Coagulants and anti coagulants
- 1. Coagulants & anti-coagulants Dr. Karun Kumar JR-II
- 2. • Haemostasis Limiting blood loss consequent to bleeding • Homeostasis Maintenance of body’s internal environment within physiological limits • Thrombus A clot that “adheres” to a vessel wall (Bad Blocks vessels) • Embolus Intravascular clot that “floats” in blood • “Detached” thrombus = Embolus • Clot Good (Stops bleeding)
- 3. Coagulation factors Factor Common synonym I Fibrinogen II Prothrombin III Tissue thromboplastin IV Calcium V Proaccelerin VII Proconvertin VIII AHF IX Plasma thromboplastin component X Stuart factor XI Plasma thromboplastin antecedent XII Hageman factor XIII Fibrin stabilizing factor
- 4. 3 mechanisms of haemostasis 1. Vascular spasm (Damage to smooth muscle) 2. Platelet plug formation 3. Blood coagulation
- 5. Intrinsic pathway • Activated by surface contact with foreign body (Contact pathway) • All factors and activators are contained within (intrinsic to) the blood • Responsible for clotting when blood is kept in a glass tube (in vitro)
- 6. Extrinsic pathway • Activated by thromboplastin • As a consequence of trauma, a tissue protein (tissue factor) leaks into the blood from cells outside (extrinsic to) blood vessels • Rate limiting step in coagulation cascade activation of factor X (converging pathway)
- 8. PT aPTT Intrinsic pathway interfered Normal (12- 14 secs) Prolonged Extrinsic pathway interfered Prolonged (WEPT) Normal (26- 32 secs) Common pathway interfered Prolonged Prolonged
- 9. Pro & anti-aggregatory factors • Pro-aggregatory factor TXA2 (platelets) ↓ blood flow & ↑ platelet aggregation • Anti-aggregatory factors 1. PGI2 Endothelial 2. NO cells ↑ blood flow & ↓ platelet aggregation
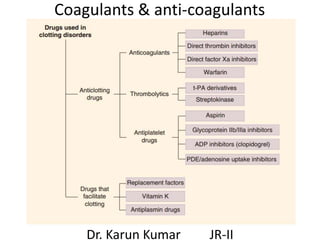
- 14. Coagulants • Indication Haemorrhagic states • Best therapy Fresh whole blood / plasma 1. Vitamin K (K1 , K2 & K3) Cofactor in the post-translational carboxylation of glutamate residues on factors II, VII, IX, and X 2. Miscellaneous • Fibrinogen • Anti-haemophilic factor • Desmopressin
- 15. Anticoagulants • Drugs that impede blood coagulation and prevent the occurrence or expansion of a thrombus
- 16. Classification 1. Vitamin K antagonist Warfarin 2. Heparin & related drugs a) Heparin b) LMWH (Enoxaparin, Dalteparin, Tinzaparin) c) Synthetic heparin derivatives (Fondaparinux – longer acting)
- 17. 3. Direct thrombin inhibitors a) Parenteral Hirudin, Lepirudin, Argatroban, Bivalirudin) b) Oral Dabigatran 4. Active factor Xa inhibitor Rivaroxaban, Apixaban RIVAR Rivarsible (Reversible) ; O Oral; XA X a ; BAN Blocker
- 18. Warfarin (WEPT) • Competitively inhibits vitamin K epoxide reductase & inhibits the posttranslational carboxylation of glutamate residues on vitamin K dependent coagulation factors II (prothrombin), VII, IX, and X • Causes WAR during pregnancy • PT should be monitored
- 21. Heparin • Antithrombin III Irreversibly inactivates thrombin & factor Xa • Heparin potentiates anti-thrombin III activity • Dosage determined by monitoring aPTT
- 24. Advantages of LMWH 1. Can be administered s.c. 2. Effects are consistent & dosing less frequent (Long t1/2 & elimin. By 1st order kinetics) 3. Do not prolong aPTT & CT (Response is predictable & monitoring not required) 4. Dose is given in mg (not in units) can be easily calculated on body weight basis 5. Chance of haemorrhage chance is less 6. Risk of osteoporosis is decreased
- 25. Heparin Warfarin Route of admin. I.v., S.c. Oral Onset of action Immediate Delayed Mechanism Activ. Of AT-III ↓ activ. Of c.f. 2,7,9,10 Antagonist Protamine sulphate Vitamin K Lab control aPTT PT Drug interact. Few Many Use To initiate therapy For maintenance
