Esophagus /certified fixed orthodontic courses by Indian dental academy
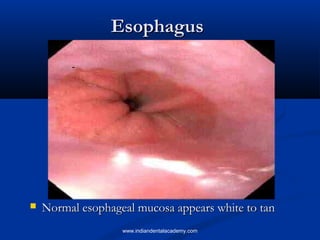
- 1. Esophagus Normal esophageal mucosa appears white to tan www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 2. INDIAN DENTAL ACADEMY Leader in continuing dental education www.indiandentalacademy.com www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 3. Esophageal mucosa is lined by non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium www.indiandentalacademy.com Gastric mucosa is lined by columnar glandular epithelium
- 4. Selected disorders of the esophagus Motor disorders: Achalasia Mechanical injury: Lacerations (Mallory-Weiss syndrome) Varices Esophagitis: Reflux, infections, drugs, irradiation Barrett’s esophagus Malignant neoplasms www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 5. Achalasia (failure to relax) Incomplete relaxation of lower sphincter during swallowing leading to functional obstruction and proximal dilatation Aperistalsis, incomplete relaxation, increased resting tone Ganglion cells of the myenteric plexus are diminished or absent Loss of inhibitory innervation to the sphincter Clinical picture: dysphagia, regurgitation and aspiration Histology: Inflammation in the area of M. plexus Hypotheses: autoimmune, viral infections May occur secondary to Trypanosoma cruzi infection (Chagas disease) 5% develop squamous cell carcinoma, at younger age www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 6. Esophageal lacerations (MalloryWeiss syndrome) Longitudinal tears at the gastroesophageal junction Clinical setting: chronic alcoholics after a bout of severe vomiting Tear may be superficial or deep affecting all layers Clinical picture: Pain, bleeding, superimposed infection Hiatal hernia is found in 75% of patients Most often bleeding stops w/o intervention, but lifethreatening hematemesis may occur. Supportive therapy and balloon tamponade. Healing is prompt with minimal or no residue www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 7. Hiatal hernia Dilatation of the space between the diaphragmatic muscles which permits a dilated segment of the stomach to protrude above the diaphragm. 95% 5% 1-20% of adult subjects; only 9% of those affected suffer from heartburn www.indiandentalacademy.com and reflux esophagitis; complications may include ulceration and bleeding
- 8. Esophagitis Reflux esophagitis Infections Crohn disease, acute graft versus host disease Prolonged gastric intubation Ingestion of irritant substance Chemotherapy and irradiation www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 9. Reflux esophagitis Reflux of gastric contents into esophagus Possible etiologies: inadequate function of lower sphincter; sliding hiatal hernia CP: “heart burn” Complications: ulceration, bleeding, stricture, Barrett esophagus www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 10. Infection-induced esophagitis More common in patients with impaired immunity Fungal : Candida Viruses: Herpes and Cytomegalovirus www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 11. Barrett esophagus A complication of long standing reflux esophagitis Replacement of squamous epithelium by columnar epithelium with goblet cells 30- to 40-fold greater risk to develop adenocarcinoma www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 12. Esophageal varices Tortuous dilated veins in the submucosa of distal esophagus www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 13. Esophageal varices Etiology: portal hypertension secondary to liver cirrhosis Asymptomatic until they rupture leading to massive hemorrhage 50% subsides spontaneously 20-30% die during the first episode Rebleeding occurs in 70% of cases within one year www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 14. Esophageal carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma More prevalent worldwide Risk factors: long-standing esophagitis, achalasia, smoking, alcohol, diet (low vitamins and zinc), genetics 50% in middle 1/3 Adenocarcinoma More common in USA Occurs on top of Barrett esophagus More in distal 1/3 www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 15. Stomach 2 1 3 1) Cardia 2) Body: Parietal and Chief cells 3) Antrum: Mucin secretion and Gcells that secrete gastrin www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 16. Selected disorders of the stomach Gastritis Peptic ulcers Gastric cancer www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 17. Chronic Gastritis Infiltration of the mucosa by chronic inflammatory cells (lymphocytes and plasma cells) Causes: Helicobacter pylori: G-ve bacilli; Noble prize in Medicine 2005, for Barry Marshal & Robin Warren Autoimmune: rare in USA, autoantibodies to parietal cells (decreased acid and intrinsic factor) Helicobacter pylori is present in 70-90% of patients with gastric and duodenal ulcers, respectively Look for intestinal (goblet cell) metaplasia as a precancerous lesion www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 18. Helicobacter pylori and associated disorders H. pylori Gastric ulcer Gastritis (chronic and acute), peptic (gastric and duodenal) ulcers Gastric adenocarcinoma, intestinal type Gastric lymphoma www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 19. Mechanisms of H. pylori-induced pathology Although the organism is not invasive, it induces intense inflammatory and immune response: cytokines and B-cell activation Enhances gastric acid secretion Bacterial products such as urease, lipases and proteases that induce epithelial injury