nothing
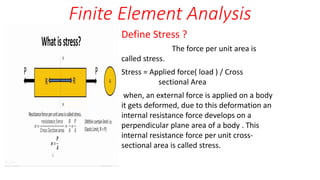
- 1. Finite Element Analysis Define Stress ? The force per unit area is called stress. Stress = Applied force( load ) / Cross sectional Area when, an external force is applied on a body it gets deformed, due to this deformation an internal resistance force develops on a perpendicular plane area of a body . This internal resistance force per unit cross- sectional area is called stress.
- 2. What is strain ? The strain is defined as the ratio of change in dimension onto the original dimension . Strain is the measure of how much distortion has been fallen on a body compare3d to its initial shape due to action of force. Types of Strain: Longitudinal strain = Ratio of change in length to the original length . Shearing Strain = Ratio of change in angle to which it is turned to its distance from the fixed layer. Volumetric Strain = Ratio of change in volume to original volume.
- 3. Young’s modulus : The Young’s modulus (E), is a property of the material that tells us how easily it can be stretch and deform. It is defined as the ratio of tensile stress to tensile strain.
- 4. Rigidity modulus: Shear modulus is also known as modulus of rigidity. The ratio of shear stress to shear strain, determines the modulus of rigidity. Within the elastic limit, it is the ratio of shear stress to shear strain It is associated with the change in the shape of a body. It exists in solids only. It describes an object’s tendency to shear.
- 5. Bulk Modulus ? Bulk modulus is a numerical constant that describes a solid’s or fluid’s elastic properties when it is in pressure on all sides. When the pressure is applied to a material, it reduces its volume, which then returns to its original volume when the pressure is removed.
- 6. Stiffness : Stiffness is the extent to which an object resists deformation in response to an applied force. where, where,
- 7. Linear & Non-Linearity : A linear analysis uses only linear elastic materials and small displacements. A non-linear analysis uses large displacements and elastoplastic materials, the superposition effect cannot be used.
- 8. Natural frequency : A natural frequency is a frequency at which a body will vibrate if excited by an external force. when, an object vibrates at a frequency equivalent to its natural frequency, the vibration of the amplitude increases significantly which could lead to irreparable damage, therefore, it is important to know the natural frequency.
- 9. Resonant frequency: The natural frequency of an object, where it tends to vibrate at a higher amplitude, is also known as the resonant frequency. For Example : If a collective oscillation force from the automobiles caused a bridge to vibrate at its frequency, we may feel it shake.
- 10. Damping: Damping in Physics, restraining of vibratory motion, such as mechanical oscillations, noise, and alternating electric currents, by dissipation of energy.
- 11. Properties of materials: Hardness – Resistance to scratching, cutting or abrasion. Toughness – Resistance to fracturing and this quality depends on the maximum energy that can be absorbed before fracturing. Brittleness – They are liable to break easily, they are hard and can’t be hammered. Ductility – They can easily be hammered or stretched into thin wires without breakage. Malleability – Capability of being shaped or extended by hammering, forging, etc… Strength – The ability of a material to resist mechanical forces when in use. A materials strength in a given application depends on many factors, including its resistance to deformation and cracking, and it often depends on the shape of the member being designed.
- 12. Finding Natural frequency: When an object vibrates at a frequency equivalent to its natural frequency, the vibration of the amplitude increases significantly, which could lead to irreparable damage, therefore, it is important to know the natural frequency.
- 13. Finite Element Method: Finite Element Method is a numerical technique for solving boundary value problems in which a large domain is divided into smaller sections or elements. The solution is determined by assuming certain polynomials. The small elements are called finite elements and the polynomials are called shape functions.
- 14. Advantages of FEM: Since the properties of each element are evaluated separately, different material properties can be incorporated for each element. There is no restriction in the shape of the medium. Any type of boundary condition can be adopted.
- 15. Various co-ordinates in the FEM: • Local coordinates • Natural coordinates • Simple natural coordinates • Area coordinator • Triangular coordinates • Generalized coordinates
- 16. Basic steps of FEM: • Discretization of the structure. • Selection of sustainable displacement function. • Finding the element properties. • Assembling the element properties. • Applying the boundary conditions • Solving the system of equations • Computing additional results
- 17. Different types of elements in FEA: It is the process of subdividing the given body into a number of elements which results in a system of equivalent finite elements. • 1D • 2D • 3D Discretization:
- 18. Why should one use Finite elements? The use of finite elements allows the modelling of multiple material types, testing of complex geometry, and the ability to capture local effects acting on a small area of the design. In practice, engineers can use finite element modelling software on a huge variety of tasks.
- 19. Node or Joint: Each kind of finite elements has a specific structural shape and is interconnected with the adjacent element by nodal point or nodes. At nodes, degrees of freedom are located. The forces will act only at nodes at any others place in the element.
- 20. Types of Boundary Conditions: • Dirichlet Boundary Condition • Neumann Boundary Condition • Robin Boundary Condition • Mixed Boundary Condition • Cauchy Boundary Condition
- 21. Three phases of FEM: • Classification of the problem • Discretization • Modelling
- 22. DOF: • The degree of freedom of a mechanical system is the number of independent parameters that define its configuration or state. • It is important in the analysis of systems of bodies in mechanical engineering, structural engineering, aerospace engineering, robotics and other fields.
- 23. Types of FEA: • Structural Analysis • Thermal Analysis • Fluid Analysis • Heat Transfer Analysis • Electromagnetic Analysis • Buckling Analysis • Electrical Analysis • Multi Physics Analysis ( coupled field ).