1-Drugs Acting on the Kidney.pptx
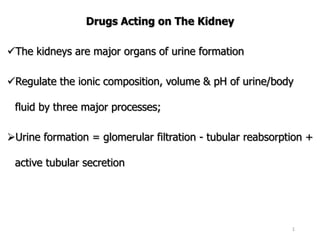
- 1. Drugs Acting on The Kidney The kidneys are major organs of urine formation Regulate the ionic composition, volume & pH of urine/body fluid by three major processes; Urine formation = glomerular filtration - tubular reabsorption + active tubular secretion 1
- 2. Functions of Renal System Excretory function: metabolic wastes, drugs, toxins, NTs, water soluble metabolites, hormones Regulatory function: Water/fluid/ balance: diluting & concentrating urine Electrolyte balance: K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl-, Pi- Acid base balance: H+, HCO3 - Endocrine function: EPO, renin, PGs Metabolic function: activation of Vitamin-D, gluconeogenesis 2
- 3. Urine formation An important interplay b/n RBF & nephron function CO RBF RPF GFR tubular flow urine CO = HR SV = 72 beats (strokes)/minute 70 mL/beat(stroke) = 5040 mL/minute 5 Liters/minute 3
- 4. RBF to both kidneys = 20-25% of CO Out of 5 Liters; 20% = 1 L/minute In the 1 L blood; 40% (400 mL) are cells & 60% (600 mL) is plasma Cells (RBCs, WBCs, platelets) do not filtered, simply circulate through the blood vessels 4
- 5. Out of 600 mL plasma 20% (120 mL/min) filtered in the glomeruli in both kidneys (60 mL/min/kidney) as it is passing in the glomerular capillaries i.e. GFR Out of 120 mL: 65% of fluid is reabsorbed in the PCT 10-15% of fluid is reabsorbed in the thin descending loop of Henle (water permeable site) Water permeability of the collecting tubule system is ADH dependent Finally 1 mL/minute urine is produced 5
- 6. 6
- 7. Diuretics Increase urine volume by promoting renal excretion of salt & water Principally used to remove excess ECF from the body 180 liters of fluid is filtered from the glomerulus into the nephron per day The normal urine out put is 1-5 liters per day The remaining is reabsorbed in d/t areas of nephron 7
- 8. 8
- 9. 9
- 10. Classification of Diuretics Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors Loop (high ceiling) diuretics Thiazides (Benzothiadiazides) & thiazide like diuretics Potassium-sparing diuretics: ENaC blockers, aldosterone antagonists Aquaretics: osmotic diuretics, ADH antagonists Adenosine A1-receptor antagonists 10
- 11. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors Acetazolamide, dorzolamide, methazolamide, brinzolamide MOA: carbonic anhydrase inhibition, results in: H+ formation inside PCT cell Na+/H+ antiport Na+ & HCO3 – in lumen diuresis 11
- 12. 12
- 13. Uses: Glaucoma: aqueous humor production Mountain sickness: reducing the formation as well as the pH of CSF – it can also be used for prophylaxis Metabolic alkalosis: enhances HCO3 – excretion Alkalinization of urine Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: CSF secretion Epilepsy: acetazolamide (adjuvant) as it seizure threshold Hyperphosphataemia:urinary phosphate excretion 13
- 14. Side effects: Bicarbonaturia & acidosis Hypokalemia Hyperchloremia Paresthesia /unusual or unexplained tingling, pricking, or burning sensation on the skin/ Renal stones: Ca2+ is lost with HCO3 – hypercalciuria Sulfonamide hypersensitivity 14
- 15. Loop Diuretics Furosemide, ethacrynic acid, torsemide, bumetanide MOA: Na+/K+/2Cl– transporter inhibition, results in: intracellular K+ in the TALH back diffusion of K+ positive potential reabsorption of Ca2+ & Mg2+ diuresis 15
- 16. 16
- 17. 17
- 18. Uses: Edema of cardiac, hepatic or renal origin: e.g. CHF Acute pulmonary edema & acute LVF: IV furosemide Acute renal failure or acute kidney injury (AKI): urine output & K+ excretion Hypertension Forced diuresis: in drug poisoning & anion overdose Acute hypercalcemia & hyperkalemia 18
- 19. 19 Furosemide in pulmonary edema
- 20. Side effects: Sulfonamide hypersensitivity (furosemide) Hypokalemia & metabolic alkalosis Hyponatremia, dehydration, hypovolemia & hypotension Hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia Hyperuricemia (actively secreted by the OAT) Ototoxicity (tinnitus & vertigo): ethacrynic acid > furosemide 20