www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 20. Acute gastritis “gastropathy” Injury to the gastric mucosa (erosions) with no significant participation of inflammatory cells Causes include: Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs Alcohol Hypovolemia Shock Stress Uremia Enterogastric reflux www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 21. Peptic ulcer Location: stomach or first portion of duodenum Life time risk is 10% in the USA More frequent in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic renal failure and hyperparathyroidism. Causes include: H. pylori and causes of acute gastritis (especially NSAID) Clinical features: Epigastric pain (worse at night and relieved by food), bleeding (30%) and perforation (5%; accounts for 2/3 of deaths). www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 22. Gastric cancer Intestinal-type: Risk factors: diet (nitrites, smoked food, increased salt), chronic gastritis (H. pylori), altered anatomy after resection On top of intestinal metaplasia Decreasing in incidence Glandular morphology Diffuse-type: Undefined risk factors ( no known relation to H. pylori) Signet cell morphology www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 23. Macroscopic growth patterns of gastric adenocarcinoma Mass Ulcer Lintis plastica Clinical picture: asymptomatic or abdominal discomfort, weight loss, anemia www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 24. Small and large bowel Developmental: Meckel diverticulum Vascular Diarrheal disease: Infections: viruses, bacteria, protozoa Idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease Malabsorption Diverticular disease Tumors www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 25. Meckel diverticulum Meckel diverticulum A blind pouch located in distal small bowel The most common congenital anomaly of the small intestine; results from failure of the involution of the omphalomesenteric (vitelline) duct The rule of 2’s: 2% of the population, 2 inches in length, 2 feet proximal to the ileocecal valve, 2 types of heterotopic tissue (pancreas and stomach); 2% are symptomatic. Symptoms are rare: Overgrowth of bacteria that depletes vitamin B12 leading to anemia “Peptic” ulcer and bleeding www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 26. Types and causes of diarrheal illness Secretory diarrhea: loss of intestinal fluid that is isotonic with plasma and persists during fasting Viruses: rotavirus: destroy the absorptive surface children 6-24 M of age, 130 million cases per year, fecal oral mode of transmission. Toxin-mediated: Vibrio cholera, E.coli (need time) Preformed toxin: Stapylococcus aureus (immediate effect) Excessive laxatives www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 27. Types and causes of diarrheal illness, continued Osmotic diarrhea: secondary to intraluminal fluids with high osmolarity; it abates with fasting. Specific therapies: Lactulose therapy: used for constipation and hepatic encephalopathy Gut lavage before endoscopy Antacids www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 28. Types and causes of diarrheal illness, continued Exudative diarrhea: pruluent bloody stool (inflammation of the mucosa and/or hemorrhage) Infections causing tissue damage: Shigella, Salmonella, Entamoeba histolytica Infections causing both tissue damage and toxins: Clostridium difficile; with antibiotic therapy, leading to pseudomembranous colitis Idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 29. Parasites Entamoeba histolytica: Invasive, amebic colitis and amebic liver abscesses Giardia lamblia: noninvasive, duodenum and jejunum, diarrhea and malabsorption Cryptosporidium: self-limited diarrhea in immunocompetent individuals; long course in AIDS patients Worms: uncommon in USA www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 30. Types and causes of diarrheal illness, continued Exudative diarrhea: pruluent bloody stool (inflammation of the mucosa and/or hemorrhage) Infections causing tissue damage: Shigella, Salmonella, Entamoeba histolytica Infections causing both tissue damage and toxins: Clostridium difficile; with antibiotic therapy, leading to pseudomembranous colitis Idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 31. Pseudomembranous colitis Membranes made of neutrophils and fibrin Seen in Cl. Difficile infection and in ischemia www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 32. Types and causes of diarrheal illness, continued Exudative diarrhea: pruluent bloody stool (inflammation of the mucosa and/or hemorrhage) Infections causing tissue damage: Shigella, Salmonella, Entamoeba histolytica Infections causing both tissue damage and toxins: Clostridium difficile; with antibiotic therapy, leading to pseudomembranous colitis Idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 33. Idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease Crohn disease Small bowel and colon (mostly right side) Patchy involvement Transmural inflammation, fistulas, strictures, serositis Non-caseating granulomas Poor response to surgery Increased risk for cancer Ulcerative colitis Colon only Continuous involvement Superficial inflammation No granulomas Good response to surgery Increased risk for cancer www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 34. Types and causes of diarrheal illness, continued Malabsorption diarrhea (steatorrhea): voluminous bulky stool with increased osmolarity resulting from unabsorbed nutrients and excess fat; usually abates on fasting. Malabsorption syndromes