- 26. Uses of anti-coagulants 1. Prevention & t/t of DVT & PE 2. Myocardial infarction 3. Unstable angina 4. Rheumatic heart disease 5. Cerebrovascular disease 6. Haemodialysis 7. Defibrination syndrome (DIC)
- 27. Antiplatelet drugs (ATD) 1. Aspirin 2. Cilostazol, Dipyridamole (PDE III inhib.) 3. P2Y12 receptor blocker a) Reversible antag. Ticagrelor, Cangrelor b) Irrev. Antag. Ticlopidine, Clopidogrel, Prasugrel 4. GP IIb/IIIa antag. Abciximab, Tirofiban, Eptifibatide
- 28. Aspirin • It irreversibly inhibits 1. COX-1 2. TX-synthase • It does NOT inhibit TXA2 directly
- 29. Why low dose Aspirin ? • 75-150 mg TXA2 formation suppressed • > 900 mg ↓ PGI2 & TXA2 • TXA2 Platelets (Life span 5-7 days) • PGI2 Endothelial cells • Low dose (80-160 mg) Antiplatelet effect • Moderate dose (650-975 mg) Analgesic & antipyretic effects • High dose (3-6 g) Anti inflammatory effect
- 32. • GP IIb/IIIa Protein complex on the surface of platelets. • When activated, it aggregates platelets by binding to fibrin
- 33. Summary
- 34. Uses of anti-platelet drugs 1. MI Low dose Aspirin 2. Unstable angina Aspirin / Clopidogrel 3. Coronary bypass implants 4. Prosthetic heart valves 5. Arteriovenous shunts 6. Venous thromboembolism 7. Peripheral vascular disease 8. Cerebrovascular transient ischemic attacks
- 35. Fibrinolytic drugs (USA) • Lyse (dissolve) the thrombi (clots) in blood vessels by activating firbrinolytic system 1. Urokinase 2. Streptokinase 3. Anistreplase 4. Alteplase 5. Reteplase 6. Tenecteplase
- 37. Uses of fibrinolytics 1. Acute myocardial infarction 2. Deep vein thrombosis 3. Pulmonary embolism 4. Peripheral arterial occlusion 5. Stroke
- 39. Anti fibrinolytic drugs 1. Epsilon Aminocaproic acid Blocks plasminogen activation (stops bleeding) 2. Tranexamic acid Cyclic heavy menstrual bleeding A/E Thrombosis
- 40. Q.1. For each drug description, select the correct answer from the following choices: (A)Eptifiatide (B) prasugrel (C) dabigatran (D) Rivaroxaban (E) enoxaparin 1. This orally administered drug directly and selectively inhibits thrombin. 2. This drug produces irreversible blockade of platelet adenosine diphosphate P2Y receptors. 3. This orally administered inhibitor of active factor X (Stuart factor) is used to prevent DVT in persons undergoing hip-replacement surgery 4. This drug is a reversible fibrinogen antagonist at GP IIb/ IIIa receptors.
- 41. Q.2. Which of the P2Y12 ADP receptor antagonists reversibly binds the receptor? A. Clopidogrel B. Prasugrel C. Ticagrelor D. Ticlopidine
- 42. Q.3. A 70-year-old female is diagnosed with nonvalvular atrial firillation. Her past medical history is significant for chronic kidney disease, and her renal function is moderately diminished. All of the following anticoagulants would be expected to require a reduced dosage in this patient except: A. Apixaban. B. Dabigatran. C. Rivaroxaban. D. Warfarin.
- 43. Q.4. An 80-year-old male is taking warfarin indefinitely for the prevention of deep venous thrombosis. He is a compliant patient with a stable INR and has no issues with bleeding or bruising. He is diagnosed with a urinary tract infection and is prescribed sulfamethoxazole/ trimethoprim. What effect will this have on his warfarin therapy? A. Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim will decrease the anticoagulant effect of warfarin. B. Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim will increase the anticoagulant effect of warfarin. C. Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim will activate platelet activity. D. Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim will not change anticoagulation status.
