Viruses
- 1. Types of Microbes 1 VIRUSES
- 2. WHAT IS A VIRUS? • A tiny, NON-LIVING particle that enters and then reproduces inside a living cell. • No organisms or cells are safe from viruses. All can be infected by a virus.
- 3. Characteristics of Viruses Viruses are NON-LIVING because: 1. They do not use their own energy to grow or respond to the environment. 2. They cannot make food, eat food, or produce waste.
- 4. Characteristics of Viruses • Viruses can ONLY multiply inside of a living cell. • A HOST is an organism that provides a source of energy for a virus or another organism. • A PARASITE is an organism that lives on or in a host and causes it harm.
- 5. Characteristics of Viruses • A virus is a parasite because almost all viruses destroy the cell in which it multiplies. It causes the host harm and that is the definition of a parasite.
- 6. Virus Shapes • Some of the shapes of viruses are: round, rod-shaped, brick shaped, thread shaped, bullet shaped, robot shaped.
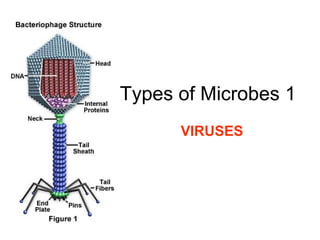
- 8. Virus Shapes • A BACTERIOPHAGE is a virus that infects bacteria. The word itself means “bacteria eater”
- 9. Virus Sizes • A virus is smaller than a cell (animal, plant or bacteria) • A NANOMETER (nm) = 1 billionth of a meter. • Diameter of the smallest virus = 20 nm • Diameter of the largest virus = 200 nm
- 10. DIAMETER Virus The DIAMETER is the length of the dashed red line.
- 12. Naming Viruses Scientists name viruses a number of ways: 1. Named after the disease they cause 2. Named after the organisms they infect 3. Named after the place where it was first found 4. Named after people
- 13. The Structure of Viruses The 2 basic parts of a virus are: 1. PROTEIN COAT that protects the virus 2. INNER CORE made of genetic material (DNA) Some viruses are surrounded by an outer membrane or envelope.
- 14. The Structure of Viruses • The proteins in a virus help to invade the host cell. • Viruses only connect to certain host cells because each virus has unique proteins that allow it to attach to only certain host cells. Its like a key (virus surface proteins) that only fit a certain lock (host cell surface proteins). Viruses won’t fit the lock on all host cells, only a specific few.
- 15. The Structure of Viruses KEY LOCK HOST CELL BRICK SHAPED VIRUS Virus surface protein Host cell’s surface protein
- 16. The Structure of Viruses
- 17. HOW VIRUSES MULTIPLY • Once a virus attaches to a host cell, it enters the cell. • Once inside the host cell, the virus’s genetic material takes over the cell’s functions. It tells the cell to produce the virus’s proteins and genetic material so that more viruses can be made.
- 18. Active Viruses Once inside the host cell, an Active Virus starts taking over: 1. The virus’s DNA takes over the cell’s functions 2. The host cell makes more of the virus’s proteins and DNA 3. New Viruses are made. 4. This continues over and over again until…. The cell fills up with viruses and bursts. 5. Hundreds of new viruses are free to find more cells.
- 19. Active Virus
- 20. Hidden Viruses Once inside the host cell, a Hidden virus hides for awhile inside the host: 1. The virus’s DNA becomes part of the host cell’s DNA 2. The virus hides out, not doing anything sometimes for years. 3. Every time the host cell divides, the virus’s DNA is copied along with the host cell’s DNA 4. Under certain circumstances, the virus’s DNA becomes active. 5. Then the Hidden Virus becomes an Active Virus and does the same thing an Active Virus does. 6. After an active period, it becomes a Hidden Virus again.
- 21. Hidden Virus
