cleavage and gastrulation in amphibians
•Descargar como PPTX, PDF•
48 recomendaciones•33,027 vistas
1. Amphibian embryos undergo radial cleavage where cell divisions are slower in the vegetal hemisphere containing yolk. Gastrulation begins with the invagination of cells at the blastopore forming the archenteron. 2. Fate mapping shows superficial cells form ectoderm and endoderm, while deeper cells form mesoderm. During gastrulation, bottle cells migrate inward expanding the archenteron. 3. Spemann and Mangold's experiments showed the dorsal lip tissue of the blastopore, known as the organizer, can induce a secondary embryonic axis when transplanted, demonstrating its inductive properties.
Denunciar
Compartir
Denunciar
Compartir
Recomendados
Recomendados
Más contenido relacionado
La actualidad más candente
La actualidad más candente (20)
Cell aggregation and differentiation in dictyostelium007

Cell aggregation and differentiation in dictyostelium007
Regeneration, Types of Regeneration,Invertebrates&Vertebrates sp. ,Mechanism,...

Regeneration, Types of Regeneration,Invertebrates&Vertebrates sp. ,Mechanism,...
Destacado
Destacado (7)
Similar a cleavage and gastrulation in amphibians
Similar a cleavage and gastrulation in amphibians (20)
Egg structure, types classification and cleavage types , sperm structure 

Egg structure, types classification and cleavage types , sperm structure
types of cleavage, blastula formation, gastrula , morphogenetic movements etc 

types of cleavage, blastula formation, gastrula , morphogenetic movements etc
Último
Último (20)
TEST BANK For Radiologic Science for Technologists, 12th Edition by Stewart C...

TEST BANK For Radiologic Science for Technologists, 12th Edition by Stewart C...
Kochi ❤CALL GIRL 84099*07087 ❤CALL GIRLS IN Kochi ESCORT SERVICE❤CALL GIRL

Kochi ❤CALL GIRL 84099*07087 ❤CALL GIRLS IN Kochi ESCORT SERVICE❤CALL GIRL
Biopesticide (2).pptx .This slides helps to know the different types of biop...

Biopesticide (2).pptx .This slides helps to know the different types of biop...
Biogenic Sulfur Gases as Biosignatures on Temperate Sub-Neptune Waterworlds

Biogenic Sulfur Gases as Biosignatures on Temperate Sub-Neptune Waterworlds
Recombinant DNA technology (Immunological screening)

Recombinant DNA technology (Immunological screening)
Chemical Tests; flame test, positive and negative ions test Edexcel Internati...

Chemical Tests; flame test, positive and negative ions test Edexcel Internati...
All-domain Anomaly Resolution Office U.S. Department of Defense (U) Case: “Eg...

All-domain Anomaly Resolution Office U.S. Department of Defense (U) Case: “Eg...
Recombination DNA Technology (Nucleic Acid Hybridization )

Recombination DNA Technology (Nucleic Acid Hybridization )
Pulmonary drug delivery system M.pharm -2nd sem P'ceutics

Pulmonary drug delivery system M.pharm -2nd sem P'ceutics
Hubble Asteroid Hunter III. Physical properties of newly found asteroids

