the market will bear Generally, a short-term corporate bond has a maturity of less than five years,intermediate is five to years and long term is more than years Corporate bonds are characterized by higher yields because there is a higher risk of a company defaulting than a government The upside is that they can also be the most rewarding fixed-income investments because of the risk the investor must take on The company's credit quality is very important: the higher the quality, the lower the interest rate the investor receives Variations on corporate bonds include convertible bonds, which the holder can convert into stock, and callable bonds, which allow the company to redeem an issue prior to maturity Zero coupon bonds Zero coupon bonds are the bonds issued at a discount and there is no interest rate for the given bond. They are bought or issued a lower price than its face value. And at the maturity date it will be repaid in full amounts (zeros) pay no regular interest They are issued at a substantial discount to par value, so that the interest is effectively rolled up to maturity (and usually taxed as such) The bondholder receives the full principal amount on the redemption date Convertible Bonds A convertible bond or convertible note or convertible debt is a type of bond that the holder can convert into specific no. of shares. A convertible bond may be redeemed for a predetermined amount of the company's equity at certain times during its life, usually at the discretion of the bondholder Convertibles are sometimes called "CVs" Issuing convertible bonds is one way for a company to minimize negative investor interpretation of its corporate actions For example, if an already public company chooses to issue stock, the market usually interprets this as a sign that the company's share price is somewhat overvalued To avoid this negative impression, the company may choose to issue convertible bonds, which bondholders will likely convert to equity should the company continue to do well From the investor's perspective, a convertible bond has a value-added component built into it: it is essentially a bond with a stock option hidden inside Thus, it tends to offer a lower rate of return in exchange for the value of the option to trade the bond into stock Callable Bonds Callable bonds, also known as "redeemable bonds," can be redeemed by the issuer prior to maturity Usually a premium is paid to the bond owner when the bond is called The main cause of a call is a decline in interest rates If interest rates have declined since a company first issued the bonds, it will likely want to refinance this debt at a lower rate In this case,the company will call its current bonds and reissue new, lower-interest bonds to save money Inflation linked bonds ( these are the bonds where the principal is indexed to inlation,they are thus designed to cut out the inflation risk of an investment) Term Bonds Term bonds are bonds from the same issue that share the same maturity dates Term bonds that have a call feature can be redeemed at an earlier date than the other issued bonds A call feature,or call provision, is an agreement that bond issuers make with buyers This agreement is called an "indenture," which is the schedule and the price of redemptions, plus the maturity dates Some corporate and municipal bonds are examples of term bonds that have -year call features This means the issuer of the bond can redeem it at a predetermined price at specific times before the bond matures A term bond is the opposite of a serial bond, which has various maturity schedules at regular intervals until the issue is retired
- 9. Page 9 Amortized Bonds An amortized bond is a financial certificate that has been reduced in value for records on accounting statements An amortized bond is treated as an asset,with the discount amount being amortized to interest expense over the life of the bond If a bond is issued at a discount - that is, offered for sale below its par (face value) - the discount must either be treated as an expense or amortized as an asset As we discussed in Section , amortization is an accounting method that gradually and systematically reduces the cost value of a limited life, intangible asset Treating a bond as an amortized asset is an accounting method in the handling of bonds Amortizing allows bond issuers to treat the bond discount as an asset until the bond's maturity (To learn more about bond premium amortization, Premium Bonds: Problems And Opportunities) Adjustment Bonds Issued by a corporation during a restructuring phase, an adjustment bond is given to the bondholders of an outstanding bond issue prior to the restructuring The debt obligation is consolidated and transferred from the outstanding bond issue to the adjustment bond This process is effectively a recapitalization of the company's outstanding debt obligations, which is accomplished by adjusting the terms (such as interest rates and lengths to maturity) to increase the likelihood that the company will be able to meet its obligations If a company is near bankruptcy and requires protection from creditors (Chapter ), it is likely unable to make payments on its debt obligations If this is the case,the company will be liquidated, and the company's value will be spread among its creditors However,creditors will generally only receive a fraction of their original loans to the company Creditors and the company will work together to recapitalize debt obligations so that the company is able to meet its obligations and continue operations, thus increasing the value that creditors will receive Junk Bonds A junk bond, also known as a "high-yield bond" or "speculative bond," is a bond rated "BB" or lower because of its high default risk Junk bonds typically offer interest rates three to four percentage points higher than safer government issues Junk bonds are fixed income instruments that carry a credit rating of BB or lower by standard & poor or Ba or below by Moody’s investor’s service Angel Bonds Angel bonds are investment-grade bonds that pay a lower interest rate because of the issuing company's high credit rating Angel bonds are the opposite of fallen angels, which are bonds that have been given a "junk" rating and are therefore much more risky An investment-grade bond is rated at minimum "BBB" by S&P and Fitch, and "Baa" by Moody's If the company's ability to pay back the bond's principal is reduced,the bond rating may fall below investment-grade minimums and become a fallen angel Floating rate notes Floating rate bonds are the bonds which have a comparable ratio with the money market ref. rate & they are also termed as variable coupon. Such as Libor,Mibor (FRNs,floaters) have a variable coupon that is linked to a reference rate of interest,such as LIBOR or Euribor For example the coupon may be defined as three month USD LIBOR + % The coupon rate is recalculated periodically, typically every one or three months. High-yield bonds (junk bonds) are bonds that are rated below investment grade by the credit rating agencies As these bonds are more risky than investment grade bonds, investors expect to earn a higher yield Convertible bonds let a bondholder exchange a bond to a number of shares of the issuer's common stock These are known as hybrid securities, because they combine equity and debt features Inflation-indexed bonds Inflation linked bonds are the bonds where the prisipal is intexed to inflation.They are thus designed to cut out the inflation risk of an investment In inflation indexed bonds the principal amount and the interest payments are indexed to inflation The interest rate is normally lower than for fixed rate bonds with a comparable maturity
- 10. Page 10 (this position briefly reversed itself for short-term UK bonds in December ) However,as the principal amount grows, the payments increase with inflation Value of a bond = (i1/1+ I ) +(i2/1+i) +(1n/1+i)+ (P/1 +i)^n 70/1.07 + 65.42/1.07+61.14/1.07+ (1000/1.07)^3 65.1+61.1+58+816.6 So the value become 1001 rs it is almost at par value or no profit or no loss so it is not advisable to take such a project which is at par or at break even i denotes interestin number , n = number of years,P = principal, I = interest in % Perpetualbonds are also often called perpetuities or 'Perps' They have no maturity date The most famous of these are the UK Consols, which are also known as Treasury Annuities or Undated Treasuries Some of these were issued back in and still trade today, although the amounts are now insignificant Some ultra-long-term bonds (sometimes a bond can last centuries: West Shore Railroad issued a bond which matures in (ie th century) are virtually perpetuities from a financial point of view, with the current value of principal near zero Bearer bond –It is an official certificate issued without a named holder In other words, the person who has the paper certificate can claim the value of the bond Often they are registered by a number to prevent counterfeiting, but may be traded like cash Bearer bonds are very risky because they can be lost or stolen Especially after federalincome tax began in the United States, bearer bonds were seen as an opportunity to conceal income or assets.The issuing company neither registers the owner of the stock nor tracks transfers of ownership. The company disburse dividends to bearer shares when a physical coupon is presented to the firm. Registered bond – It is a bond whose ownership (and any subsequent purchaser) is recorded by the issuer, or by a transfer agent It is the alternative to a Bearer bond Interest payments, and the principal upon maturity, are sent to the registered owner A government bond, also called Treasury bond, is issued by a national government and is not exposed to default risk It is characterized as the safest bond, with the lowest interest rate A treasury bond is backed by the “full faith and credit” of the relevant government For that reason, for the major OECD countries this type of bond is often referred to as risk-free Municipal bond is a bond issued by a state,city, local government, or their agencies Interest income received by holders of municipal bonds is often exempt from the federal income tax and from the income tax of the state in which they are issued, although municipal bonds issued for certain purposes may not be tax exempt War bond is a bond issued by a country to fund a war Serial bond is a bond that matures in instalments over a period of time In effect,a $,, -year serial bond would mature in a $, annuity over a -year interval Revenue bond is a special type of municipal bond distinguished by its guarantee of repayment solely from revenues generated by a specified revenue-generating entity associated with the purpose of the bonds Revenue bonds are typically "non-recourse", meaning that in the event of default, the bond holder has no recourse to other governmental assets or revenues Climate bond is a bond issued by a government or corporate entity in order to raise finance for climate change mitigation- or adaptation-related projects or programmes Subordinated bonds are those that have a lower priority than other bonds of the issuer in case of liquidation In case of bankruptcy, there is a hierarchy of creditors First the liquidator is paid, then government taxes,etc The first bond holders in line to be paid are those holding what is called senior bonds After they have been paid, the subordinated bond holders
