Sci q3 b human reproduction
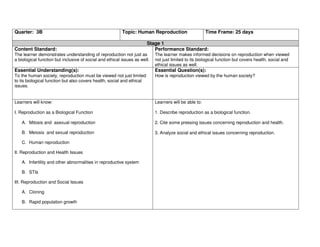
- 1. Quarter: 3B Topic: Human Reproduction Time Frame: 25 days Stage 1 Content Standard: Performance Standard: The learner demonstrates understanding of reproduction not just as The learner makes informed decisions on reproduction when viewed a biological function but inclusive of social and ethical issues as well. not just limited to its biological function but covers health, social and ethical issues as well. Essential Understanding(s): Essential Question(s): To the human society, reproduction must be viewed not just limited How is reproduction viewed by the human society? to its biological function but also covers health, social and ethical issues. Learners will know: Learners will be able to: I. Reproduction as a Biological Function 1. Describe reproduction as a biological function. A. Mitosis and asexual reproduction 2. Cite some pressing issues concerning reproduction and health. B. Meiosis and sexual reproduction 3. Analyze social and ethical issues concerning reproduction. C. Human reproduction II. Reproduction and Health Issues A. Infertility and other abnormalities in reproductive system B. STIs III. Reproduction and Social Issues A. Cloning B. Rapid population growth
- 2. C. Use of infertility drugs IV. Reproduction and Ethical Issues A. In vitro fertilization as used beyond health reasons B. Artificial insemination and surrogate motherhood as applied to humans C. Abortion, early and unwanted pregnancy Stage 2 Product or Performance Task: Evidence at the level of understanding Evidence at the level of performance Making informed decisions on reproduction EXPLANATION Performance assessment on the learner’s when viewed not just limited to its biological decision on matters pertaining to reproduction function but covers health, social and ethical Describe reproduction as a biological function based on the following criteria: issues as well Criteria: a. Informed a. Thorough b. Inclusive of health, social and ethical issues b. Clear c. Justifiable INTERPRETATION Document how the reproductive system is affected by certain diseases categorized as a) genetic b) cancers c) infections d) functional problem caused by environmental problems
- 3. Criteria: a. Meaningful b. Illustrative APPLICATION Propose how understanding of reproduction can be used as basis in developing advocacy materials Criteria: a. Appropriate b. Practical PERSPECTIVE Infer how recent technologies promote and improve the existing knowledge on reproduction. Criteria: a. Insightful b. Credible c. Reflective of critical thinking
- 4. EMPATHY Assume the role of a gynecologist counseling patients with problems regarding the reproductive system. Criteria: a. Sensitive b. Responsive SELF-KNOWLEDGE Realize how one is influenced by the broader understanding of reproduction which covers its biological function as well as health, social and ethical issues. Criteria: a. Reflective b. Responsive
- 5. Stage 3 Teaching/Learning Sequence: EXPLORE: As part of initial activities, learners shall be given an overview of reproduction, what they are expected to learn and how their learning shall be assessed. In this stage, diagnosis of their understanding of the reproductive system gained from elementary science shall form part of the prerequisites. Learners shall: 1. undergo an assessment to diagnose what they learned previously on reproduction (Suggestion: Greater emphasis is focused on the human reproductive system and concepts on reproductive health learned in elementary science and Q2 of MAPEH II respectively. Results of this diagnosis shall be used to determine the prior knowledge and/or alternative conceptions, if there are any. Relate it to the present content. Teachers can use graphic organizers, Cluster/Word Web1, video presentation of the reproductive parts of human organ systems. Learners work on attached suggested activity R # 1.) 2. be given time to formulate questions on reproduction and cluster these to initially find out what is/are interesting to them (Suggestion: KWAL, Focus Group Discussion, brainstorming, think-pair & square, dyads, round robin, etc. Learners work on the attached activity R2.) 3. be given time to formulate other questions leading to the Essential Question focusing on the usefulness of acquiring knowledge on reproduction
- 6. (Suggested Strategies: brainstorming, think-pair & square, dyads, round robin, etc.) 4. generate as many tentative ideas (TI) related to the Essential Question (EQ) as possible to show what they already know about the usefulness or non-usefulness of reproduction (Suggested Strategies: brainstorming, Focus Group Discussion, graphic organizer, concept mapping, etc. At this point, the teacher should be careful not to reject learners’ opinion but shall encourage them to give their ideas without being judged as right or wrong. Each tentative idea (TI) shall be written on the board.) 5. be grouped accordingly to choose some of the identified prior knowledge/ prior knowledge and tentative ideas (TI) (Suggested Strategies: Whatever each group of learners selected, the group shall be asked to challenge or explore the validity of these prior knowledge or tentative ideas during the Firm Up Stage.) 6. be oriented that they need to show their understanding of reproduction not just as a biological function but inclusive of social and ethical issues as well (Suggested Strategies: Learners may explore the internet and other available resources, brain storming, dyads, round robin, etc.) 7. be informed that learner’s decision on matters pertaining to reproduction is based on the following criteria: a.) Informed b.) Inclusive of health, social and ethical issues (Suggested Strategies: Brainstorming may be used to discuss how these criteria shall be used. Learners need to be clarified on the details on how their performance shall be assessed. Such details of criteria may be revised based on agreements reached.)