www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 35. Malabsorption syndromes Defective intraluminal digestion: pancreatic insufficiency Defective bile secretion Mucosal abnormalities: Disaccharide deficiency (lactose intolerance) Reduced surface area Gluten-sensitive enteropathy (Celiac disease) Surgical resection Infections: Tropical sprue, whipple disease www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 36. Selected malabsorption syndromes Gluten-sensitive enteropathy (celiac disease): 1:300 persons are affected, hypersensitivity to gliadin, a component of gluten (present in wheat flour) leading to blunted villi and increased intraepithelial lymphocytes. Increased risk for lymphoma. Tropical sprue: malabsorption and diarrhea after a visit to the tropics. Infectious etiology, responds to antibiotics. Whipple disease: systemic disease that affects GIT, nervous system and joints. Caused by T. whippelii (gram-positive actinomycete). www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 37. Clinical features of malabsorption syndromes Hematopietic system: Musculoskeletal system: Amenorrhea, impotence, infertility Skin: Osteopenia: calcium and vitamin D deficiency Endocrine system: Anemia: iron, folate and B12 deficiency Bleeding: vitamin K deficiency Purpura: vitamin K deficiency Dermatitis: vitamin A deficiency Nervous system: Peripheral neuropathy: folate and B12 deficiency. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 38. Diverticulosis Herniation of the mucosa and submucosa through the muscle wall 50% after age 50 Related to low-fiber diet, increased intraluminal pressure and focal defects in muscular layer Mostly in sigmoid colon Asymptomatic unless infected www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 39. Tumors of the large bowel Hyperplastic polyps: not precancerous Adenomatous polyps: precancerous Familial polyposis syndrome: Autosomal dominant; 500-2500 polyps, 100% risk for developing cancer; mutations in APC gene www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 40. Colonic adenocarcinoma: Almost always arises from adenomatous polyp Risk factors: low fiber, high fat, decreased vit A, C, E, idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease, familial adenomatous polyposis Several hits to different genes: APC, k-ras, p53; or DNA mismatch repair genes Survival depends on stage (depth of invasion and node metastasis) www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 41. Colonic adenocarcinoma Exophytic tumor leading to partial obstruction Clinical picture: Asymptomatic or fatigue, weakness and iron deficiency anemia in tumors of right side. Left sided tumors may produce bleeding, change in bowel habits and crampy pain www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 42. Colonic adenocarcinoma Course: tumor invades bowel wall and lymphatics/blood vessels with metastasis to lymph nodes, liver, lungs, and bones. 25% of patients have metastatic disease at presentation Diagnosis is based on endoscopy and biopsy Prognosis depends on stage (depth of invasion, nodal and distant metastasis), and 5-year survival varies from >90% in stage I, to 4% with distant metastasis. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 43. A 47-year-old man has a history of drinking 1 to 2 liters of whisky per day for the past 20 years. He has had numerous episodes of nausea and vomiting in the past 5 years. He experiences a bout of prolonged vomiting, followed by massive hematemesis. On physical examination in the emergency room, he has vital signs with T 36.8 C, P 110, RR 22, and BP 80/40 mm Hg. His heart has a regular rate and rhythm with no murmurs and his lungs are clear to auscultation. There is no abdominal tenderness or distension and bowel sounds are present. His stool is negative for occult blood. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Barrett’s esophagus Esophageal stricture Esophageal lacerations (Mallory Weiss syndrome) Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Achalasia www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 44. All these statements about Barrett’s esophagus are true, except: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. It is associated with 30- to 40-fold greater risk to develop adenocarcinoma It appears as salmon-pink mucosa on endoscopy It is associated with high risk for esophageal bleeding It represents replacement of the stratified squamous epithelium by columnar epithelium with goblet cells It could be a complication of long-standing reflux esophagitis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 45. All these statement about Helicobacter pylori are correct except: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. H. pylori organisms are Gram negative bacilli It is associated with intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma It is associated with gastric lymphoma It is associated with diffuse-type gastric adenocarcinoma It is associated with peptic ulcer www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 46. 1. 2. 3. 4. A 20-year-old man has noted cramping abdominal pain for the past week associated with fever and lowvolume diarrhea. On physical examination, there is right lower quadrant tenderness. Bowel sounds are present. His stool is positive for occult blood. A colonoscopy reveals mucosal edema and ulceration in the ascending colon, but the transverse and descending portions of the colon are not affected. Which of the following microscopic findings is most likely to be present in biopsies from his colon Entamoeba histolytica organisms Adenocarcinoma Non-caseating granulomas Diverticulosis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 47. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A 35-year-old woman has a 10 year history of intermittent, bloody diarrhea. She has no other major medical problems. On physical examination there are no lesions palpable on digital rectal examination, but a stool sample is positive for occult blood. Colonoscopy reveals a friable, erythematous mucosa with focal ulceration that extends from the rectum to the mid-transverse colon. Biopsies are taken and all reveal mucosal acute and chronic inflammation with crypt distortion, occasional crypt abscesses, and superficial mucosal ulceration. This patient is at risk for development of which of the following conditions? Diverticulitis Acute pancreatitis Colonic adenocarcinoma Peri-rectal fistula Appendicitis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 48. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A 25-year-old man complains of a low volume but chronic, foul smelling diarrhea for the past year. He has no nausea or vomiting. On physical examination there is no abdominal pain or masses and bowel sounds are present. His stool is negative for occult blood. Laboratory studies include a quantitative stool fat of 10 g/day. Upper GI endoscopy is performed with biopsies of the duodenum. The biopsies reveal the absence of villi, and increased surface intraepithelial lymphocytes. Which of the following therapies is most likely to be useful for this man? Antibiotics Anti-Entamoeba therapy Corticosteroids Gluten-free diet Surgical resection www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 49. Diseases of the liver Sherif Tawfic, MD, Ph.D. Surgical Pathology Fairview University Medical Center, and University of Minnesota tawfi001@umn.edu www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 50. Liver Normal liver has smooth brown surface Weight: 1200-1600 g Maintaining body metabolic homeostasis: Lipid and carbohydrate metabolism: production and secretion of glucose Protein synthesis: albumin, coagulation factors Detoxification and drug metabolism Conjugation and excretion of bilirubin Synthesis and excretion of bile salts www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 52. Patterns of hepatic injury Inflammation Steatosis: accumulation of fat droplets within hepatocytes Cell death: those cells closer to the central vein are more susceptible to ischemia, toxins and drugs leading to “centrilobular” necrosis Fibrosis: Irreversible, affect blood flow and hepatocyte function Cirrhosis: End stage liver disease with diffuse fibrosis and regenerating nodules www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 53. Steatosis Alcohol Obesity Diabetes Hyperlipidemia Clinical picture: Silent, or fatigue, malaise, right upper quadrant discomfort www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 54. Liver cirrhosis Definition: bridging fibrous septa and parenchymal nodules with disruption of architecture. End stage for many diseases affecting the liver Mechanism: cell death, regeneration and fibrosis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 55. Clinical consequences of liver disease (life-threatening complications are in yellow) Hepatic dysfunction: Decrease synthesis capacity leading to : Decrease detoxification capacity leading to: Hypoalbuminemia: edema, ascitis, muscle wasting, weight loss Hypoglycemia: weakness and syncope Coagulation factor deficiency: bleeding Hyperammonemia and increase toxic metabolites: Encephalopathy (altered behavior and disturbances in consciousness that may lead to deep coma and death) Injury to other organs by active toxins Hepatorenal syndrome: Renal failure without intrinsic or functional causes of renal failure. ? Altered blood flow to the kidney. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 56. Clinical consequences of liver disease, continued Jaundice: yellow discoloration of skin and sclera due to accumulation of bilirubin Cholestasis: systemic accumulation of bilirubin in addition to bile salts and cholesterol (usually secondary to obstruction) Portal hypertension in cirrhosis: increased resistance to portal blood flow Esophageal varices Ascitis Splenomegaly Hemorrhoids Malignancy on top of cirrhosis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 57. Jaundice Accumulation of bilirubin in tissue leading to yellow discoloration of skin and sclera (icterus) Normal serum level: 0.3-1.2 mg/dl; jaundice appears with levels above 2.0-2.5 mg/dl Source of bilirubin: the breakdown of senescent red blood cells in the spleen releases heme that changes into bilirubin by specific enzymes. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 58. Bilirubin Conjugation is a function of the liver by adding glucuronic acid to bilirubin - Unconjugated Albumin bound Insoluble in water, toxic - - Conjugated Loosely bound to albumin Water soluble, non-toxic, excreted in urine www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 59. Laboratory evaluation of liver disease Hepatocyte function: Hepatocyte injury (enzymes normally present inside the hepatocytes and released with injury): Serum albumin Prothrombin time: measuring coagulation factors (II, V, VII, X); prolonged in liver cirrhosis Serum ammonia Serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) Serum lactate dehydrogenase Biliary excretory function: Serum bilirubin Serum alkaline phosphatase Serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 60. Laboratory evaluation of liver