- 11. Page 11 are paid As a result, the risk is higher Therefore, subordinated bonds usually have a lower credit rating than senior bonds The main examples of subordinated bonds can be found in bonds issued by banks, and asset-backed securities The latter are often issued in tranches The senior tranches get paid back first, the subordinated tranches later Covered bonds are backed by cash flows from mortgages or public sector assets Contrary to asset-backed securities the assets for such bonds remain on the issuers balance sheet Exchangeable bonds allows for exchange to shares of a corporation other than the issuer Asset-backed securities are bonds whose interest and principal payments are backed by underlying cash flows from other assets Examples of asset-backed securities are mortgage-backed securities (MBS's), collateralized mortgage obligations (CMOs) and collateralized debt obligations (CDOs) Which of the following statements is true regarding an investment in mortgage-backed securities? a There is little default risk b The stated maturity is generally years c They receive a fixed payment per month d All of the above are true Stocks Bonds They have equity stake in the company They have a creditor stake in the company Being creditor of the company they have a creditor stake in the company & paid before stock holders of the company They are paid after bond holders Bond have definite term or maturity They are typically outstanding indefinitely The shareholder/Stake holders have voting rights They do not carry voting rights In case of insolvency or liquidations the equity shareholders will be paid after bondholders At the liquidation they will be paid before shareholders Difference between mutual funds & Shares Mutual funds Shares They are not much volatile They are volatile Mfs are known to deliver good returns,So you can expect handsome returns from mutual funds but not unbelievable like stock returns Those requires analysis ,Patience& belieif in what you have picked Monitoring in MFS is relatively low because the job of monitoring is done by fund manager who is paid to filter through fluctuations Investing in shares is a personal affairs,even in case of long term investment you might have to keep an eye on every quarter or yearly results Mfs are known for the SIP SIP does not work that good in case of shares Types of debentures On the basis of Security Secured Debentures Unsecured Debentures
- 12. Page 12 On the basis of Convertibility Convertible Debentures Nonconvertible Debentures On the basis of Negotiability Registered Debentures Bearer Debentures On the basis of Permanence Redeemable Debentures Irredeemable Debentures Key Differences between Bonds and Debentures The following are the major differences between bonds and debentures: 1. A financial instrument issued by the government agencies, for raising capital is known as Bonds A financial instrument issued by the companies whether it is public or private for raising capital is known as Debentures 2. Bonds are backed by assets Conversely, the Debentures may or may not be backed by assets 3. The interest rate on debentures is higher as compared to bonds 4. The holder of bonds is known as bondholder whereas the holder of debentures is known debenture holder 5. The payment of interest on debentures is done periodically whether the company has made profit or not while accrued interest can paid on the bonds 6. The risk factor in bonds is low which is just opposite in case of debentures 7. Bondholders are paid in priority over debenture holders at the time of liquidation Risks in investing in shares;- Diversification;- If you invest in single or two stocks then if any bad news comes in about the same stock it may result in a great loss & in case of mutual funds risk is diversified & portfolio is also diversified so less risk is there. Awareness;-People are not aware about stocks or equity shares when people are not aware that means they will invest in some illiquid stocks which may result in losses greatly & people get stuck for the stocks for years. 1. Difference between bonds & stocks Indentures— An indenture is a formal debt agreement that establishes the terms of a bond issue, Covenants --while covenants are the clauses of such an agreement Covenants specify the rights of bondholders and the duties of issuers, such as actions that the issuer is obligated to perform or is prohibited from Difference between OTC & Exchange traded instruments Over the counter ;For OTC derivatives the contract between the two parties are privately negotiated & traded between the two parties directly,therefore the contract can be trailor maidto the parties likings Disadvantages
- 13. Page 13 The value of your derivatives is as gooods as the creditworthiness of your counter party If your counterparty goes bust ,your derivatives becomes worthless It is very hard to pass the derivatives to a third party because the contract is already signed between the two original arties Exchange traded insturments ;- For ETI derivatives,the situation is different,they are traded via an intermediatary the exchange,which Is a strong institution with deep pockets For example if Tom sells an ET Derivative to Dick,the exchangeacts as a buyer to the buyer or Tom,& A Seller to Dick The advantage of such an agreement is They are standardized contracts There is no counter party risksbetween market participants for example if Tom has no need to fear IF Dick defaults on the contract ,it is exchange that has to bear the consequences Roles ofcustodian ;- Maintaining books of accounts on behalf of clients Safegaurding financial assets Call money – Money lent for 1 day is called call money Notice money ;- Money lent for more than 1 day but lessthan 15 days is called notice money Term money ;- Money lent for more than 14 days is called term money T bills or treasury bills are sold by the governments A short tem credit instrument guaranteed by a bank is called as banker’s acceptance market The distribution of firms’ capital between debt & equity is its ;-Capital structure Governments never issue shares because it does not want to sell its ownership claims The _____ value of a bond that the issuer must pay at maturity .Ans ;- Face value Investments avenues & there average returns per year Equity MF –> 12 TO 20 % Balanced funds - > 8% -15 % EPF & PPF ;- 8.70 Bonds- 7-9 % Foreign overseas mf- 8-15 % Valuation of investment avenues Calculation of fair value ,stock/shares/other investment avenues PE ratio comparision ( It should be compared with company with similar characterstics & can be compared with industry pe ratio)
- 14. Page 14 MUTUAL FUNDS A mutual fund is a pool of investment is a pool of saving of a number of investors who share a common financial goal, the money thus collected & invested in equities, debentures, & other securities Regulation All mutual funds need to be registered under SEBI So its surveillance is under SEBI’S directives A mutual fund is an investment vehicle made up of a pool of funds collected from many investors for the purpose of investing in securities such as stocks, bonds, money market instruments and similar assets. Mutual funds are operated by money managers,who invest the fund's capital and attempt to produce capital gains and income for the fund's investors. A mutual fund's portfolio is structured and maintained to match the investment objectives stated in its prospectus. Mutual funds are considered by many to be a "set it and forget it" investment (the official term would be a buy-and-hold investment). That's because a mutual fund involves the safety-in-numbers factor. They include not one security, but many, so they tend to be less volatile than many individual stocks. Related question Objectives of mutual funds study To check mutual funds schemes available in the market To compare various mf vs shares To know awareness about the mfs To assess perception of investors towards mutual funds What is NAV? NAV= Assets ofthe bonds – Liabilities ofthe bonds /No ofunits outstanding How do you calculate NAV Calculating the Net Asset Value ofa Fund Net asset value (NAV)is significant only for open-end mutual funds. It is a simple calculation - just take the current market value of the fund's net assets (securities held by the fund minus any liabilities) and divide by the number of shares outstanding. Thus, if a fund has total net assets of $50 million and there are one million shares of the fund, then the NAV is $50 per share. (Fund liabilities include items such as fees owed to investment managers.) For closed-end funds, share value is determined in the secondary markets (the formal exchanges) where the shares are traded. The NAV of a closed-end fund is the price per share multiplied by the total number of shares. Obviously, the value of a closed-end mutual fund changes continuously throughout the trading day. It is the value of Mutual fund at which a mf unit can be bought or sold Concepts ofMutual Funds Step 1 -Many investors with common financial objectives pool their money Step 2- Investors, on a proportionate basis allot the units for the sum contributed to the pool Step 3- The money collected from investors is invested in shares,debentures,& other securities Step 4- The fund manager realizes gains or losses & collects dividends or interests Schemes examined Axis equity fund Axis mid cap fund(Dividends) Axis mid cap fund(growth) Axis gold etf