- 7. FIRM UP Varied learning experiences shall be introduced to help learners disprove alternative conceptions, examine/assess prior knowledge and begin to discover the relevance of tentative ideas (TI) to the EQ; make their understanding of reproduction thorough; equip them with skills and knowledge; and undergo differentiated instruction to address their unique strengths and needs. This involves acquiring scientific knowledge which is about accessing information, i.e., what information is needed, where information can be located and how information can be gathered focusing on reproduction. This also involves understanding or making meanings out of the scientific knowledge obtained. I. Reproduction as a Biological Function (Main Idea: Reproduction is the biological process by which new ("offspring" individual organisms) are produced from their "parents". Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual organism exists as the result of reproduction. The known methods of reproduction are broadly grouped into two main types: sexual and asexual. ) A. Mitosis and asexual reproduction Using the chosen prior knowledge, alternative conceptions and/or tentative ideas (TI) related to the EQ as starting/focal points of investigation, learners shall: 1. describe how mitosis results to asexual reproduction (Main Idea: In asexual reproduction, one individual produces offspring that are genetically identical to itself. These offspring are produced by mitosis. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. Learners work on the attached suggested activity R # 3.) (Suggestion: Include viewing of video clip on asexual reproduction followed by group discussion; documentation of asexual reproduction in lower forms of organisms; conduct of laboratory activities; plant reproduction is not included
- 8. since it was already discussed in Q2.) (Suggested Activities: Search the internet and textbooks .Learners will observe some asexual reproduction in the classroom. They will compare their observations to the real specimen, photographs and diagrams of organisms that reproduce asexually including fission, budding, fragmentation and parthenogenesis, spore formation and autotomy. Learners work on attached suggested activity R # 3.) 2. revisit prior knowledge, and/or TI on asexual reproduction, if any (Suggestion: The teacher may ask each group of learners to discuss those prior knowledge, alternative conceptions and/or tentative ideas.) B. Meiosis and sexual reproduction Using the chosen prior knowledge, alternative conceptions and/or tentative ideas (TI) related to the EQ as starting/focal points of investigation, learners shall: 3. describe the importance of the meiosis in gamete formation (Main idea: Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. In animals, meiosis produces gametes like sperm and egg cells, while in other organisms like fungi it generates spores. In many organisms, including humans, meiosis begins with one cell containing two copies of each chromosome—one from the organism's mother and one from its father—and produces four gamete cells containing one copy of each chromosome. Each of the resulting chromosomes in the gamete cells is a unique mixture of maternal and paternal DNA, ensuring that offspring are genetically distinct from either parent. ) (Suggested Strategies: FGD/ Group interview, use of checklist/ questionnaire, picture analysis, comparative analysis, etc) (Suggested Activities: Learners construct a flip book that shows the stages of meiosis, use available ICT materials about gamete formation. Learners work on attached the suggested activity R # 4a and 4b ) 4. compare different types of sexual reproduction in lower forms of life and in animals