- 21. Drug interactions: Furosemide & ethacrynic acid are highly protein bound: displacement Aminoglycosides generate free radicals within the inner ear, with subsequent permanent damage to sensory cells & neurons permanent hearing loss (enhanced ototoxicity) Lithium: chronic loop administration Li+ clearance Digoxin: toxicity due to hypokalemia 21
- 22. 22
- 23. MOA: Na+/Cl– transporter inhibition, results in: luminal Na+ & Cl– in DCT diuresis Thiazides (derived from acetazolamide) inhibit CA at the PCT (weak diuretic effect) 23
- 24. Uses: Hypertension CHF (edema) Nephrolithiasis (calcium stones) Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (rarely) 24
- 25. 25
- 26. 26
- 27. Side effects: Sulfonamide hypersensitivity Hypokalemia & alkalosis (due to H+ excretion) Hypercalcemia, mild hypomagnesemia (unknown) Hyperuricemia (actively secreted by the OAT into the PCT) Hyperglycemia: due to hypokalemia b/c insulin release depends on K+ level ( insulin release) Dose dependent hyperlipidemia ( cholesterol, LDL, TG); worsened insulin sensitivity &/reflex RAAS & SNS activation Impotency (rare): is likely a result of reduced volume 27
- 28. Potassium-sparing Diuretics Spironolactone: aldosterone-receptor antagonist Uses: Hyperaldosteronic state Adjunct to K+ wasting diuretics Antiandrogenic uses (female hirsutism) Congestive heart failure SEs: hyperkalemia & acidosis, antiandrogen Eplerenone: selective, devoid of antiandrogenic effect 28
- 29. 29 Canrenoate is not active but is converted to canrenone
- 30. Amiloride & triamterene: Na+ channel blockers Use: Adjunct to K+ wasting diuretics Lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (amiloride) SEs: hyperkalemia & acidosis 30
- 31. 31
- 32. Osmotic Diuretics Mannitol, Glycerin, Isosorbide, Sorbitol, Urea After IV administration mannitol ECF: extracting fluid from the cell (fluid shift) results in; Renal blood flow by; Viscosity of blood Inhibition of RAAS as ECF ed Sympathetic tone no activation of 1 ➨Diuresis 32
- 33. Clinical indications To ICP in ABI, hemorrhagic stroke To IOP before ophthalmologic procedures Adverse Effects Extracellular volume expansion (prior to diuresis) Dehydration (hypovolemia) & hypernatremia 33
- 34. 34
- 35. 35
- 36. ADH Antagonists ADH: octapeptide produced in the hypothalamus Medical conditions (CHF, SIADH) stimulate ADH secretion water retention Patients with CHF who are on diuretics frequently develop hyponatremia secondary to excessive ADH secretion dangerous hyponatremia Use: treatment of hypervolemic & euvolemic hyponatremia Ethanol, water: inhibit ADH secretion from hypothalamus 36
- 37. ADH receptors: V1 (V1a, V1b) & V2 V1: expressed in the vasculature & CNS V2: expressed specifically in the kidney Antagonists: Non specific agents: Lithium & demeclocycline Now replaced by vaptans due to ADR (renal failure) 37
- 38. Conivaptan (available in IV): act on both V1a & V2 Orals (tolvaptan, lixivaptan & satavaptan): V2 selective Tolvaptan: FDA-approved, very effective for hyponatremia Lixivaptan & satavaptan: under clinical dev’t t½ of conivaptan & demeclocycline: 5-10 hrs, tolvaptan 12-24 hrs 38
- 39. Clinical indications: Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion If water restriction is not successful Other causes of elevated ADH Thirst: IV conivaptan is effective by blocking V1a Refractory ascites Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Cyst development in polycystic kidney disease is mediated through cAMP ADH is a major stimulus for cAMP production in the kidney via V2: tolvaptan 39
- 40. Adverse Effects Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: caused by Li+ Can be treated with thiazides & amiloride HCTZ causes ed osmolality in the inner medulla (papilla) & a partial correction of the Li+-induced reduction in aquaporin-2 expression Amiloride blocks Li+ entry into collecting duct cells & reverses Li+- induced polyuria Acute renal failure: Li+ & demeclocycline Chronic interstitial nephritis: in long-term Li+ therapy Hypotension & elevation in liver function tests: tolvaptan 40