- 15. Page 15 Axis focused 25(g) funds L&t gilt fund Types of mutual funds available now days On OCT 6th SEBI has announced new guidelines categorizing MF can be divided in 5 ways Equity funds ;- These funds invests in stocks.These funds aim to grow faster than money market or fixed income funds,so there is usually a higher risk that you could lose money. You can choose from different types of equity funds including those that specialize in growth stocks ( which usually don’t pay dividends),income funds (which includes the companies that pay large dividends),value stocks ,large cap stocks,mid cap stocks,small cap stocks or combination of these. Debt funds (Fixed income funds or bonds or Gilt funds ) ;- These funds buys investments that pay a fixed rate of return like government bonds,investment grade ,corporate bonds,high yield corporate bonds.They aim to have money coming into the fund on a regular basis,mostly through interest that the fund earns.High yield bond corporate bond funds are generally riskier than funds that hold government & investment grade bonds. Hybrid funds (Balanced funds);- These funds invest in a mixture of equities & fixed income securities.they try to balance the aim of achiving higher returns against the risk of losing money.Most of these funds follow a formula to split money among the different types of investments.They tend to have more risk than fixed income funds ,but less risk than pure equity funds.Aggressive funds hold more equities & fewer bonds while conservative funds hold fewer equities relative to bonds. Solution oriented fund ;- As the name suggests these are trailor made funds or according to the choice investor has made. Others ;- Others could be Money market funds Index funds Investors Fund manager Securities Returns
- 16. Page 16 Fund of funds Speciality funds Mfs according to investment objective funds Findings Investors are mainly concerned about risk factors of mfs There are various mfs schemes available about which common man is not aware of Formulas & concepts Classification of ratios Profitability ratio Liquidity ratios Solvency ratios Profitabilty ratio Gross profit ratio: it indicates the efficiency of the production/trading operations ( Gross profit =Net income –COGS) Gross profit -------------------X 00 Net income Net profit ratio: it indicates net margin on sales net profit /net income (Net profit = operating expenses- tax –interest -& all the other expenses ) Net profit --------------- X 00 Net income Return on share holders’ funds: it indicates measures earning power of equity capital Profits available for Equity shareholders -----------------------------------------------X 00 Average Equity Shareholders Funds Return on investment (Return on capital employed ROCE ) = Profit before interest & tax & Dividend / Capital employed Why net profit is recorded in liablity account
- 17. Page 17 Ans ;- Because it is a amount left which need to be distributed to the shareholder (In form of dividends or any other way such as bonus) Therefore business’s liablities remains the same & shareholder’s equity in the business will increase. The profit or net income belong to the owner of sole proprietorship or to the stockholders of a corporation,The owner’s or stockholder’s equity is reported on liablity side (with retained earnings) of the balancesheet Operating profit ratio =Operating profit /net income( Operating profit – (operating expenses )R & D expenses –dep- amortisation) Earning per Equity share (EPS): it shows the amount of earnings attributable to each equity share Profits available for Equity shareholders ---------------------------------------------- Number of Equity shares Dividend yield ratio: it shows the rate of return to shareholders in the form of dividends based in the market price of the share,A financial ratio that indicates how much a company pays out in dividends how much a company pays out in dividends each year relative to its share price Annual Dividend per share ---------------------------- X 00 Market price per share Price earnings ratio: it a measure for determining the value of a share May also be used to measure the rate of return expected by investors It is the ratio for valuing a company that measures its current share price relative to its per share earnings OR it is the ratio indicating how much an investor is willing to pay based on its current earnings FuLL CONCEPT;- The price earning ratio indicates the dollar /rupee amount an investor can expect to invest in a company in order to receive one dollar of that company’s earnings.This is why the pe ratio is called earnings multiple because it shows how much an investor is willing to pay based on per dollar of earning Example ;-If a company were trading currently trading at a multiple of 20(pe ratio =20 ) The interpretation is an investor is willing to pay 20 dollar for 1 dollarof earning Market price of share (MPS) ------------------------------------ X 00 Earnings per share (EPS) How pe ratio can misled How does PE Ratio of a firm will change after stock split There is no effect on a stock’s pe ratio when it splits Earning per share trailing twelve months =45.15
- 18. Page 18 Price /earnings ratio = Stock price/EPS= 650/45.15 14.4 Post split 650/7 = 92.86 Earning per share = Stock price /EPS 92.86/6.45 14.4 Conclusion math tell us P/E ratio pre /post Split Liquidity or solvency ratio Solvency liquidity ratio are both termed to an enterprise’s state of financial health but some notebale differences.Solvency refers to an enterprise’s capacity to meet its long term financial commitments. Liquidity refers to enterprise’s ability to pay short term obligations. What would happen if liquidity ratio is less then 1 Ans ;- A ratio under 1 indicates that a company’s liablities are greater than its assets & suggests that the company would be unable to pay off its obligations if they come due at that point. A current ratio below 1 is ussually is not a good sign. Current ratio: it measures short-term debt paying ability Current Assets ------------------------ Current Liabilities Quick Ratio: The ratio termed as ‘liquidity ratio’ The ratio is ascertained y comparing the liquid assets to current liabilities. The quick ratio measures a company’s ability to meet its short term obligations with its most liquid assets & therefore excludes inventory from its current assets.it is also known as acid test ratio. Liquid Assets(current assets – inventories) ------------------------ Current Liabilities Cash & cash equivalents + marketable securities + account receivables ------------------------ Current liablities Solvency ratio Debt-Equity Ratio: it indicates the percentage of funds being financed through borrowings; a measure of the extent of trading on equity The ratio indicates the degree of financial leverage being used by the business & includes both short term & long term debt.
- 19. Page 19 A rising debt to equity ratios implies higher interest rate expenses & beyond a certain point ,it may attract company’s credit rating making it more expensive to raise debt Total Long-term Debt --------------------------- Shareholders’ funds Debt to assets Total debts/total assets This ratio quantifies the percentages of a company’s assets that have been financed with debt( short term & long term) Interest coverage ratio Operating income (EBIT) ------------------------ Interest expense This ratio measures companies’ ability to meet the the interest expense on its debt with its operating income,which is equivalent to its earning before interest & taxes Put call ratio The put call ratio is an indicator ratio that provides information about trading volume of put option to call option. Technical trades use the put –call ratio as an indicator of performance & as a barometer of overall market sentiment. Interpretation-> One way to interpret the put call ratio is to say that 1. If the ratio is higher than 1 it suggests that the ratio is higher than 1 ,It suggests that traders are buying more put then calls in option segment. 2. Another way of interpretation is higher rartio means it time to sell & a lower ratio means it is time to buy. The higher the ratio the better the company’s ability to cover interest expense IPO PROCESS A brief note on the promoters * management Company profile Copy of annual report for three years Copy of draft offer documents Memorundum & article of association Hedgers;- An investor who is aiming to reduce the level of risk is ussually called hedger Speculator ;-Usually try to protect price movements & enter into respective postions in order to maximise their gains ,we can say that the speculators are risk takersi Arbitrageurs ;- They usually participate in an excessively rapid environmentmwith the decisions taken in the blink of an eye sometimes the price of the commodity may be below or exceed its price in the derivatives market Arbitrageaurs usually took to dispose of such imperfactions & ineffecianciesin the marketthey also play key role in increasing market liquidity Who is a scalper? Scalper represents another type of trader who play a crucial role in the economic functioning of the equities and futures market They are the individuals who engage in continuous buying and selling of securities on their own behalf they work on low marginsbut their continuous trading makes good profits on their investment