- 9. (Main Idea: Types of sexual reproduction that happens in simple organisms like conjugation in bacteria, spirogyra, paramecium, etc. syngamy in sponges, hydra, planaria, earthworm, etc. (Suggested Strategies : actual observation, library/internet search, simulation, information gathering, oral/ visual Presentation) (Suggested Activities: Describe the sexual reproduction in lower forms of life. Illustrate some lower forms of life that perform sexual reproduction. Learners work on attached suggested activity R # 5 and 6. ) 5. revisit prior knowledge, and/or TI on sexual reproduction, if any C. Human reproduction Using the chosen prior knowledge, alternative conceptions and/or tentative ideas (TI) related to the EQ as starting/focal points of investigation, learners shall: 6. describe the menstrual cycle (Main Idea: The menstrual cycle is the series of changes that human female’s body goes through to prepare for a possible pregnancy. About once a month, the uterus grows a new, thickened lining [endometrium] that can hold a fertilized egg. When there is no fertilized egg to start a pregnancy, the uterus then sheds its lining. This is the monthly menstrual bleeding [also called menstruation or menstrual period] that women have from their early teen years until their menstrual periods end at around age 50 [menopause]. Include in the discussion uterine and ovarian cycle and the role of hormones in each event.) (Suggested Strategies: Use of ICT materials, concept mapping, library work, include viewing of video clip on menstrual cycle. (Suggested Activities: Learners trace the menstrual cycle. Describe each cycle and the role of hormones involved in it. Learners work on the attached suggested activity R #7. ) 7. describe the process of fertilization
- 10. (Main Idea: Fertilization is the fusion of egg and sperm, which usually takes place in the fallopian tube. After fertilization takes place, the fertilized egg moves toward the uterus.) (Suggested Strategies: discussion of alternative conceptions about number of sperm that can fertilize an egg cell, motility of sperm and the conditions of the female tract) (Suggested Activities: Learners will draw the process of fertilization using a given article. Learners work on the attached suggested activity R # 8. ) 8. trace the development of the zygote up to the fetal stage (Main Ideas: In animals, the development of the zygote into an embryo proceeds through specific recognizable stages of blastula, gastrula, and organogenesis. The blastula stage typically features a fluid-filled cavity, the blastocoel, surrounded by a sphere or sheet of cells, also called blastomeres. The embryo of a placental mammal is defined as the organism between the first division of the zygote (a fertilized ovum) until it becomes a fetus. In humans, the embryo is defined as the product of conception from implantation in the uterus through the eighth week of development.) (Suggested Strategies: library/internet search, role play, simulation, information gathering, oral/visual presentation.) (Suggested Activities: Learners work on the attached suggested activity R # 9.) 9. revisit prior knowledge, and/or TI on meiosis, fertilization and development of embryo, if any. (Suggested Strategies: The teacher may ask each group of learners to discuss those prior knowledge, alternative conceptions and/or tentative ideas.) II. Reproduction and Health Issues A. Infertility and other abnormalities in reproductive system
- 11. (Main Ideas: Infertility is defined as the inability for a couple to become pregnant after a year of unprotected intercourse. The male partner, the female partner, or both may have a fertility problem.A person who is infertile has a reduced ability to have a child. It usually does not mean a person is sterile -- that is, physically unable ever to have a child.) Using the chosen prior knowledge, alternative conceptions and/or tentative ideas (TI) related to the EQ as starting/focal points of investigation, learners shall: 10. identify the causes and risks of the abnormalities in the male and female reproductive system and cite ways how to prevent them (Main Ideas: Men and women are equally likely to have a fertility problem. In about 1 in 5 infertile couples, both partners have contributing problems and, in about 15% of couples, no cause is found after all tests have been done, called "unexplained infertility”.) (Suggested Strategies: panel discussion, forum, concept mapping, workshop, reflection, use of resource persons, gap analysis, use of internet and other multimedia sources, brainstorming, etc.) (Suggested Activities : Learners make a research paper and interview their barangay health official about the causes and risks of the abnormalities in the male and female reproductive system and suggest ways to prevent it. Learners work on the attached suggested activity R # 10 ) 11. revisit prior knowledge, and/or TI on infertility and other abnormalities in the reproductive system, if any (Suggested Strategies: The teacher may ask each group of learners to discuss those prior knowledge, alternative conceptions and /or tentative ideas.) B. Sexually transmitted infections ( STIs ) Using the chosen prior knowledge, alternative conceptions and/or tentative ideas (TI) related to the EQ as starting/focal points of investigation, learners shall:
- 12. 12.investigate common sexually transmitted infections (Main Ideas: In 2010 sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) have become very common. This is undoubtedly true because more and more people are having immoral sex lives – often with several partners.) (Suggested Strategies: FGD/ Group interview, actual observation, use of checklist/ questionnaire, picture analysis, comparative analysis, noting details, etc.) (Suggested Activities: Conduct research on the characteristics of various sexually transmitted diseases. Learners will present the information on the disease through role-playing a scene with the doctor and a patient. Differentiated topics will be assigned to the group. Review statistics about teens and sexuality. Learners research the prevalence of sexually transmitted diseases STIs and write an informational brochure on STIs. In addition, they present their outputs to the class. Identify sources for accurate information about STIs.) 13. examine their personal responsibility in preventing the spread of STIs (Main Ideas: One of the daily worries of parents is keeping their children healthy and safe In today's world, where kids are bombarded with messages about sex constantly — online, in the media and from their friends — children need to learn more than ever and must have a personal responsibility in preventing the spread of STIs.) (Suggested Strategies: panel discussion, forum, concept mapping, workshop, reflection, use of resource persons, gap analysis, use of internet and other multimedia sources, brainstorming, etc) (Suggested Activities: Reflection paper, role playing and other activities may be done.) 14. revisit prior knowledge, and/or TI on STIs, if any (Suggested Strategies: The teacher may ask each group of learners to discuss those prior knowledge, alternative conceptions and /or tentative ideas.)
- 13. III. Reproduction and Social Issues A. Cloning Using the chosen prior knowledge, alternative conceptions and/or tentative ideas (TI) related to the EQ as starting/focal points of investigation, learners shall: 15.investigate the development of animal and human cloning (Main Ideas: Cloning in biology is the process of producing similar populations of genetically identical individuals that occurs in nature when organisms such as bacteria, insects or plants reproduce asexually.) (Suggested Strategies: use of internet, brainstorming, use of video footages, use research papers, etc) (Suggested Activities: Teacher could present a downloaded cloning simulation [http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/tech/cloning/clickandclone/] and perform the activity. The teacher may allow the students to watch/ click the activity until the offspring is born. Learners will identify the materials used in cloning and the steps involved. Explain how to create a clone. Draw the situations/events that happen to the cells involved. Learners work on the attached suggested activity R # 11.) Learners may report their finding both orally and visually to their colleagues at a classroom-based symposium on cloning research.) 16. investigate how cloning becomes a social issue (Main Ideas: Scientists have successfully cloned mice, sheep, and monkeys, raising questions as to whether humans could be next. In March 1997 President Bill Clinton banned the use of federal money for cloning humans and urged a moratorium on all human cloning research. In the following viewpoint, John F. Kilner supports Clinton’s actions and argues that human cloning should not be allowed. Cloning research, he asserts, would destroy the lives of human embryos and infants. In addition, he contends that making genetic copies of humans for utilitarian purposes is unethical and demeaning.) (Suggested Strategies: use of internet, brainstorming, use of video footages, use research papers, etc.)