disease Searching for etiology: Hepatitis viral antigens and antibodies Autoimmune antibodies: for autoimmune hepatitis Tissue iron and copper: for hemochromatosis and Wilson disease www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 61. Selected disorders of the liver Viral hepatitis Drug-induced hepatitis Autoimmune hepatitis Alcoholic hepatitis Hemochromatosis Wilson disease Neoplasms of the liver www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 62. Hepatitis A virus RNA virus Mode of transmission: fecal-oral (contaminated water and food) Incubation period: 2-6 weeks Virus shedding: 2-3 weeks before and 1 week after appearance of jaundice 50% of population above age 50 are seropositive in USA, no carrier state No increase risk for chronic hepatitis, or carcinoma Because viremia is transient, no need to screen donated blood www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 63. Hepatitis B virus dsDNA virus Mode of transmission: parenteral (blood products, contaminated needles and IV drug abuse), and body fluids (including saliva) Incubation period: 4-26 weeks Carrier state: yes, 350 million carriers around the world www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 64. Hepatitis B infection: Possible outcomes Possible outcomes of infection: Subclinical or acute hepatitis with recovery and clearance (85%); 1% of those may develop fulminant hepatitis and death Healthy carriers (10%) Persistent infection (5%): 80% recover and 20% develop chronic hepatitis 20% of chronic hepatitis patients develop cirrhosis and 10% of those develop hepatocellular carcinoma www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 65. Hepatitis C ssRNA virus Mode of transmission: parenteral, sexual and vertical, 40% unknown source. It is present in the saliva. Incubation period: 2-26 weeks Outcomes of infection: HCV is the leading cause for chronic liver disease www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 66. Hepatitis D Defective RNA virus that needs Hep B capsule to replicate Mode of transmission: Parenteral Coinfection of B and D: mild disease with recovery in most cases, <5% chronic hepatitis Superinfection by D after B: accelerated more severe hepatitis; 80% chronic hepatitis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 67. Hepatitis E ssRNA virus Mode of transmission: waterborne Incubation period: 2-8 weeks Endemic in certain populations; 40% in Indian population Self-limited infection but with higher mortality in pregnant females www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 68. The points to remember Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Transmission Oral-fecal Parenteral Parenteral Carrier state None Present Present Chronic hepatitis None 5-10% >70% Fulminant hepatitis 0.1% 0.1-1.0% Rare Carcinoma No Yes Yes www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 69. Drug-indued hepatitis Predictable or unpredictable (idiosyncrasy) Mechanisms: direct toxicity, conversion of drug to an active toxin, immune-mediated A long list of drugs can cause different forms of injury: hepatitis, fibrosis, granulomas, necrosis, cholestasis, vascular disorders and neoplasia Example: Acetaminophen overdose induces centrilobular necrosis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 70. Autoimmune hepatitis More in females (70%) The absence of serologic markers for viral hepatitis Elevated serum IgG levels High titers of autoantibodies (antinuclear, anti-smooth muscle, and anti-microsomal) Increased frequency of HLA-B8 and DRw3 Associated with other forms of autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis Risk for cirrhosis is 5% Respond to immunosuppressive drugs www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 71. Alcoholic liver disease 100,000 death annually related to alcohol; 20,000 are related directly to end-stage liver cirrhosis; the rest is related to car accidents Effects on liver: 80% fatty liver (steatosis) 10% alcoholic hepatitis 10% cirrhosis Short-term ingestion of 80 g (8 beers) of ethanol per day leads to reversible steatosis Daily ingestion of 160 g for 10-20 years leads to severe injury www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 72. Hereditary hemochromatosis Autosomal recessive disease characterized by increased accumulation of body iron, most of which is deposited in the liver and pancreas. Mostly due to increased iron absorption and accumulation over the years. Normal total body iron is 2-6 g. In hemochromatosis it may reach 50 gm. Due to mutations in the hemochromatosis gene (HFE); a gene that regulates iron absorption. The frequency of being heterozygous is 10% (1 of every ten persons) and that of being homozygous is 0.45% (1 of every 220 persons) www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 73. Hereditary hemochromatosis Excess iron damages DNA, lipids and stimulates collagen formation (fibrosis) Clinical picture: Males are more affected; 50-60 years old Liver cirrhosis, skin pigmentation, diabetes (pancreatic fibrosis), risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagnosis: elevated serum and tissue iron. Early detection and therapy by phlebotomy and iron chelators lead to normal life expectancy www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 74. Wilson disease Autosomal recessive disorder characterized by accumulation of copper in liver, brain and eyes, among other organs The frequency of being heterozygous is 1:200 (less common than hemochromatosis) The mutated gene (ATP7B) is located on chromosome 13; the mutation leads to failure