Mechanisms of coagulation B.pharmacy 2 semester
•Descargar como PPTX, PDF•
5 recomendaciones•4,163 vistas
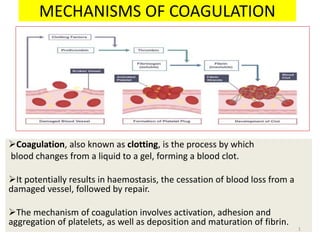
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in haemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism of coagulation involves activation, adhesion and aggregation of platelets, as well as deposition and maturation of fibrin.
Denunciar
Compartir
Denunciar
Compartir
Recomendados
Recomendados
Más contenido relacionado
La actualidad más candente
La actualidad más candente (20)
Therapeutic and diagnostic applications of enzymes isozymes and coenzymes

Therapeutic and diagnostic applications of enzymes isozymes and coenzymes
Similar a Mechanisms of coagulation B.pharmacy 2 semester
Similar a Mechanisms of coagulation B.pharmacy 2 semester (20)
phsiology of blood coagulation by dr chandbaby ansari.pdf

phsiology of blood coagulation by dr chandbaby ansari.pdf
Más de Kondal Reddy
Más de Kondal Reddy (16)
Elements and types of communication; B.pharmacy 1 semester

Elements and types of communication; B.pharmacy 1 semester
Prespectives of communcation; B.pharmacy 1 semester

Prespectives of communcation; B.pharmacy 1 semester
Último
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? webinar
Thursday 2 May 2024
A joint webinar created by the APM Enabling Change and APM People Interest Networks, this is the third of our three part series on Making Communications Land.
presented by
Ian Cribbes, Director, IMC&T Ltd
@cribbesheet
The link to the write up page and resources of this webinar:
https://www.apm.org.uk/news/making-communications-land-are-they-received-and-understood-as-intended-webinar/
Content description:
How do we ensure that what we have communicated was received and understood as we intended and how do we course correct if it has not.Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...Association for Project Management
Último (20)
HMCS Max Bernays Pre-Deployment Brief (May 2024).pptx

HMCS Max Bernays Pre-Deployment Brief (May 2024).pptx
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...
Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx

Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx
Unit 3 Emotional Intelligence and Spiritual Intelligence.pdf

Unit 3 Emotional Intelligence and Spiritual Intelligence.pdf
Food safety_Challenges food safety laboratories_.pdf

Food safety_Challenges food safety laboratories_.pdf
HMCS Vancouver Pre-Deployment Brief - May 2024 (Web Version).pptx

HMCS Vancouver Pre-Deployment Brief - May 2024 (Web Version).pptx
Python Notes for mca i year students osmania university.docx

Python Notes for mca i year students osmania university.docx
Fostering Friendships - Enhancing Social Bonds in the Classroom

Fostering Friendships - Enhancing Social Bonds in the Classroom
Interdisciplinary_Insights_Data_Collection_Methods.pptx

Interdisciplinary_Insights_Data_Collection_Methods.pptx
Sensory_Experience_and_Emotional_Resonance_in_Gabriel_Okaras_The_Piano_and_Th...

Sensory_Experience_and_Emotional_Resonance_in_Gabriel_Okaras_The_Piano_and_Th...
Mechanisms of coagulation B.pharmacy 2 semester
- 1. MECHANISMS OF COAGULATION Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in haemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism of coagulation involves activation, adhesion and aggregation of platelets, as well as deposition and maturation of fibrin. 1
- 2. 2
- 3. 3
- 4. 4
- 5. 5
- 6. 6
- 7. INTRINSIC PATHWAY FOR THE FORMATION OF PROTHROMBIN ACTIVATOR • During the injury, the blood vessels are ruptured. Endothelium is damaged and collagen under the endothelium is exposed. (Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, found in the bones, muscles, skin, and tendons. Its provide strength and structure.) 1. When factor XII(12) comes and contact with this collagen, it is converted into activated factor XII. (FACTOR 12+COLLAGEN=ACTIVATED FACTOR 12) 2. The activated factor XII converts factor XI(11) into activated factor XI. 3. The activated factor XI activates factor IX(9) in the presence of factor IV(4)(calcium ions) 4. The activated factor IX activates factor VIII(8) in the presence of factor IV (calcium ions) 5. Both these activated factor VIII(8) and factor IV(4) (calcium ions) activates the factor X(10). 6. Here the platelets which are release from the damaged blood vessels contact with collagen and activates and releases phospholipids. (PLATELETS+COLLAGEN=PHOSPHOLIPIDS) 7. Now the activated factor X(10) reacts with platelets phospholipids and activated factor V(5) to form prothrombin activator. This needs the presence of calcium ions (ca++). 7
- 8. EXTRINSIC PATHWAY FOR THE FORMATION OF PROTHROMBIN ACTIVATOR • In this pathway the formation of prothrombin activator initiated by the tissue thromboplastin (factor III) , which are released from damaged tissues. • Now the tissue thromboplastin converts factor X into activated factor X in the presence of factor VII(7) and factor IV (calcium ions) (ca++). • Now the activated factor X(10) reacts with activated factor V(5) to form prothrombin activator. This needs the presence of calcium ions (ca++). 8
- 9. • Blood clot is all about thrombin formation. Once thrombin is formed definitely colt is formed. • Prothrombin activator which are formed from intrinsic and extrinsic pathways converts prothrombin(factor II) into thrombin. In the presence of calcium ions (factor IV). • Once formed thrombin initiates the formation of more thrombin molecules. • The initially formed thrombin activates factor V. • This factor V in turn accelerates formation of both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways prothrombin activator, which converts prothrombin into thrombin. 9
- 10. • Thrombin converts inactivated fibrinogen (factor I) into activated fibrinogen. The activated fibrinogen is called fibrin monomer. • Fibrin monomer forms loosely arranged strands of fibrin. • Later these loose strands are modified and formed into dense and tight fibrin threads by fibrin stabilizing factor (factor XIII) in the presence calcium ions. • All the tight fibrin threads are arranged to form a meshwork of stable clot. 10
- 11. 11