- 14. (Suggested Activities: Students will review the concepts of cloning and participate in a round-table discussion based on the potential of cloning. Every learner should write an essay on the topic stemming from the discussion. Individually, the students keep a list of the articles related to cloning focusing on why it is a social issue.) 17. revisit prior knowledge, and/or TI on STIs, if any B. Rapid population growth Using the chosen prior knowledge, alternative conceptions and/or tentative ideas (TI) related to the EQ as starting/focal points of investigation, learners shall: 18. give some implications of rapid population growth (Main Ideas: While population growth is at times a beneficial thing for a species, there are many factors that define when growth becomes detrimental. When population growth becomes faster than the ecosystem’s natural resources can support there is a great chance that the counter-productive level has been reached. The most accurate index is the balance between population and sustainability.) (Suggested Strategies: reflection paper, role playing, etc.) (Suggested Activities: Learners discuss potential issues associated with the world’s growing population , evaluate public policy in the area of population growth, and make a variety of mathematical calculations designed to illustrate the current size and growth rate of the human population. They analyze a graph that shows human population growth over time.) 19. examine the laws concerning birth control (Main Ideas: Family planning involves decisions made by women and men concerning their reproductive lives and whether, when, and under what circumstances they have children. Family planning most often involves the decisions of whether to engage in sexual activity that could lead to pregnancy, whether to use birth control, and whether to terminate a pregnancy. Individuals faced with these decisions often rely on moral or religious beliefs. Because moral and religious beliefs vary, family planning laws are frequently controversial. )
- 15. (Suggested Strategies: FGD, interview, document analysis, etc.) (Suggested Activities: Learners express their opinions about control issues, explain and justify their opinions.) 20. debate about the proposed bill on reproductive health (Main Ideas: Within the framework of WHO's definition of health as a state of complete physical, mental and social well- being, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity, reproductive health addresses the reproductive processes, functions and system at all stages of life. Reproductive health, therefore, implies that people are able to have a responsible, satisfying and safe sex life and that they have the capability to reproduce and the freedom to decide if, when and how often to do so.) (Suggested Strategies: internet/library search, document analysis, brain storming, noting details, etc.) (Suggested Activities: Divide the class into four to five groups. Let them share what each one knows about RH bill and its highly debatable issue. Conduct discussion and group sharing. Learners work on the attached suggested activity R # 12) 21. revisit prior knowledge, and/or TI on STIs, if any C. Use of fertility drugs Using the chosen prior knowledge, alternative conceptions and/or tentative ideas (TI) related to the EQ as starting/focal points of investigation, learners shall: 22. analyze current and emerging techniques used to aid in conception. (Main Ideas: Having problems with fertility can be very frustrating. Even more frustrating can be the fact that most fertility specialists would not even consider testing a couple for problems with conception until they have been trying to conceive for very long time. In the interim, or even alongside fertility treatments, many couples have looked to other avenues to help aid
- 16. in conception. ) (Suggested Strategies: panel discussion, forum, concept mapping, workshop, reflection, use of resource persons, gap analysis, use of internet and other multimedia sources) (Suggested Activities: Learners may play the role of a doctor explaining the possible side effects of fertility drugs.) 23. determine how fertility drugs affect one’s health. (Main Ideas: Fertility drugs are medications that are used to influence ovulation. Some fertility drugs are meant to strengthen or trigger ovulation, while others suppress ovulation. Fertility drugs can also be used in men to treat male factor infertility, but this is less common. Side effects can include hot flushes and mood swings early in the cycle; and depression, nausea and breast tenderness later in the cycle. Severe headaches or visual problems, though rare, are indications to stop the medication.) (Suggested Strategies: use of internet and other multimedia sources, brainstorming, etc) (Suggested Activities: Provide with a real life example of research about women with multiple births. Learners may discuss case studies of women with multiple births and analyze the possible cause of it.) 24. revisit prior knowledge, and/or TI on STIs, if any IV. Reproduction and Ethical Issues A. In vitro fertilization as used beyond health reasons 25.investigate new tools, techniques and dilemmas presented by in vitro fertilization (Main Ideas: Since 1978 and Louise Brown's birth in Great Britain, this technique has greatly surpassed its initial purpose, specifically as a means to deal with tubal infertility. Today, more than half of all IVF procedures are performed for other reasons; for example, it is used in response to unexplained infertility and is used to increase the success rate in cases of male infertility.)