- 20. Page 20 Repurchase agreement- A purchase agreement or Repo for short is a type of short term loan much used in money markets where by the seller of the security agrees to buy it back at specified price & time The seller pays an interest called repo rate while buying back the securities Strong rupee will benefit which of the country(AMBA RESEARCH,ONGC,INFOSYS,Answer the ONGC as hey are the importers & has to pay less money for purchasing Raw material Among those which one is developing nation (Singapore,Japan,china,US,Ans China) American option;- It is followed in INDIA ,In this option one can excersize the contract anytime before the expiry of the contract European option;- It can be exercized only at maturity,its theoritical price of option is calculated by BLACK SCHOLE MODEL Relationship between futures & spot prices /Spot-futures parity formula The price difference between spot & future price is called or leads to spot –futures parity. The spot future parity arises due to variable such as interest rate,dividends,time to expiry etc. In a very loose sense it is simply is a mathamatical expression to equate the underlying price & its its corresponding futures price.this is also known as futures price formula Futures price ;- Formula ;- Spot price * 1+ rf (x/365) –d Spot price = price trading in equity market Rf = risk free rate ( It can be taken as a proxy as 91 day’s trasury bill for short term liquidity) X= no. of days to expiry D= dividend in most of the time while calculating values it is taken as 0 & it is expected company did not expect any dividend during the period of calculation say for example 7 days to expiry so the company is not giving any dividends in next 7 days so its value is kept as 0 Fair value or intrinsic value = the value derived from the predetermined formula Futures price = 2299 ( 7 days to expiry) Far month calculations No. of days to expiry = 80 days = 2280.5* ( 1 + 8.3528 % *(80/365) =2322 So we can say that the value is at fair future value is at premium or at over valued So it can be inferred as sell in the futures market Other round we can when fair price is lower then spot futures then it is said to be at discount * When futures prices are higher than spot price it is called as contango. Calander spread= In a calander spreads , we attempt to extract & profit from the spread created between two futures contracts of the same underlying but different expiries. In common paralance Premium = contango Discount =backwardization Characterstics offutures /factors affecting futures Organized exchanges ;- Unlike forwards contracts which are traded in an over the counter market,futures are traded on organized exchanges. Standardization ;- In case of forwards currency contracts ,the amount of commodity to be delivered & the maturity date are negotiated between the buyer & seller & can be tailor made to buyer’s requirements, Where as in the futures contract both these are standardized by the exchange on which contract is traded. Clearing house;- The exchange acts as a clearing house to all the contracts stuck on the trading floor Margins ;- The exchange requires that the margins must be deposited with the clearing house by a member who enters into a futures contract Actual delivery is rare ;- In futures contracts actual delivery takes place rarely. CAPM or Capital assetpricing model Method of defining expected market return of the security is known as CAPM
- 21. Page 21 If the expected rate of return is more then minimum standards the project or inestment is selected otherwise rejected Formula Expected return = Rf +B(Rm-Rf) Rf= risk free rate B=Beta of the portfolio Rm=risk of market or Market return Participants in secondary market Brokers / members of stock exchange Portfolio manager Investment advisors Share transfer agent Depository participants Types ofrisk Systematic risk (Inflation risk,interest rate risk,market risk,foreign exchange risk,Political risk) Unsystematic risk (Controllable risk,business risk,financial risk/credit risk,oprerational risk) Spot price ;- The price at which security can be bought & sold Floating rate bonds ;- Typicaly the rates are based on either federal funds rate or libor plus n an added amount say LIBOR + % For example ;- A rate is quoted as Libor + 5 % suppose LIBOR stands at % the new rate would be 5 % Difference between floating rate bonds & Fixed rate bonds The main difference is that the coupon rates are fixed in fixed rate bondswhile in floating rates bond it would be based on Either LIBOUR/MIBOR SAY if Government of india isues bonds paying 9% coupon or interest during entire tenure of bond it is called fixed rate against that inflation indexed bond is a floated rate bond where RBI pays X % ,say % over CPI & WPI to the bond holder So this CPI or WPI figures would be different every year in most cases & hence coupon payment also varies Distinguish between Financial accounting & managerial accounting Owner’s capital ;- the capital given by a shareholders in a business firm/ company is known as owner’s capital Long term liablities ;- Any liablities which is kept for a longer period of time is known as long term liablities Liablities not due within the next months such as loans & debentures are called long term liablitiesthey are also known as long term debtor Non-current liablities Current liablities;- which are due or repaid are called current liablities Contigent liablities ;- A contigent liablity that may arise /occur depending on the outcome of an uncertain event, It is recorded in accounting records if the contigent is probale & the amount of the liablity can be reasonably estimated Examples are The outcome of a law suit Contigent asset A contigent is a possible asset that may arise because of gain that is contigent on future event that are not in entity’s control Retained earnings;-Retained earnings represents the corporation’s cumulative earnings that have not been distributed to its stockholders, Retained earnings refers to the percentages of net earnings not paid out as dividends,but retained by the company to be reinvested in its core business or to pay debt Amount of retained earnings of a balancesheet is reported as separate line item in the stockholder’s equity section of a balancesheet What is the purpose of the cash flow statement The purpose of cash flow statement is to provide information about company’s gross receipt & gross payments for a specified period of time Capital expenditure ;- any expenditure which is incurred in aquiring or increasing the value of a fixed asset is termed as capital expenditure ,such as ,the amount spent on the purchase or errection of building,Plant,furniture etc
- 22. Page 22 Revenue expenditure ;- Any expenditure the full benefit of which is received during one accounting period is termed as revenue expenditure SWAP Swaps are financial instruments /agreements to exchange cash flows,swaps can be based on interest rates ,foreign currencies etc. A swap is a derivative contract through which two parties exchange financial instruments.these instruments can be almost anything ,but most swaps involve cash flows based on a notional principal amount that both parties agree to. Interest rate swap Currency swap Credit default swap Plain vanilla swap Credit default swap ;- A credit default swap is a particular swap designed to transfer the credit exposure of fixed income products between two or more parties Example ;- Aditya has 00 rs ,B wants 00 rs as a loan where B has been Rated BB rating which is not a good rating so the party Azhar has come to the picture who has been given AA rating So Azhar gives the assurance tha money will be paid according to terms on the maturity surely Because Azhar has AA rating Party Aditya has given the loan to Party B Aditya is getting 0 % interest over the loan ,In which % is given to Azhar for thee assurance given about the loan so 9 % interest is earned by Aditya & % is by Azhar The whole concept is known as Credit default swap Plain vanilla swap ;-In this SWAP party agrees to pay floating rate of interest & party b agrees to pay fixed rate of interest as they have mentioned in the agreement Format of trading account & profit and loss account Format of balance sheet Format of trial balance Format of income statement What items are considered liquid assets A liquid asset is cash on hand or an asset that can be readily converted tocashor is similar to cash itselfbecause the asset can be sold with little or no impact on its value. Liquid assets are the assets which can be converted into cash within a year Investments are considered liquid assets because they can be readily liquidated for example shares of stock,bonds,money market funds & mutual funds are considered liquid asset. What are the items which may be considered as non liquid assets An example of non liquid asset is a real Estate investment because it can take months for a person or company to receive cash from sale. If a company wants to sell the property quickly ,the value of the property can result in loss. Gross profit ;- Gross profit is the difference between revenues earned & cost of goods sold for a given period of time . Example ;- if you sell $ 100 worth of widgets & if cost you 75 $ to product then the Gross profit is 15 $. Gross profit is the first component in income statement operating income /operating profit is second. Operating profit / EBIT /Operating income/EBITDA
- 23. Page 23 It is referred as earnings before interest and tax,Operating profit represents the earning power of the company with regard to revenues generated from ongoing operations.Operating profit gives an indication of the current operational profitabilty of the business & allows a comparision of profitabilty between different companies after removing ot expenses. The profit earned from firms’ core business operations is called operating profit so a a shoe company’s operating profit will be the profit earned from solely selling shoes. Operating profit does not include any profits earned from investments & interests , It is also known as operating income ,PBIT,EBIT Net profit /Net income The word net means after all the deductions therefore the profit after all the deduction have been called net profit Net profit /Net revenue = Total revenue-total cost Examples Total =operating + non operating revenues & gains=60000 Total operating + non operating exp./ losses= 40000 Net profit =total revenues –total cost =60000-40000 Net profit or net revenue/net income Profit before tax Profit before tax deducts all expenses from revenue including interest & operating expenses ,excluding tax.PBT gives investors a good idea about the company’s profits every year Profit after tax Profit after tax also referred as the bottom line,is a measure of the profitabilty of the company after deducting all the expenses. Net worth It is the difference between a company’s total assets –totalliablities ,its is also known as shareholder’s equity.