to excrete copper into bile, and its accumulation in tissue Clinical picture: neuropsychiatric manifestations, acute and chronic liver disease and Kayser-Fleisher rings in the cornea (green to brown deposits) Diagnosis: Clinical picture, increased hepatic and urinary copper, and decreased serum ceruloplasmin (a copper binding protein). www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 75. Biliary disease Secondary biliary cirrhosis: secondary to extrahepatic bile obstruction by stones, atresia or tumors Primary biliary cirrhosis: immune-mediated destruction of intrahepatic bile ducts, more in females, presence of anti-mitochondrial antibodies Primary sclerosing cholangitis: chronic fibrosis of intra- and extra-hepatic bile ducts; more in men, association with ulcerative colitis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 76. Tumor of the liver Liver cell adenoma Occurs in women of childbearing age in relation to oral contraceptives; it regresses on discontinuation of hormones Sheets of hepatocytes with no www.indiandentalacademy.com portal tracts Well circumscribed mass
- 77. Liver cell adenoma Significance of this benign tumor: It may be mistaken for carcinoma Subcapsular adenomas are at risk for rupture, especially during pregnancy leading to lifethreatening intraabdominal hemorrhage www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 78. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) Risk factors: Strongly associated with hepatitis B and C infection. The carrier state for hepatitis B carries 200-fold increased risk for HCC Chronic liver disease (e.g. alcohol) Hepatotoxins (aflatoxin present on moldy peanuts and grains) www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 79. Hepatocellular carcinoma Clinical picture: Often patient already has liver cirrhosis, with rapid increase in liver size, worsening ascites, fever and pain; elevated serum alpha fetoprotein levels (>1000 ng/ml) Median survival is 7 months (death from bleeding, liver failure, or profound cachexia) www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 80. Metastatic carcinoma The most common malignant tumors in the liver Usually multiple lesions The most common primary sites are colon, lung, breast, pancreas and stomach www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 81. Oral manifestation of liver dysfunction Hematoma, gingival bleeding Jaundiced mucosa Glossitis (in alcoholic hepatitis) Reduced healing after surgery www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 82. 1. 2. 3. 4. A 48-year-old man has a long history of chronic alcohol abuse. On physical examination his liver is firm on palpation of the abdomen, but does not appear to be enlarged. An abdominal CT scan reveals that the liver has cirrhosis. He joins a support group for persons with chronic alcohol abuse and he stops drinking. Despite his continued abstinence from alcohol, he most likely remains at risk for development of which of the following diseases? Liver cell adenoma Hepatocellular carcinoma Gallbladder stones Lymphoma www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 83. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A 28-year-old woman with recent onset of depression ingests an entire bottle (100 capsules, 500 mg each) of a medication containing acetaminophen. She becomes progressively obtunded. Which of the following microscopic findings is most likely to be present in her liver 3 days following this ingestion? Normal histology Steatosis Centrilobular necrosis Cirrhosis Chronic inflammation www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 84. 1. 2. 3. 4. Hepatitis C infection is characterized by which one of the following: Absence of carrier status Highest incidence of chronic hepatitis among other viral hepatitis No increase risk for hepatocellular carcinoma It can be transmitted by eating contaminated food www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 85. 50 year-old male presented with jaundice and pruritus. Lab studies show elevated serum conjugated bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase. ALT and AST levels were only slightly elevated. The most likely diagnosis is: Hepatitis B Steatosis Hepatitis C Extrahepatic bile duct obstruction Autoimmune hepatitis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 87. The Pancreas 85% exocrine: enzymes for digestion Acute and chronic pancreatitis Cystic fibrosis Tumors 15% endocrine: insulin, glucagon and others Diabetes Tumors www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 90. Acute pancreatitis Clinical presentation: abdominal pain radiating to the back, elevated serum amylase and lipase, hypocalcemia Rise in serum lipase is more specific for pancreatitis. Complications: infections, abscess, pseudocyst Mortality is high: 20-40%, from shock, sepsis or acute respiratory failure, acute renal failure, disseminated intravascular coagulation www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 91. Chronic pancreatitis Progressive destruction of pancreatic parenchyma and its replacement by fibrosis Predisposing factors: alcohol, hypercalcemia or idiopathic 30% of idiopathic cases have been found to have mutation in CFTR gene Complications: Pseudocyst, malabsorption, 2ry diabetes Diagnosis: abdominal pain, malabsorption, calcifications on X-ray www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 92. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma The 5th most frequent cause of death from cancer Risk factors: smoking CP: symptoms are late; pain and jaundice Prognosis is poor: 5% survive for 5 years www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 93. Islet cell tumors Rare compared to adenocarcinoma Insulinomas: secrete insulin ⇒ hypoglycemia ⇒ behavioral changes, confusion and coma. Over 90% are benign Gastrinomas: secrete gastrin ⇒ increase acid production ⇒ duodenal and gastric ulcers www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 94. Gallbladder Gallstones (cholelithiasis) Afflict 10% of adult population in Western countries Costs of management: $6 billion a year 20 million patients are estimated to have gallstones totalling several tons Made of cholesterol, bilirubin and calcium salts with different concentrations Two types: cholesterol and pigmented stones www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 95. Gallstones Cholesterol Western > others Advancing age Female sex Obesity Hyperlipidemia and bile stasis Pigmented Asian > Western Hemolytic anemia Biliary infection Complications: empyema, perforation, fistula, inflammation, obstruction, pancreatitis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 96. Acute cholecystitis Calculous: acute inflammation of a gallbladder that has stones. It may represent a medical emergency; no associated infection initially Acalculous: no stones, in severely ill patients, severe trauma, burns and sepsis Chronic cholecystitis Almost always associated with gallstones www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 97. 1. 2. 3. 4. The risks factors for developing acute pancreatitis include all of the following except: Gallstones Hypocalcemia Alcoholism Shock www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 98. 1. 2. 3. 4. All of the following statement about pigmented gallstones are correct except: Hyperlipidemia is a risk factor Hemolytic anemias could be a cause Biliary infections may be present They are more common in Asians www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 99. 1. 2. 3. 4. A 38-year-old woman has experienced episodes of light-headedness, irritability, and difficulty concentrating at her work for the past year. On physical examination there are no abnormal findings. Laboratory studies show her hemoglobin is 14.2 g/dL. An abdominal CT scan shows a 1 cm mass in the tail of the pancreas. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Pancreatic adenocarcinoma Pancreatic pseudo-cyst Insulinoma Chronic pancreatitis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 100. 1. 2. 3. 4. A 50-year-old man gives a history of chronic alcohol abuse. He has had bouts of abdominal pain in the past year. For the past month, he has had more frequent and worsening abdominal pain. Physical examination reveals right upper and left upper quadrant pain with guarding. An abdominal plain film radiograph reveals no free air, but there is extensive peritoneal fluid collection along with dilated loops of small bowel. An abdominal CT scan reveals a 7 to 8 cm cystic mass in the tail of the pancreas. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Pancreatic adenocarcinoma Metastatic carcinoma Pancreatic pseudocyst Acute pancreatitis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 101. The Pancreas Sherif Tawfic, MD, Ph.D. Surgical Pathology U of MN tawfi001@umn.edu http://www.tc.umn.edu/~tawfi001/ www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 102. 1. 2. 3. 4. A 48-year-old man has a long history of chronic alcohol abuse. On physical examination his liver is firm on palpation of the abdomen, but does not appear to be enlarged. An abdominal CT scan reveals that the liver has cirrhosis. He joins a support group for persons with chronic alcohol abuse and he stops drinking. Despite his continued abstinence from alcohol, he most likely remains at risk for development of which of the following diseases? Liver cell adenoma Hepatocellular carcinoma Gallbladder stones Lymphoma www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 103. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A 28-year-old woman with recent onset of depression ingests an entire bottle (100 capsules, 500 mg each) of a medication containing acetaminophen. She becomes progressively obtunded. Which of the following microscopic findings is most likely to be present in her liver 3 days following this ingestion? Normal histology Steatosis Centrilobular necrosis Cirrhosis Chronic inflammation www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 104. 1. 2. 3. 4. Hepatitis C infection is characterized by which one of the following: Absence of carrier status Highest incidence of chronic hepatitis among other viral hepatitis No increase risk for hepatocellular carcinoma It can be transmitted by eating contaminated food www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 105. 50 year-old male presented with jaundice and pruritus. Lab studies show elevated serum conjugated bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase. ALT and AST levels were only slightly elevated. The most likely diagnosis is: Hepatitis B Steatosis Hepatitis C Extrahepatic bile duct obstruction Autoimmune hepatitis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 106. The Pancreas 85% exocrine: enzymes for digestion Acute and chronic pancreatitis Cystic fibrosis Tumors 15% endocrine: insulin, glucagon and others Diabetes Tumors www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 107. Acute pancreatitis CP: abdominal pain radiating to the back, elevated serum and urine amylase, hypocalcemia Most important causes: Gallstones, alcoholism, shock, hypercalcemia Mechanism: Interstitial edema ⇒ impaired blood flow and ischemia ⇒ acinar cell injury with release and activation of trypsinogen and lipases ⇒ proteolysis + fat necrosis + hemorrhage (destruction of blood vessels by elastases) Complications: infections, abscess, pseudocyst Mortality is high: 20-40%, from shock, sepsis or acute respiratory failure www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 108. Chronic pancreatitis Progressive destruction of pancreatic parenchyma and its replacement by fibrosis Predisposing factors: alcohol, hypercalcemia or idiopathic 30% of idiopathic cases have been found to have mutation in CFTR gene Fibrosis, chronic inflammation and protein plugs within ducts Diagnosis: abdominal pain, malabsorption, calcifications on X-ray www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 109. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma The 5th most frequent cause of death from cancer Risk factors: smoking CP: symptoms are late; pain and jaundice Prognosis is poor: 5% survive for 5 years Some of the adverse effects of smoking to remember: Cancer of the oral cavity, lips, tongue, larynx, lungs, esophagus, pancreas, kidney, bladder and vulva Emphysema and chronic bronchitis, atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 110. Islet cell tumors Rare compared to adenocarcinoma Insulinomas: secrete insulin ⇒ hypoglycemia ⇒ behavioral changes, confusion and coma. Over 90% are benign Gastrinomas: secrete gastrin ⇒ increase acid production ⇒ duodenal and gastric ulcers www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 111. Gallbladder Gallstones (cholelithiasis) Afflict 10% of adult population in Western countries Costs of management: $6 billion a year 20 million patients are estimated to have gallstones totalling several tons ! Made of cholesterol, bilirubin and calcium salts with different concentrations Two types: cholesterol and pigmented stones www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 112. Gallstones Cholesterol Western > others Advancing age Female sex Obesity Hyperlipidemia and bile stasis Pigmented Asian > Western Hemolytic anemia Biliary infection Complications: empyema, perforation, fistula, inflammation, obstruction, pancreatitis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 113. Acute cholecystitis Calculous: acute inflammation of a gallbladder that has stones. It may represent a medical emergency; no associated infection initially Acalculous: no stones, in severely ill patients, severe trauma, burns and sepsis Chronic cholecystitis Almost always associated with gallstones www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 114. 1. 2. 3. 4. The risks factors for developing acute pancreatitis include all of the following except: Gallstones Hypocalcemia Alcoholism Shock www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 115. 1. 2. 3. 4. All of the following statement about pigmented gallstones are correct except: Hyperlipidemia is a risk factor Hemolytic anemias could be a cause Biliary infections may be present They are more common in Asians www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 116. 1. 2. 3. 4. Hepatitis C infection is characterized by which one of the following: Absence of carrier status Highest incidence of chronic hepatitis among other viral hepatitis No increase risk for hepatocellular carcinoma It can be transmitted by eating contaminated food www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 117. 1. 2. 3. 4. A 38-year-old woman has experienced episodes of light-headedness, irritability, and difficulty concentrating at her work for the past year. On physical examination there are no abnormal findings. Laboratory studies show her hemoglobin is 14.2 g/dL. An abdominal CT scan shows a 1 cm mass in the tail of the pancreas. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Pancreatic adenocarcinoma Pancreatic pseudo-cyst Insulinoma Chronic pancreatitis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 118. 1. 2. 3. 4. A 50-year-old man gives a history of chronic alcohol abuse. He has had bouts of abdominal pain in the past year. For the past month, he has had more frequent and worsening abdominal pain. Physical examination reveals right upper and left upper quadrant pain with guarding. An abdominal plain film radiograph reveals no free air, but there is extensive peritoneal fluid collection along with dilated loops of small bowel. An abdominal CT scan reveals a 7 to 8 cm cystic mass in the tail of the pancreas. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Pancreatic adenocarcinoma Metastatic carcinoma Pancreatic pseudocyst Acute pancreatitis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 119. Thank you www.indiandentalacademy.com Leader in continuing dental education www.indiandentalacademy.com
Notas del editor
- ,
- .
- P
- Salmonella causes half a million case of food poisoning contaminated eggs, chicken.
- Salmonella causes half a million case of food poisoning contaminated eggs, chicken.
- Salmonella causes half a million case of food poisoning contaminated eggs, chicken.
- It has enormous functional reserve and regeneration occurs as long there is no extensive damage to the connective tissue framework. Surgical removal of 75% of liver produces minimal hepatic impairment and regeneration restores liver size in a few weeks
- Pruritis due to deposition of bile acids in skin, increased alkaline phosphatase, conjugated bilirubin, skin xanthomas due to decreased secretion of cholesterol, inadequate absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, A, D, E, K