- 44. Q.5 Which must heparin bind to in order to exert its anticoagulant effect? A. GP IIb/IIIa receptor. B. Thrombin. C. Antithrombin III. D. von Willebrand factor.
- 45. Q.6. Which is most appropriate for reversing the anticoagulant effects of heparin? A. Aminocaproic acid B. Protamine sulfate C. Vitamin K D. Tranexamic acid
- 46. Q.7. A 58-year-old business executive is brought to the emergency department 2 h after the onset of severe chest pain during a vigorous tennis game. She has a history of poorly controlled mild hypertension and elevated blood cholesterol but does not smoke. ECG changes confirm the diagnosis of myocardial infarction. The decision is made to attempt to open her occluded artery.
- 47. I) Which of the following drugs accelerates the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin? (A) Aminocaproic acid (B) Heparin (C) Lepirudin (D) Reteplase (E) Warfarin
- 48. II) If a fibrinolytic drug is used for treatment of this woman’s acute myocardial infarction, which of the following adverse drug effects is most likely to occur? (A) Acute renal failure (B) Development of antiplatelet antibodies (C) Encephalitis secondary to liver dysfunction (D) Hemorrhagic stroke (E) Neutropenia
- 49. III) If this patient undergoes a percutaneous coronary angiography procedure and placement of a stent in a coronary blood vessel, she may be given eptifibatide. Which of the following most accurately describes the mechanism of eptifibatide anticlotting action? (A) Activation of antithrombin III (B) Blockade of post-translational modification of clotting factors (C) Inhibition of thromboxane production (D) Irreversible inhibition of platelet ADP rec. (E) Reversible inhibition of GP IIb/IIIa receptors
- 50. Q. 8. A 65-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 30 min after the onset of right-sided weakness and aphasia (difficulty speaking). Imaging studies ruled out cerebral hemorrhage as the cause of his acute symptoms of stroke.
- 51. I) Prompt administration of which of the following drugs is most likely to improve this patient’s clinical outcome? (A) Abciximab (B) Alteplase (C) Factor VIII (D) Streptokinase (E) Vitamin K
- 52. II) Over the next 2 d, the patient’s symptoms resolved completely. To prevent a recurrence of this disease, the patient is most likely to be treated indefinitely with which of the following? (A) Aminocaproic acid (B) Aspirin (C) Enoxaparin (D) Lepirudin (E) Warfarin
- 53. Q.9. A 67-year-old woman presents with pain in her left thigh muscle. Duplex ultrasonography indicates the presence of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the affected limb.
- 54. I) The decision was made to treat this woman with enoxaparin. Relative to unfractionated heparin, enoxaparin (A) Can be used without monitoring the patient’s aPTT (B) Has a shorter duration of action (C) Is less likely to have a teratogenic effect (D) Is more likely to be given intravenously (E) Is more likely to cause thrombosis and thrombocytopenia
- 55. II) During the next week, the patient was started on warfarin and her heparin was discontinued. Two months later, she returned after a severe nosebleed. Laboratory analysis revealed an INR (international normalized ratio) of 7.0 (INR value in such a warfarin-treated patient should be 2.0–3.0). To prevent severe hemorrhage, the warfarin should be discontinued and this patient should be treated immediately with which of the following? (A) Aminocaproic acid (B) Desmopressin (C) Factor VIII (D) Protamine (E) Vitamin K
- 56. Q. 10. A patient develops severe thrombocytopenia in response to treatment with unfractionated heparin and still requires parenteral anticoagulation. The patient is most likely to be treated with which of the following? (A) Abciximab (B) Cilostazol (C) Lepirudin (D) Plasminogen (E) Vitamin K1
Notas del editor
- ADP activates platelets through P2X1 Ion channel P2Y1 Gq P2Y12 Gi
- GP Iib/IIIA adhesive receptor (integrin) on platelet surface for platelet aggregation