- 24. Page 24 Book value Book value = Assets – Liablities Wherein assets = assets are what the company ownslike factory ,building products,what ca company owns that can sell it can sell for money ,Liablities a company owes debt mortgage payments these would be examples of liablities So basically when you are looking if the company close down pay ,sold everything they had and paid off all the things they had & paid off all the things the financial payments they needed to fulfill paid off paid out all their debt all their mortgage payments how much would they be left with,sell verything pay off everything what’s that number ; that number is what we call book value Example of book value Price of company A is 18 $ Assets =80 million Liablities = 5 million Assets – liablities =book value 80-75= 5 million So lets say this company has say 5 million shares so book value per share would be book value /share So think the company close down tommorow they have paid off all their debt their mortgage payments they would be at 75 million but 75 million is not owned by 1 person this is owned by 5 million person so you divide that 75million shares by 5 million shares so you get 15 $ So this is a good deal for an investor paying 18 dollars for a book value of 15 dollars. Or the book value is 15 dollars So If the company lquidiate or sell off every thing what they are going pay out to an investor is 15 $. (what I feelis evry quarter book value is calculated) So if we are comparing book value to its current price then it would be called over valued which could be one of the factor while determining whether the stock is undervalued or over valued I have noticed the term “diluted share” used more frequently in financial reports. What is a diluted share and how did this term evolve. — Lloyd J. What is the meaning of diluted shares A: Companies have taken a lot of flak recently for watering down their financial reporting, but in this case reporting on dilution means giving you more information — not less. In this context, “dilution” refers to the effect of adding more shares to the pool of stock that is already trading in the open market. For example, if you own stock in a company with 1 million shares trading at $10 each, and the company decides to issue another 1 million shares, you’re holdings would be “diluted” by those new shares. Since the company hasn’t done anything to increase its value, the stock would drop to $5. It’s not much different than what happens to your savings when the government starts printing too much money. Extra shares can be issued for a variety of reasons, but one common source is “convertible preferred shares” — a special class of stock that allows the holder to convert those shares to common stock. (Preferred shares, which often pay a special dividend, are really more like bonds than stocks.) How to value a stock 1 Earning per share =Net income /O.S. shares 2 Profit margins = Net profit margins= Net income /revenue
- 25. Page 25 3 Return on equity =Net income /shareholder’s equity 4. PEG ratio = Stock’s PE ratio/Growth over 12 months 5. Book value comparision to its CMP price = 214 vs 298 for vedanta as on 15 -12- 17 The book value tells if company liquidiates the price paid to its shareholders is called as book value Providend fund ;- It gives the lump sum payment at he time of exit from the organization.in providend fund 12 % of basic salary is retained ,and another 12 % is paid by the company. Pension fund;- A pension fund have both the elements which are a lump sum,monthly payments Red tapism ;- Rad tape is an idom refers that refers to excessive regulation or rigid conformity to formal reules that is considered redundant or beuracratic & hinders or prevents action or decrision making.it is usually applied to govt,corporations & other large organisation. A struggle to get burecratic approvals ,struggle to get certificates sometimes may be birth certificate or even for death certificates as well.everyone in the system is asking for ‘ mujhe kya milega’. Contango ;- It occurs when the current future price of an asset ( in futures market) is higher that the current spot price of the underlying assets If the quoted future price is higher than the spot price ,the commodity is contago. For example ;- An airline company ,which requires vast amounts of oil in order to operate ,may be afraid that oil prices will go up in the future.To hedge against that possibility that Future oil prices will increase so much that the airline will be forced out of business ,the business ,the airline may buy future contracts to lock in the price of oil at its future prices,even if the futures prices is higher than the spot prices ,the airline does not want to be caught in a situation where oil goes up even more than the futures market expected. Backwardization;- If the crude oil is trading at 100$ per barrel,but the price of delivery in six months is 110 per barrel,that market will be contango. On the other hand ,if crude oil is trading at 100 $ per barrel for delivery right now & the six month contract is trading at 95 $ per barrel then the market will be called as backwardization Authorized capital Authorized caiptal is the total value which will be the maximum amount company can allot to the investors or in public. Paid up capital Suppose a company has authorized capital of 50000 rs.It has allowed 20000 worth of shares in the pyublic it is paid up capital Corporate action – The initiation taken by a corporate entity that brong in a change to its stock,it is initiated by board of directors & approved by company’s shareholders Corporate action is formed by following ways Right issue Buyback of shares Splits Bonus shares Dividends Offer for sale FPO CAGR Right issue
- 26. Page 26 This is A second IPO for a select group of people( existing shareholders) the right issue could be an indication of a promisingnew development in the company ,It refers to offering additional shares to the current shareholders of the stock. This is done by companies to raise capital for further expansion which provide its existing shareholders the right to buy the stock at discounted rates than price making it more lucrative. Adjustments for Rights Issues When a company, included in the compilation of the index, issues right shares,the free-float market capitalization of that company is increased by the number of additional shares issued based on the theoretical (ex-right) price. An offsetting or proportionate adjustment is then made to the Base Market capitalization. Buyback ofshares A buy back can be seen as method for a company to invest in itself by buying shares from the investors in the market. Buyback reduces number of shares outstanding in the market,there could be many reasons why corporate choos to buy back shares,these are listed below, Buyback is an action in which company offers to buys back its stock from the current share holders at an attractive price. The reason is to reduce the shares outstanding in the market or to reduce the stake of shareholders in company Improve the profitability /Earnings on per share basis To consolidate their stake in the company To present other companies from taking over To show the confidence of the promotors about the company To support the share price from declining To company will do it only when it is cheaper / below its intrinsict/fair value. Stock Split and Reverse Spilt:A corporate action in which a company’s existing shares are divided into multiple shares. For Ex. A company with 100 shares of stock price Rs 50 per share (100*50 = 5000). The company splits it shares 2 for 1. There are now 200 shocks for Rs 25 each (200*25 = 5000) . The reason why companies split their stock is to make them more affordable to investors because stock price reduces after it is split. Likewise, reverse split increases the stock price while reducing number of outstanding shares. Primary motive of splits The primary motive is to make shares seem more affordable to small investors even though underlying value of the company is not changed Bonus share;- It is an additional dividend given to the shareholders that can be in cash or in the form of stock. When companies have outstanding performance with surplus profit, they may decide to issue bonus to the shareholders. Primary motive of bonus shares Company may prefer to give bonus shares rather than cash dividend as a method of providing income to shareholders because bonus shares increases share capitalof the company ,the company is perceived as being bigger than really it is ,making it more attractive to investors Adjustments for Bonus Issue When a company, included in the compilation of the index, issues bonus shares,the market capitalization of that company does not undergo any change. Therefore,there is no change in the Base Market capitalization; only the 'number of shares' in the formula is updated. Spin-Offs: Spin off means a company breaking up itself into smaller units. The creation of an independent company through the sale or distribution of new shares of an existing business/division of a parent company.