- 41. Adenosine A1-Receptor Antagonists Renal adenosine concentrations rise in response to hypoxia & ATP consumption In the hypoxic kidney, adenosine actually decreases blood flow and GFR Adenosine increases Na+ reabsorption from the reduced flow in the cortex, so that delivery to medullary segments will be even further reduced 41
- 42. Adenosine is known to affect ion transport in the PCT, the medullary TAL, and collecting tubules Reduces blood flow to the glomerulus & GFR via A1 receptors on the afferent arteriole Is also the key signaling molecule in the process of tubuloglomerular feedback (TGF) 42
- 43. Adenosine A1–Receptor Antagonists Prevent tubuloglomerular feedback Interfere with the activation of Na+/H+ exchanger in the PCT Interfere the adenosine-mediated enhancement of collecting tubule K+ secretion (K-sparing) Several naturally occurring methylxanthines (e.g., caffeine, theophylline, and theobromine) are A1 receptor antagonists (albeit nonselective) and consequently cause diuresis 43
- 44. Pamabrom: Is a mild diuretic consisting of a one-to-one mixture of 8- bromotheophylline & 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol 8-bromotheophylline (a methylxanthine), is the active component of pamabrom Use: for the treatment of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms (water weight gain, bloating, swelling, muscle cramps/pan, tension, fullness feeling) Works by increasing the production of urine which eliminates unwanted water retention 44
- 45. ADH/AVP (Vasopressin) Agonists Vasopressin & desmopressin are used in the treatment of central diabetes insipidus DI is due to either deficient production of ADH (neurogenic or central DI) or inadequate responsiveness to ADH (nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI)) 45
- 46. ADH secretion is regulated by serum osmolality & by volume status AQP2, apical aquaporin water channels AQP3,4, basolateral aquaporin water channels V2, vasopressin V2 receptor 46
- 47. V2 Receptor Agonist: Vasopressin Major Therapeutic Uses V1 receptors cause GI & vascular smooth muscle contraction Postoperative abdominal distention Abdominal roentgenography (X-ray) Bleeding, cardiac arrest, hypovolemic shock Contraindicated in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus Not for long-term therapy of central diabetes insipidus Use with extreme caution in patients with vascular disease 47
- 48. V2 Receptor Agonist: Desmopressin V2 receptors cause water conservation & release of blood coagulation factors (von Willebrand factor) Uses: Central diabetes insipidus (DOC) Primary nocturnal enuresis Prevention of blood loss in patients with specific bleeding disorders Can be administered orally at high doses ADR: water intoxication CI: in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus 48
- 49. Diuretic Resistance Is inability to reduce plasma sodium levels despite using full therapeutic dose of diuretics Could be due to multiple reasons like higher sodium intake, reduced absorption of the diuretic, inadequate renal blood flow as in CCF leading to lower amounts of it reaching the kidney Chronic renal failure & nephrotic syndrome patients may also be refractory to diuretics 49
- 50. Diuretic resistance may be managed with: Upgradation from a lower to a higher efficacy diuretic Using a suitable combination Reduced salt intake Timing the diuretic intake 30 – 60 minutes before food also works because renal diuretic levels would be high enough to avoid slat retention Avoid NSAIDs, b/c they can cause salt & water retention & are a common cause of diuretic resistance 50
- 51. Drug Interactions with Diuretics Hypokalaemia induced by diuretics enhance digitalis toxicity NSAIDs blunt the effect of diuretics b/c of inhibition of PG synthesis in the kidneys Diuretics enhance lithium toxicity by reducing renal excretion of lithium Drugs that cause hyperkalemia (ACEIs/ARBs) & oral K+ supplements should be avoided with K+ sparing diuretics 51
- 52. Diuretics potentiate the antihypertensive effects of drugs used in hypertension Probenecid competes with furosemide & thiazides for tubular secretion & counter their diuretic effect as smaller amounts of these diuretics reach the tubular fluid Diuretics also counter the uricosuric effects of probenecid as they cause hyperuricemia 52
