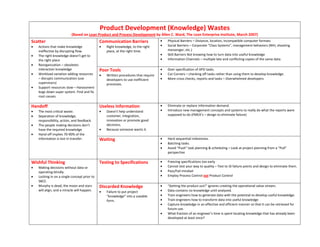
Product Development Wastes Lpds
- 1. Product Development (Knowledge) Wastes (Based on Lean Product and Process Development by Allen C. Ward, The Lean Enterprise Institute, March 2007) Scatter Communication Barriers Physical Barriers – Distance, location, incompatible computer formats Actions that make knowledge Right knowledge, to the right Social Barriers – Corporate “Class Systems”, management behaviors (NIH, shooting ineffective by disrupting flow. place, at the right time. messenger, etc.) Skill Barriers Not knowing how to turn data into useful knowledge The right knowledge doesn’t get to the right place Information Channels – multiple late and conflicting copies of the same data. Reorganization – obsoletes interaction knowledge Poor Tools Over specification of APD tasks. Workload variation adding resources Written procedures that require Cut Corners – checking off tasks rather than using them to develop knowledge. – disrupts communication (use developers to use inefficient More cross checks, reports and tasks – Overwhelmed developers supervisors) processes. Support resources slow – Harassment bogs down super system. Find and fix root causes. Handoff Useless Information Eliminate or replace information demand. The most critical waste. Doesn’t help understand Introduce new management concepts and systems to really do what the reports were Separation of knowledge, customer, integration, supposed to do (FMEA’s – design to eliminate failure) responsibility, action, and feedback. innovation or promote good The people making decisions don’t decisions. have the required knowledge Because someone wants it. Hand‐off implies 70‐90% of the information is lost in transfer. Waiting Hard sequential milestones. Batching tasks. Avoid “Push” task planning & scheduling – Look at project planning from a “Pull” perspective Wishful Thinking Testing to Specifications Freezing specifications too early Making decisions without data or Cannot test your way to quality – Test to ID failure points and design to eliminate them. operating blindly. Pass/Fail mindset Locking in on a single concept prior to Employ Process Control not Product Control SBCE. Murphy is dead, the moon and stars Discarded Knowledge “Getting the product out!” ignores creating the operational value stream. will align, and a miracle will happen. Failure to put project Data contains no knowledge until analyzed. “knowledge” into a useable Train engineers how to generate data with the potential to develop useful knowledge. form. Train engineers how to transform data into useful knowledge Capture knowledge in an effective and efficient manner so that It can be retrieved for future use. What fraction of an engineer’s time is spent locating knowledge that has already been developed at least once?