Hubble Asteroid Hunter III. Physical properties of newly found asteroids
cleavage and gastrulation in amphibians
- 1. CLEAVAGE AND GASTRULATION IN AMPHIBIANS
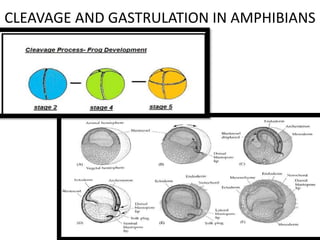
- 2. Amphibian Cleavage • Radially symmetrical, holoblastic • but unlike sea urchin, mesolecithal egg • Yolk is concentrated in vegetal pole • Cell divisions are slower in the vegetal hemisphere • First cleavage bisects the grey crescent – Second cleavage begins in animal pole, while first cleavage is not yet complete in vegetal pole – As in sea urchins, there are no Gap phases in the cell cycle to allow for rapid divisions
- 3. • First & Second cleavage – Meridional – At right angle to first one and also Meridional • Third cleavage – Equatorial (but not actually at the equator) – Divides the embryo into 4 small – micromeres, 4 large micromeres • As cleavage continues _ animal pole packed with many small cells -vegetal pole has fewer large yolk-laden cells
- 4. • At 16-64 cells, embryo is called a morula – Solid ball of cells • At 128 cell stage, embryo is a blastula – Open cavity called blastocoel has appeared in animal pole • FUNCTION OF BLASTOCOEL 1. Permits cell migration during gastrulation 2. Prevents cells below from interacting with the cells above prematurely.
- 5. Amphibian Gastrulation • Different in different species • Goals –Bring endoderm cells to the inside of the embryo –Allow ectoderm cells to coat the outside of the embryo –Position mesoderm cells in between
- 6. Fate-maps Fate-mapping of blastula stage embryos has p provided some insight – Using vital dyes to mark cells – Superficial layers of embryo form ectoderm and endoderm – Mesoderm lie mostly in the deeper layers of cells – Surface of animal hemisphere will become cells of ectoderm – Vegetal hemisphere will form cells of gut and associated organs – Mesodermal cell will form internal cytoplasm around equator
- 7. Cell Movements in Amphibian Gastrulation • Gastrulation begins on future dorsal side –Below the equator, in region of grey crescent –Cells invaginate to form a slit like blastopore –Dorsal lip of blastopore will become important organizing region of embryo (Spemann organizer) –Cells become elongated as they contact the inner surface (Bottle cells)
- 8. • Bottle cell line the archenteron as it forms • Invagination of cells initiate archenteron formation • Gastrulation begins at marginal zone ,not at vegetal zone as in sea urchin
- 10. Cell Movements in Amphibian Gastrulation • Next steps: –Involution of the cells at the marginal zone (outer sheet spreads over inner sheet) –Cells from Animal pole undergo epiboly • Converge at the blastopore • When reach blastopore, travel inward –Bottle cells continue to migrate, form leading edge of archenteron (primitive gut)
- 11. Amphibian Gastrulation • Cells from the dorsal lip (the first cells that migrated inward) become prechordal plate (will form head mesoderm) • Next cells that involute form chordamesoderm (will become notochord) – Important for patterning the nervous system • Next yolk plug formation
- 12. • YOLK PLUG : Yolk plug is the remaining patch of endodermal cells that is created during the formation of the dorsal lip of the blastopore which remains exposed on the vegetal surface of the blastula that will eventually be internalized by epiboly.
- 13. Dorsal lip of the blastopore yolk plug ventral lip of the blastopore.
- 14. Amphibian Axis Formation and “The Organizer” • Amphibian gastrulation and axis formation are an example of regulative development • Inductive interactions occur between cells • This was demonstrated by Hans Spemann and Hilde Mangold – Nobel Prize winners
- 15. Spemann and Mangold • Performed many types of transplants at the early gastrula and late gastrula stages in the newt embryo • These experiments showed that in most cases, the cells of the embryo are not committed until at least the late gastrula stage • But - There is ONE tissue from the early gastrula that is already committed. . .
- 17. CONDITIONAL DEVELOPMENT Early newt gastrula cells were not committed to a specific fate .such cells are said to exhibit conditional development AUTONOMOUS DEVELOPMENT Late newt gastrula cells that were committed to specific fate such cells are said to exhibit autonomous development
- 18. • There is ONE tissue from the early gastrula that is already committed is dorsal lip of blastophore,the tissue derived from the gray crescent cytoplasm • When this tissue transplanted into presumptive belly skin region of another gastrula not only continued to form blastopore lip • but also initiated gastrulation and embryogenesis in the surrounding tissue • Two conjoined embryos were formed instead of one