- 17. (Suggested Strategies: Document analysis, library/ internet search) (Suggested Activities: Learners may recognize dilemmas presented by in vitro fertilization. They analyze differing views of individuals towards in vitro fertilization. Learners in group may search on the article about the first test tube baby and have a brainstorming activity based on it. Learners work on the attached suggested activity R # 13A and 13B ) 26. revisit prior knowledge, and/or TI on STIs, if any B. Artificial insemination and surrogate motherhood as applied to humans Using the chosen prior knowledge, alternative conceptions and/or tentative ideas (TI) related to the EQ as starting/focal points of investigation, learners shall: 27. discuss the moral and ethical issues involved with the test tube babies (Main Ideas: IVF is the short form of in-vitro fertilization. In vitro means inside a glass and that is why babies born through this procedure are called test tube babies. It is a semi-artificial way of producing babies, and is mainly used by infertility clinics to help people who do not have children of their own. However the process has raised several concerns on moral and ethical grounds.) (Suggested Strategies: document analysis, library/ internet search, use of resource person, role playing, etc. ) (Suggested Activities: After having document analysis, library/ internet search, learners may conduct their own “symposium” in a class.) 28. analyze surrogacy and the existing laws (Main Ideas: Surrogacy is a relationship in which one woman bears and gives birth to a child for a person or a couple who then adopts or takes legal custody of the child; also called mothering by proxy. In surrogate motherhood, one woman acts as a surrogate, or replacement, mother for another woman, sometimes called the intended mother, who either cannot produce fertile eggs or cannot carry a pregnancy through to birth, or term. Medical science continues to devise new procedures and treatments that test the boundaries of law and ethics. Surrogate motherhood has both advocates and
- 18. detractors, each with strong arguments in their favor. A number of important questions lie at the heart of the debate over the ethics and legality of surrogacy. (Suggested Strategies: document analysis, library/ internet search, interview, movie review ) (Suggested Activities: Learners may conduct debates, skits and teen forums regarding the subject of surrogacy. Learners work on the attached suggested activity R # 14.) 29. revisit prior knowledge, and/or TI on STIs, if any C. Abortion, Early and Unwanted Pregnancy Using the chosen prior knowledge, alternative conceptions and/or tentative ideas (TI) related to the EQ as starting/focal points of investigation, learners shall: 3o. discuss scientific implication and ethical issues on abortion (Main Ideas: While infanticide is legally and socially treated as murder and few in our culture would approve of it, the killing of unborn infants [often called fetuses in order to still the conscience and minimize the social stigma] has become both legally and socially acceptable. For some women, unmarried and married, abortion is just another form of birth control.) (Suggested Strategies: movie review, library/ internet search, brain storming, video review, essay writing ) (Suggested Activities: Learners will watch videos of: flight of sperm to the egg [fertilization] to the development of a fetus; then followed by the videos of cases of abortion/aborted fetus. Group the learners into 5. Each group will answer questions based on the videos presented. Let the learners discuss the scientific implication and ethical issues on abortion to their group and report it to the class.) 31. realize the impact of premature parenthood on their future lives (Main Ideas: With the emerging problem of premarital sex also comes premature parenthood. Teenage parenthood ruins young people’s lives and those of their children, as well as threatening wider social and moral
- 19. breakdown.) (Suggested Strategies: interview, movie review “Katorse” played by Dina Bonnavie, Gabby Concepcion and Alfie Anido, discussion, library/internet search, noting details ) (Suggested Activities: Analyze demographic data relating to teen pregnancy trends. Learners develop skills to locate and interpret data. Discuss the factors that influence teenage pregnancy such as social, economic, and educational issues. Describe the current trend in the Philippine teen-pregnancy rate. After reading an article chronicling the decline in the teen pregnancy rate. Learners may brainstorm ideas as to why this has occurred. They list at least two barriers to teens assessing emergency contraception.) 