- 53. Contraindications for Diuretics Toxaemia of pregnancy (preeclampsia): Diuresis induced in pregnancy results in reduced fetal circulation which may result in fetal death Hence diuretics are contraindicated in pregnancy-induced hypertension Hepatic cirrhosis: diuretics can cause mental disturbances & hepatic coma in cirrhosis patients The combined effect of raised NH3 levels, alkalosis & hypokalemia may be responsible for this Cautiously used! 53
Notas del editor
- Pi: inorganic phosphate (HPO42-, H2PO4-), EPO: Erythropoietin Nephrons: epithelial tubes, NTs: neurotransmitters
- The glomerular capillary membrane is similar to that of other capillaries, except that it has three (instead of the usual two) major layers: (1) the endothelium of the capillary, (2) a basement membrane, and (3) a layer of epithelial cells (podocytes) surrounding the outer surface of the capillary basement membrane.
- ECF excessive extracellular fluid
- Actions of Diuretics at the Various Renal Tubular Segments
- True thiazide diuretics are derivatives of sulfonamides (sulfonamide diuretics). Many also inhibit carbonic anhydrase, resulting in diminished bicarbonate (HCO3 2) Reabsorption by the proximal tubule. 2. Specific agents a. Prototype true thiazides include chlorothiazide and hydrochlorothiazide. Other agents include methyclothiazide. Chlorothiazide is the only thiazide available for parenteral use.
- Carbonic anhydrase is present in the nephron, ciliary body of the eyes, gastric mucosa, pancreas and other sites.
- Inhibition of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase increases the concentration of hydrogen ions intracellularly and decreases the pH. The potassium ions shift to the extracellular compartment to buffer the acid-base status. This event results in hyperpolarization and an increase in seizure threshold of the cells. Eye: The ciliary body of the eye secretes bicarbonate into the aqueous humour. Carbonic anhydrase inhibition results in decreased formation of aqueous humour and thereby reduces intraocular pressure. 2. Brain: Bicarbonate is secreted into CSF and carbonic anhydrase inhibition reduces the formation of CSF.
- Metabolic alkalosis is generally treated by correction of abnormalities in total body K+, intravascular volume, or mineralocorticoid levels. However, when the alkalosis is due to excessive use of diuretics in patients with severe heart failure, replacement of intravascular volume may be contraindicated. In these cases, acetazolamide can be useful in correcting the alkalosis as well as producing a small additional diuresis for correction of volume overload. Patients experiencing a sulfonamide antimicrobial allergy may experience a variety of clinical manifestations. These may include hypersensitivity reactions from each of the Gel and Coombs classifications. Type 1 immunoglubulin E (IgE)-mediated reactions result in manifestations such as anaphylaxis, angioedema, and urticaria [2]. Regarding IgE-mediated type 1 reactions, it is important to note that the sulfonamide-defining NH2-SO2 moiety has not been found to be bound by IgE. Instead, the N1 heterocyclic ring has been found to be recognized by IgE, especially if a methyl group is in the position on the isoxazole ring. Non-type 1 reactions are mediated by three potential mechanisms: (1) the parent molecule or reactive metabolites acting as haptens; (2) the molecule binding to a native protein stimulating a cellular or humoral immune response, or (3) a cellular protein causing direct cytotoxicity, or stimulation of T-cells to produce an immune response
- TALH: thick ascending loop Henle
- Furosemide and bumetanide contain a sulfonamide moiety. Ethacrynic acid is a phenoxyacetic acid derivative; torsemide is a sulfonylurea. Furosemide and bumetanide are available as oral and injectable formulations. Torsemide is available as an oral formulation; ethacrynate sodium is a available as an injectable solution and ethacrynic acid as an oral tablet.