- 27. Page 27 Dividend Payouts:Dividend is the payment made to the investor for sharing the profits a company has made. Mergers and Acquisitions:Mergers is a event where two or more companies merge into one aiming to be more competitive and for more profitability. Likewise Acquisition means a bigger company acquiring a smaller one for further expansion. MERGER;- Mergers generally refers to a circumstances in which the assets & liablities of a company are vested into another company The merging entity loses its identiy Horizontal merger ;- Any ENTITIES merging which are the competitors or in competiting businesses ,which are same stage of industrial process A horizontal merger takes a company closer towards monopoly by eliminating a competitor & establishing a stronger presence in the market Example ;- Kotak aquired INGvaishya bank Vodafone aquired tata tele services Vertical merger;- it refers to the combination of two entities of different stages of industries or production process for ex;- a company engaged in construction business with a company engaged in production of brick or steel would lead to vertical integration rewliance & flag telecom group conglomerate merger;- A merger between firms that are involved into totally unrelated business activites is callsed conglomerate merger Reason ;- Utilization for finanical resources L& t merge into voltas ltd Concentric merger ;- A merger of firms which are into similar types of business Generally these are the merger between entities in the same general industry or somewhat inter related Amalgamation ;- Amalgamation is the union of two or more companies made with an intention to form a new company , It is an agreement between two or more companies to consolidate their business activities by establishing a new company having a separate legal existence Ex;- Maruti motors operating in india & suzuki based Japan amalgamated to form a new company called Maruthi suzuki india ltd Amalgmation vs acquisition WHEN A COMPANY takes over control of another company establishes itself as owner ,the transaction or process is called as acquisition When two or more companies joins together to consolidate & form a new company in an effort to have larger customer base ,larger market share & posibally more profits ,the process is called amalgamation Amalgamation is between equals whereas Acquisition is between unequals or unequal sizes Offer for sale;- the company wants to dilute their ownership so issue its ownership further at a discount price say about 5 % is called offer for sale Followon public offering ;-,An fpo is essentially a stock issue of suppliment shares made by a company that is already listed on the exchange How does bonus of 1; 2 affect the equity holdings or f & o positions L & T goes ex-bonus in the ratio 1;2 ON 13 JULY 2017 It means bonus 1 share is issued at Rs 0, for every two shares held in demat account of all eligible shareholders. Effect on holding ;- When a bonus is issued the share price drops ,In case of 1 ;2 the adjustment will be (1+2/2) so the multiplier would be 1.5 ,so if you held LT shares at an average price of 1500 ,the price of each share after bonus would adjust to 1500/1.5= 1000 you will be given 1 share at rs 0 for two shares held there by maintaining your overall investment value. Suppose the investor held 100 shares now he will have 150 shares now. So total value of investment portfolio would be same as 150000(100*1500) vs 150000 (150*1000) Note ;- A bonus issue only increases liquidity not your investment value
- 28. Page 28 P & L drop Untill the bonus shares are credited to the demat accounts ,it will show a decrease of approximately 33 % ,Once the bonus shares are credited of an avg price of 0 ,your p & l account in the portfolio will be credited to its correct value. You will receive an SMS from CDSL when your Bonus shares are credited to your demat which could take upto 2 weeks Effects on f & o positions Option strike prices are divided by the factor 1.5 ,A strike price of 1800 becomes 1200. F & O lot sizes are multiplied by factor of 1.5 ,the Old lot size of 500 will be multiplied by 1.5 & will be revised to a new market lot size of 750. Record date;- On the basis of day which is alloted like 29th is record date means the investor who holds the share on that day will be alloted the bonus share What is dividend It is a payment made by a company to its shareholders usually as a distribution of profits,when a company makes profits it can re invest into business or it can distribute to its current shareholders by way of dividends Dividend Yield WHAT IT IS: Dividend yield is a stock's dividend as a percentage of the stock price. The formula for dividend yield is: Dividend Yield = Annual Dividend / Current Stock Price For example, let's assume you own 500 shares of Company XYZ, which pays $1.10 per share in annual dividends. If the current stock price is $12.00, then using the formula above we can calculate that the dividend yield on Company XYZ stock is: $1.10 / $12.00 = .0916 = 9.2% Note that there is an inverse relationship between yield and stock price. For example, if the stock price rose to $15, the yield would be $1.10/$15 or 7.3%. The 500 share investment would be worth $7,500 (vs. $6,000 originally) but the yield on the investment would fall from 9.2% to 7.3%. Further note that the dividend stays the same,meaning even though the stock price falls (or rises), you still receive $1.10 per share (unless the company changes the dividend). For example If a stock has paid an annual dividend of Rs 22 & cmp is 440 ,the dividend yield is 5 % Indication ;-If the dividend yield is low ,A share is relatively higher than the dividend paid & hence the stock may be undervalued this means positive decline in the future. Possible example 22/500 =4.4 High dividend yield means it is undervalued WHY IT MATTERS:
- 29. Page 29 Dividend yields are a measure of an investment’s productivity, and some even view it like an "interest rate" earned on an investment. A security's dividend yield can also be a sign of the stability of a company and often supports a firm's share price. Normally, only profitable companies pay out dividends. Therefore,investors often view companies that have paid out significant dividends for an extended period of time as "safer" investments. Thus, should events occur which are detrimental to the share price, the allure of the dividend combined with the stability of the company can support the price somewhat. Why do companies pay a dividend,while other companieesdon’t Dividends are the corporate earnings that a company pass on to their shareholders There are a number of reasons why a corporation might not to choose to pass some of its earnings on as dividends A company that is still growing rapidly usually won’t pay dividendsbecause it want to invest as much as possible into further growth Even a mature firm that belives it will do a better job of increasing its share price by reinvesting its earnings will choose not to pay dividends Companies that don’t pay dividends might use the money to start new project,aquire new assets,repurchase some of their shares or even buy out other company. Also,the choice to not pay dividends may be more beneficial to investors from a tax perspective ,dividends are taxable to investors as ordinary income Effects ofdividends on the futures prices When the company announces the dividends before the ex-dividend dates the prices will go up ( in greed of dividends ) when dividend record date is over the next day or next few days the stock prices will go down. In case the dividends are lower than the other companies then the other companies or lower in amount then it might not give much fluctuations By investopedia If a company announces a higher than normal dividend ,public sentiments tends to soar. * The declaration of a dividend naturally encourages investors to purchase stock.Because investors know that they will receive a dividend if they purchase the stock before ex dividend date ,they are willing to pay premium (extra amount ) this causes the prices of a stock go up or increase in the days leading up to the ex dividend date. On the ex dividend date ,the exchange reduces the price of the stock by the amount of dividend to account for fact that new investors are not eligible to receive dividends & are these for not willing to pay a premium ,so share prices comes down because of more selling of shares ,or may be because of short sell based on news. * An investor should always choose a company which gives regular dividends not a company which gives dividend sometime not gives other time because these could be because of conning or deceiting people. Put call ratio Capital budgeting Introduction
- 30. Page 30 An efficient allocation of capital Is most important finance function in modern times. It involves decisions to commit the firm’s long term assets. Capitalbudgeting or investment decisions are of considerable importance to the firm, since they tend to determine its value by influencing its growth, profitability & risk. Nature of investment decisions Investment decisions of a firm are generally known as the capital budgeting, or capital expenditure decisions. A capital budgeting decision may be defined as the firm’s decision to invest its current funds most efficiently in the long – term assets in anticipation of an expected flow of benefits over a series of years. Importance ofinvestment decisions 1. They influence the firm’s growth in the long run 2. They affect the risk of the firm 3. They involve commitment of large amount of funds 4. They are irreversible Types ofinvestment decisions Expansion of existing business Replacement & modernization Capital budgeting techniques 1. Discounted cash flow Net present value Internal rate of return Profitability index 2. Non discounted cash flow Payback Discounted cash back Accounting rate of return NPV(Net present value) It Is the method of calculating present value of a project or an investment as on today. Present value always decreases as and when rate or interest or R is increased Example 100 rs worth today is may be 98 rs after two years down the line. Formula NPV=C1 /(1=r)^1 +C1/(1+r)^2 + C1/(1=r)^n Acceptance criteria
- 31. Page 31 Accept if NPV >0 Reject if NPV<0 May accept if NPV=0 Evaluation of the NPV Time value Maximizing shareholder’s funds Measure of true profitability Internal rate of return It takes same formula to calculate Cash flow assessment or present value of a sum IRR=C1 /(1=r)^1 +C1/(1+r)^2 + C1/(1=r)^n Acceptance rule Accept if opportunity cost of capital or rate of return is higher than required rate of return R>k R= rate of return on investment calculated Where in k is required rate of return or cost of capital OR opportunity cost = Suppose if we take another investment or project into consideration which one is better this is known as opportunity cost of capital Accept if NPV >0 Reject if NPV<0 May accept if NPV=0 Profitability index It is the ratio of present value of cash inflows,at the required rate of return,to the intitiial cash outflow of the investment. It is also know as benefit –cost ratio PI=Annual cash iinflow /initial cash outflow or outlay In Another words= pv of cash inflows/initial cash outlay Acceptance = if ratio is more than 1 as it shows project is in benefit over the cost of project for ex 2:1 For the cost of 1 benefit is 2 or 100 % Non discounted cash flow Pay back period