32. revisit prior knowledge, and/or TI on STIs, if any DEEPEN Here, learners shall be engaged in understanding scientific knowledge which includes the processing and making meanings out of the information. Learners need to reflect, revisit, revise and rethink their ideas; express their understandings and engage in meaningful self-evaluation; and undergo in-depth exploration of reproduction using multiple sources of information and various modalities of manifesting learning. Learners shall: 1. record in their journal their thoughts regarding their personal responsibilities with regards to human reproduction ; and (Suggestion: Journals should be checked by the teacher and can be shared to their group mates.) At the level of understanding, learners shall: 2. describe reproduction as a biological function (FU: Explanation) (Suggested Activity: Ask learners to revisit the data from the previous activity done in items 9-11. This could be presented
- 20. through a panel discussion.) 3. document cases where the reproductive system is affected by certain diseases categorized as a) genetic b) cancers c) infections d) functional problem caused by environmental problems (Suggested Activity: interview, symposia, and fora) 4. propose how understanding of reproduction can be used as basis in developing advocacy materials (FU: Application) 5. infer how recent technologies promote and improve the existing knowledge of reproduction (FU: Perspective) 6. realize how one is influenced by the broader understanding of reproduction which covers biological function as well as health, social and ethical issues. (FU: Self-Knowledge) To draw out the essential understanding, learners shall: 7. contemplate on the essential question “How is reproduction viewed by the human society?” 8. reexamine their revised TI; and 9. justify their previous answers based on the understanding(s) gained. TRANSFER There is a need to encourage learners to organize their learning experiences so that they can move from teacher-guided and concrete activities to independent applications where they create or produce new knowledge in science. This is to challenge learners to transfer their learning in new settings and use this creatively to generate new ideas, view things differently and reengineer processes. Learners shall be involved in designing, constructing, planning, producing new knowledge and/or Learners shall: inventing products which can contribute to the protection of the environment and sustainable use of resources.
- 21. 1. Make an informed decision on reproduction when viewed not just limited to biological function but covers health, social and ethical issues as well 2.evaluate their product/ performance based on the following criteria: a) informed, b) inclusive of health, social and ethical issues Resources (Web sites, Software, etc.) • http://www.webmd.com/infertility-and-reproduction/guide/understanding-infertility-basics • http://www.netdoctor.co.uk/health_advice/facts/venerealdiseases.htm • http://www.enotes.com/social-issues-article/human-cloning-should-banned-45267 • http://www.ehow.com/about_5140073_effects-rapid-population-growth.html • http://www.enotes.com/everyday-law-encyclopedia/family-planning-abortion-birth-control • http://www.babyhopes.com/articles/vitamins-conception.html • http://sciencespot.net/Media/mitosisbook.pdf • http://www.who.int/topics/reproductive_health/en/ • http://www.woodrow.org/teachers/bi/1992/invitro_fertilization.html • http://www.homemorals.com/moral-value/health-ethics/Ivf-And-Ethics.html • http://legal-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/surrogacy • http://www.anabaptists.org/tracts/deathtrc.html • http://www2.lse.ac.uk/newsAndMedia/publications/books/2010/TeenageParenthood.aspx • http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/. • http://biology.about.com/od/basicgenetics/a/aa062708a.htm • http://www.surrogacy-surrogate-mother.com/baby-m-surrogacy-case.html • http://2010presidentiables.wordpress.com/reproductive-health-bill-5043/text-of-rh-bill-no-5043/ • http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/tech/cloning/clickandclone/ • Hands-On-Laboratory in Science Biology by Gonzaga, Peralta and De Guzman • Biology by Rabago, Joaquin and Lagunzad • CliffsStudySolver Biology by Max Retchman • Functional Biology Modular Approach by Rabago, Joaquin and Lagunzad • Teaching for Understanding based on UbD Functional Biology Modular Approach by Rabago, Joaquin and Lagunzad
- 22. • Biology a Guide to Natural World by David Krogh • Biology by Capco and Yang • Science and Technology II DepEd • Essentials of Biology Seventh Edition by Campbell and Reece • Prentice Hall Biology by Miller and Levine • Biology Laboratory Manual by Sylvia S. Mader Materials: • Microscope • Glass slide • Cover slip • Wet mount of yeast • Moldy bread • Illustrations/photograph of organisms performing asexual reproduction • Flip book • Meiosis template(diagram master) • Pencil coloring materials • scissors