- LVF: left ventricular failure. Acute pulmonary oedema and acute LVF: It is quickly relieved by IV frusemide due to its immediate vasodilator effect and then by diuretic action.
- Tinnitus: ringing or buzzing in the ears. Vertigo: loss of balance
- CA: carbonic anhydrase.
- Thiazide and thiazide‐type diuretics increase urinary excretion of Mg2+ via a poorly understood mechanism possibly involving the reduced Mg2+ channel abundance. This effect may lead to a mild magnesuria, and long‐term use of the drugs may cause magnesium deficiency, particularly in the elderly. Due to volume depletion reflex RAAS & SNS activation occur.. Due to both impaired insulin release & reduced sensitivity Thiazides stimulate ATP-sensitive K+ channels & cause hyperpolarization of beta cells → inhibiting insulin release
- ABI: acute brain injury
- However, in the case of Li+-induced NDI, it is now known that HCTZ causes increased osmolality in the inner medulla (papilla) and a partial correction of the Li+-induced reduction in aquaporin-2 expression. HCTZ also leads to increased expression of Na+ transporters in the DCT and CCT segments of the nephron.
- As in all tissues, renal adenosine concentrations rise in response to hypoxia and ATP consumption. In most tissues, hypoxia results in compensatory vasodilation and, if cardiac output is sufficient, increased blood flow. The kidney has different requirements because increased blood flow leads to an increase in GFR and greater solute delivery to the tubules. This increased delivery would increase tubule work and ATP consumption. In contrast, in the hypoxic kidney, adenosine actually decreases blood flow and GFR. Because the medulla is always more hypoxic than the cortex, adenosine increases Na + reabsorption from the reduced flow in the cortex, so that delivery to medullary segments will be even further reduced.
- Four distinct adenosine receptors (A1 , A2a , A2b , and A3 ), in the kidney. However, probably only A1 is importance for the pharmacology of diuretics The adenosine A1 receptor is found on The pre-glomerular afferent arteriole, PCT other tubule segments.
- more selective A1 antagonist, rolofylline, was recently withdrawn from study because of CNS toxicity and unexpected negative effects on GFR. However, newer adenosine inhibitors that are much more potent and more specific have been synthesized. Several of these (Aventri [BG9928], SLV320, and BG9719) are under study and if found to be less toxic than rolofylline, may become available as diuretics that avoid the diuretic effects of K + wasting and decreased GFR resulting from tubuloglomerular feedback.
- Thiazide diuretics can reduce polyuria and polydipsia in both types of diabetes insipidus (DI). Lithium, used in the treatment of manic-depressive disorder, is a common cause of NDI, and thiazide diuretics have been found to be very helpful in treating it. This seemingly paradoxic beneficial. However, in the case of Li + -induced NDI, it is now known that HCTZ causes increased osmolality in the inner medulla (papilla) and a partial correction of the Li + -induced reduction in aquaporin-2 expression. HCTZ also leads to increased expression of Na + transporters in the DCT and CCT segments of the nephron. Thus, the maximum volume of dilute urine that can be produced is significantly reduced in NDI. Dietary sodium restriction can potentiate the beneficial effects of thiazides on urine volume in this setting. Serum Li + levels must be carefully monitored in these patients, because diuretics may reduce renal clearance of Li + and raise plasma Li + levels into the toxic range.
- V1 receptor–mediated therapeutic applications are based on the rationale that V1 receptors cause GI and vascular smooth muscle contraction.
- V2 receptor–mediated therapeutic applications are based on the rationale V2 receptors cause water conservation and release of blood coagulation factors.