- 32. Page 32 Pay back is the number of years required to recover the original cash outlay invested in a project. PAY BACK PERIOD=Initial investment /annual cash inflow Acceptance- If period is lower it better for the company after reaching BREAK EVEN POINT it is profit on the investment Accounting rate ofreturn Accounting rate of return is also known as average rate of return which gives the financial ratio used in capital budgeting. The ratio takes time value of money factor which calculates the return & net income can be generated from the purposed capital investment. Other words The accounting rate return, also known as the return on investment, uses accounting information, as revealed by financial statements,to measure profitability of an investment. The accounting rate of return is the ratio of the average after tax profit divided by the average investment PAT OR EAT /Average investment Alternatively, it can be found out by dividing the total of the investment’s book values after depreciation by the life of the project. Book value after depreciation /life of the project ARR=Average investment /Average investment Acceptance rule This method will accept all those projects whose ARR is higher than the minimum rate established by the management & reject those projects which have ARR less than the minimum rate. Higher rank would a project as number one if it has highest ARR & lowest rank would be assigned to the project with lower ARR. What is owner’s equity? Owner’s equity is also known as capital of the business, it is a claim of the owner or shareholder of the business against the assets of the business .it is also known as shareholder’s funds It is shown in liabilities side in the balancesheet Total equity –equity of creditor = Owner’s equity Acid test ratio-it is a liquidity ratio which measures the ability of a company touse its near cash or quick asstes to extinguish its current liabilities Acid test ratio -Current assets- inventory /current liabilities List of things which come under intangible asstes Patent Goodwill Copyrights
- 33. Page 33 Trademarks Brandnames Domain names etc Mention what does financial statement ofa company includes Balancesheet Income statement Equity statement Cash flow statement Why financial reports are prepared 1. Tax return ;- They are prepared to determine the amount of tax for the period as required by income tax,pay roll & property tax laws. 2. Accounting reports keep managers informed about what’s going on & the financial position of the business.These accounting reports are absolutely essential to help managers control the persormance of a business.Identifyproblems as they come due & plan the future course of action. 3. External financial statements – The accounting reports & financial statements are prepared to show the financial position of the company to outsiders who need to stayinformed about the business’s financial affairs.These people may have invested capital in the business.These statements may help the following people such as creditors,auditors,shareholders,Governments etc. What does a liability? What does it include? Liablity can be defined as an obligation towards another company or party It cludes Accounts payable Interest & dividends payable Bonds payable Short term loans Consumer deposits Reserves for federaltaxes Difference between depreciation & amortization Depreciation Amortisation It refers to prorating a tangible asset’s cost over that assets life for example,A patent on a piece of medical equipment usually have 17 years. In intangible ,It refers to prorating the cost of an intangible asset over the assets life.For example patents are provided for 10 years so it will divide the cost for 10 years annually either compounded or on equal amount basis Depreciation cost is calculated in the terms of intangible It is calculated in terms of intangible asstets like
- 34. Page 34 asstet like furniture,building etc goodwill,trademark,patents etc Example;- A car worth 3000 rs has estimated life of 10 years after that it will have no value in the market.The cost or loss in value throught this 10 years is known as depreciation. Example-Pharma company spent 20million dollar on a Drug patent with usful life of 20 years the amortized value would be 2 million each year. What are the three factors that can affect your cash flow & business profitability? CASH FLOW FROM OPERATINGACTIVITIES- Cash flow from operating activities focuses on cash inflow & outflow from a companies main business activities of buying & selling merchandise, providing services etc.It will also include the other activities included in next pages Cash flow from Investment activities- Any kind of investment commonly long term is known as investment activities Example Purchase or sale of plant and machinery, bonds, shares etc CASH FROM FINANCINGACTIVITIES- Any provisions made to aquire these assets will be financing activities like interests, dividends, money paidout or borrowed in order to finance the projects. Cash flow statements It is a statement showing changes in cash position of the firm from one period to another,It explains inflow & outflow of cash over period of time.The inflows may occur from sale of goods,sale of assets,receipts from debtors,interest,dividend,rent,issue of new shares& debentures,raising of loans,short term borowings etc. Cash flow from operating activities Net profit 10000 (-) Depreciation (500) (+) Loss on sale of goods 300 (-) gain on sale of goods (200) (-) Dividend received (300) (-)Interest received (400) Trade receivable 000 Other receivable 000 OPERATING PROFIT 9300 (+)Decrease in current assets 400 (+)Increase in current liabilities 300 (-)Increase in current assets (-500) (-)Decrease in current liabilities (-400) Cash generated from operating activities 9100 (-) income taxes paid (-500) Net cash from operating activities 8600 Cash flow from investing activities 10100 Receipts from sale of assets 10000 (-) Purchase of fixed assets -1500 Dividend received 500
- 35. Page 35 Sale of investment 1000 (-) Purchase of investments -1200 Interest received 1300 Net cash flowfrom investing activities 10100 Cash flow from financing activities 800 Proceeds from issuance of share capital 500 Proceeds from long term borrowings 1500 (-) Interest paid -200 (-) Dividend paid -300 (-) Repayment on borrowing -200 Net cash flowfrom financing activities 800 Net increase in cash & cash equivalents 500 Cash & cash equivalents at beginning period 600 Cash & cash equivalents at the end ofperiod 1900 Note ;- If dividend & interest is received it is under investment but if it is paid under financing activities Note ;-Cash from operating activities Add loss on sale of goods,decrease in CA & increase in CL because we have deducted in previous statements like ( Profit & loss account Most probably not sure) Decrease dividends received ,interest recived ,increase in Current assets & Decrease in CL because We have taken into P/L statements. Income tax is direct expense so it will decrease in cash Is it possible for a company to showpositive cash flows but be in grave trouble? Two such examples are It involves lack of revenues going into pipeline It involve unsustainable improvements in working capital, a company is selling inventory & delaying payables Table ofDifference between Funds FlowStatement and Cash FlowStatement Basis of Difference Funds FlowStatement Cash FlowStatement 1. Basis of Analysis Funds flow statement is based on broader concept i.e. working capital. Cash flow statement is based on narrow concept i.e. cash,which is only one of the elements of working capital. 2. Source Funds flow statement tells about the various sources from where the funds generated with various uses to which they are put. Cash flow statement starts with the opening balance of cash and reaches to the closing balance of cash by proceeding through sources and uses. 3. Usage Funds flow statement is more useful in assessing the long-range financial strategy. Cash flow statement is useful in understanding the short-term phenomena affecting the liquidity of the
- 36. Page 36 business. 4. Schedule of Changes in Working Capital In funds flow statement changes in current assets and current liabilities are shown through the schedule of changes in working capital. In cash flow statement changes in current assets and current liabilities are shown in the cash flow statement itself. 5. End Result Funds flow statement shows the causes of changes in net working capital. Cash flow statement shows the causes the changes in cash. 6. Principal of Accounting Funds flow statement is in alignment with the accrualbasis of accounting. In cash flow statement data obtained on accrual basis are converted into cash basis. Advantages ofCash FlowStatement 1. It shows the actualcash position available with the company between the two balance sheet dates which funds flow and profit and loss account are unable to show. So it is important to make a cash flow report if one wants to know about the liquidity position of the company. 2. It helps the company in accurately projecting the future liquidity position of the company enabling it arrange for any shortfall in money by arranging finance in advance and if there is excess than it can help the company in earning extra return by deploying excess funds. 3. It acts like a filter and is used by many analyst and investors to judge whether company has prepared the financial statements properly or not because if there is any discrepancy in the cash position as shown by balance sheet and the cash flow statement,it means that statements are incorrect. Disadvantages ofCash FlowStatement 1. Since it shows only cash position, it is not possible to deduce actual profit and loss of the company by just looking at this statement. 2. In isolation this is of no use and it requires other financial statements like balance sheet, profit and loss etc…, and therefore limiting its use. Cash flow statement advantages & disadvantages Fund flow statement A Funds flow statement is prepared to show changes in the assets,liabilities and equity between two balance sheet dates, it is also called statement of sources and uses of funds. It states changes in working capital of business in relation to the operations in one time period The advantages of such a financial statement are many fold. Some ofthese are: 1. Funds flow statement reveals the net result of Business operations done by the company during the year. 2. In addition to the balance sheet,it serves as an additional reference for many interested parties like analysts, creditors, suppliers, government to look into financial position of the company. 3. The Fund Flow Statement shows how the funds were raised from various sources and also how those funds were deployed by a company, therefore it is a great tool for management when it wants to know about where and from what sources funds were raised and also how those funds got utilized into the business. 4. It reveals the causes for the changes in liabilities and assets between the two balance sheet dates therefore providing a detailed analysis of the balance sheet of the company.
- 37. Page 37 5. Funds flow statement helps the management in deciding its future course of plans and also it acts as a control tool for the management. 6. Funds flow statement should not be looked alone rather it should be used along with balance sheet in order judge the financial position of the company in a better way. Disadvantages ofFund FlowStatements Funds flow statement has many advantages; however it has some disadvantages or limitations also. Let’s look at some ofthe limitations offunds flow statement. 1. Funds Flow statement has to be used along with balance sheet and profit and loss account for inference of financial strengths and weakness of a company it cannot be used alone. 2. Fund Flow Statement does not reveal the cash position of the company, and that is why company has to prepare cash flow statement in addition to funds flow statement. 3. Funds flow statement only rearranges the data which is there in the books of account and therefore it lacks originality. In simple words it presents the data in the financial statements in systematic way and therefore many companies tend to avoid preparing funds flow statements. 4. Funds flow statement is basically historic in nature, that is it indicates what happened in the past and it does not communicate anything about the future, only estimates can be made based on the past data and therefore it cannot be used the management for taking decision related to future.Conclusion We can conclude that shorter the period is cash flow is more relevant & longer the planning period is more relevant is fund flow statement Why following items are added to profit to calculate cash flowfrom operating activities ? Depreciation--is added because it is a non cash expense so it will increase cash in cash flow statement Loss on sale of a fixed asset-- is added because it is a non cash expense so it will increase cash in cash flow statement Goodwill writtern off--is added because it is a non cash expense so it will increase cash in cash flow statement State two objectives ofcash flowstatements It is prepared to assess deviation of cash & cash equivalents It helps in formulating dividend policy What are cash equivalents? Cash equivalents means short term & highly liquid investments,which can be converted into cash without any loss in value& they present no change in value. Generally assets which can be converted into cash within three months are known as cash equivalents.classify the following types of activities in a financing a company Purchase of machinery –Cash outflow in investing a company Issue of share capital –cash infllow infinancing activities Reciept of interest – cash inflow in financing activities
- 38. Page 38 Sale of long term investment –cash inflow from investment activities Redemption of debentures – cash outflow in financing activities Why finanicial statements are prepared? knowing the profitablity of the business knowing the solvency of the business judging he growth of the business judging the growth of the business judging the earings capacity of the business forcasting & preparing budgets communicating with different parties making with other firsms Parties interested in financial analysis Management Investors Creditors Government Employees Taxation authorities Other parties Ratio analysis Ratio analysis is an art of determining relationship between different component of financial statement so as to afford a meaningful understanding of profitabilty & solvency of the business concern. Objectives of ratio analysis Simplyfication of data Estimation of business earnings Judging Managerial efficiency Solvency determination Making comparison Formulation of budget & policies
- 39. Page 39 Forcasting What is balancesheet? What is the difference between profit & oss statement & income expenditure statement? What is cash flow statement? What are changes in equity? What is fund flow statement? What is working capital? For all the statements prepare a format (Check the yellow book) LIBOR ;London interbank offer rate Short sell ;- He has shortsell shares that he currently does not hold Beta ;- it is a measure of the volatility or systematic risk,of a security or a portfolio in comparision to the market as a whole,Beta is used in capital asset pricing model which calculate return of investment based on its beta (Other details can be found in blue book) What is beta & how it is calculated It is a measure to calculate systematic risk only. it is used in fundamental analysis to determine the voltality of an asset of or portfolio in relation to overall market. It is used in Capital asset prising model which calculates expected return of an investment & expected market return 𝛽= E(Rs)-Rf/E(Rm)-Rf 𝛽=Beta Rs = Expected return on investment Rm=Expected market return Rf=Risk free rate Accept =If beta is less than 1 then the investment is less volatile than the market or benchmarkbut when the beta is more than 1 it means it is more volatile than the market A greater beta or more than 1 represents the stock is volatile tends to move up & down with the market Systamatic risk arise due to Interest rate risk Inflation risk Political risk It is not specific to a sector Alpha It is an excess return on an investment based on all the other things like beta remaining the same
- 40. Page 40 Alpha is the excess return an investment produces compared to a benchmark It gauges investment performance given its price risk or volatility as compared to other investments If alpha is positive the investment has outperformed & should be seen as selected If it is not positive than it has underperformed & should not be undertaken Delta;- It is measured as a measure of volatality,A measure of the likelihood that an option will be in the money on the expiration day Formula ; Change in the premium/ change in price unit of underlying asset Gamma;- The Gamma represents the amount by which an option delta would move in response to a unit change in the response to a unit change in the underlying stock price or index Formula; Change in delta/change in unit price Theta;- the theta is obtained by considering value of an option as a funstion of time when all other parameters of pricing model remain constant Formula; change in option premium/change in time to expiry Vega ;- Vega measure the rate of change of the value of an option with regard to value of an option with regard to volality of the underlying stock Formula =change in option premium/change in volatility Howto calculate option prices ofEuropean call option using black scholes model? Black scholes model It was developed by fisher black,Robert Morton ,& Myron scholes in 1973 It is used to determine theoretical price of European call option It takes following formula to calculate option prices Variation in stock/Underlying price Time value of money( risk free rate) Time to expiry Option strike price Assumptions The option is European & can only be excersized only at expiry The option is European & can be excersized only at expiry No dividends are paid out during life of an option There is no transaction cost The risk free rate (Time value of money) & the volatility are known & constant
- 41. Page 41 That the returns on the underlying are normally distributed Limitations It may be noted that the black school option pricing model works well for the options that are near the money & options with next striking price on either side of the stock price. However it does not yield satisfactory results for the options that are deep in the money or out of the money. Examples of bonds IFRC tax free bonds Issue size-40000 cr 7.29 % Nhai tx free bonds 3300 cr 7.29 for 15 yrs 7.69 for 20 years List of credit rating agencies Crisil limited ICRA –Investment information & credit rating agencies CARE-Credit analysis & research ltd Brick work rating india pvt ltd SME Rating india private ltd Thomson reuters Why to prefer bonds over shares What are the types of bonds? Tell me about Zero coupon bonds, what is point to get zero coupon bonds? What are credit rating agencies? Types of credit rating agencies What are mutual funds & how does it work? Examples of bonds NHAI Rate of interest 7.29 & 7.69 –IFRC,NHAI It depends based on Maturity What is GDP? What does it denote? What is Repo rate? & reserve repo rate?
- 42. Page 42 Credit rating agencies It is a company that assigns credit rating, which rates a debtors ability to pay back debt by making timely interest payments & the likelihood of default.An agency may rate the credit worthiness of issuers of debt obligations. The debt instruments rated by CRA’s include Govt bonds, corporate bonds, Certificate of deposits, Muncipal bonds, Preferred stocks& collaterized securities such as mortgage backend securities etc. Rating given are AAA,Aaa,AA,Aa2,A,BBB,Baa2,BB,CCC Q: What is a deferred tax liability and why might one be created? A: Deferred tax liability is a tax expense amount reported on a company’s income statement that is not actually paid to the IRS in that time period, but is expected to be paid in the future. It arises because when a company actually pays less in taxes to the IRS than they show as an expense on their income statement in a reporting period. Differences in depreciation expense between book reporting (GAAP) and IRS reporting can lead to differences in income between the two, which ultimately leads to differences in tax expense reported in the financial statements and taxes payable to the IRS. Green field investment ;- It occurs when a parent company begins a new venture in a country outside of where company is headquartered Brownfield investment investment ;- It occurs when a company or governement purchases an existing facility to begin new production WACC;- Weighted average cost of capital ;- The cost of buying a set of equity and debt is called weighted average cost of capital.Foe example ;- You take a debt of say 100 rs may be 5 rs you are paying as cost of it which you pay. In other words ;- it is the average rate of return a company expects to compensate all its investors. It includes all the sources of capital,including common stock,preferred stock,bonds & any other long term debtare included in WACC calculations. WHY WACC MATTERS: It's important for a company to know its weighted average cost of capital as a way to gauge the expense of funding future projects. The lower a company's WACC, the cheaper it is for a company to fund new projects. A company looking to lower its WACC may decide to increase its use of cheaper financing sources. For instance, Corporation ABC may issue more bonds instead of stock because it can get the financing more cheaply. Because this would increase the proportion of debt to equity, and because the debt is cheaper than the equity, the company's weighted average cost of capital would decrease Interpretation ;- from the company’s perspective the lower is the cost of capital the better for the company Example ;- capital is 100 which is being financed from equity & debt ,suppose 70 rs is taken from equity shareholders & 30rs is being taken from creditors , Cost of equity is 10% ,cost of debt is 7 % So the WACC would be = 0.7*10%+ 0.3*7% =.07+0.021 =0.091
