Vertebral Canal Lecture Notes
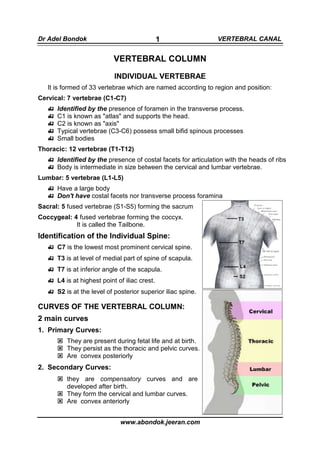
- 1. Dr Adel Bondok 1 VERTEBRAL CANAL m VERTEBRAL COLUMN INDIVIDUAL VERTEBRAE It is formed of 33 vertebrae which are named according to region and position: Cervical: 7 vertebrae (C1-C7) Identified by the presence of foramen in the transverse process. C1 is known as "atlas" and supports the head. C2 is known as "axis" Typical vertebrae (C3-C6) possess small bifid spinous processes Small bodies Thoracic: 12 vertebrae (T1-T12) Identified by the presence of costal facets for articulation with the heads of ribs Body is intermediate in size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae. Lumbar: 5 vertebrae (L1-L5) Have a large body Don't have costal facets nor transverse process foramina Sacral: 5 fused vertebrae (S1-S5) forming the sacrum Coccygeal: 4 fused vertebrae forming the coccyx. It is called the Tailbone. Identification of the Individual Spine: C7 is the lowest most prominent cervical spine. T3 is at level of medial part of spine of scapula. T7 is at inferior angle of the scapula. L4 is at highest point of iliac crest. S2 is at the level of posterior superior iliac spine. CURVES OF THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN: 2 main curves 1. Primary Curves: They are present during fetal life and at birth. They persist as the thoracic and pelvic curves. Are convex posteriorly 2. Secondary Curves: they are compensatory curves and are developed after birth. They form the cervical and lumbar curves. Are convex anteriorly www.abondok.jeeran.com
- 2. Dr Adel Bondok 2 VERTEBRAL CANAL Therefore, there are 4 curves: 2 primary and 2 secondary. From above downward: 1. The Cervical Curve: Is a secondary curve that appears after birth. Is convex forward and is the least marked of all the curves. It appears at the 3rd month when the child raises his head. 2. The Thoracic Curve: Is a primary curve (kyphotic curve) that appears at birth. Is concave forward. 3. The Lumbar Curve: Is a secondary curve (lordotic curve ) that appears after birth. Is convex forward and is more marked in the female than in the male. It appears at the 9th-18th month when the child sits upright and begins to walk. 4. The Pelvic (Sacral) Curve: Is a primary curve that appears at birth. Is concave forward (follows the concavity of the sacrum). VERTEBRAL (SPINAL) CANAL Definition: Is the space between the bodies and the vertebral arches of the vertebrae. It contains the spinal cord and the meninges (and cauda equina below L2). Protection: the canal is protected by the: 1. Ligamentum flavum posteriorly 2. Posterior longitudinal ligament anteriorly. Meningeal Spaces in the Canal: The meninges (dura, arachnoid & pia mater) divide the spinal canal into 3 spaces: 1. The epidural space: outside the dura. It contains: a. loose fatty tissue b. The internal vertebral venous plexus formed by the anterior vertebral venous plexus and the posterior vertebral venous plexus 2. The subdural space: potential space between the dura and arachnoid. 3. The subarachnoid space: between the arachnoid and pia mater. It contains: a. Cerebrospinal fluid. b. spinal arteries, namely the anterior spinal artery and the 2 posterior spinal arteries. c. Corresponding spinal veins. www.abondok.jeeran.com
- 3. Dr Adel Bondok 3 VERTEBRAL CANAL ABNORMALITIES OF THE VERTEBRAL CANAL 1. Spina bifida: Is cleft in the arches of the vertebrae (absent spine). A protrusion of the spinal membranes through the defect forms meningocele Protrusion of the spinal cord and the menibese forms meningomyelocele. Spina bifida is most common in the lumbosacral region, but it may occur in the thoracic or cervical region. 2. Vertebral canal stenosis (narrowing): causing spinal cord compression. 3. Abnormal curvatures: a. Kyphosis: Is an exaggerated kyphotic (posterior) curvature in the thoracic region. It is commonly observed in osteoporosis. b. Lordosis: Is an exaggerated lordotic (anterior) curvature of the lumbar region. Temporary lordosis is common in pregnant women. c. Scoliosis: Is lateral curvature of the vertebral column. Is the most common abnormal curvature (in 0.5% of the population). It is more common among females May result from unequal growth of the two sides of 1 or more vertebrae. BLOOD SUPPLY OF THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN & SPINAL CORD Arteries Supplying the Vertebral Column and Spinal Cord: 1. One anterior spinal artery: by union of 2 branches from the vertebral arteries. 2. 2 Posterior spinal arteries: each arises from the vertebral artery or the PICA. 3. Radicular arteries: a. In the neck: from the 1. Vertebral artery: arises from the 1st part of the subclavian artery. 2. Ascending cervical artery: arises from the inferior thyroid artery. b. In the thorax: from the posterior intercostal arteries (thoracic aorta). c. Lumbar region: from the lumbar arteries (abdominal aorta). d. Sacrum and Coccyx: 1. Median sacral artery: arises from the abdominal aorta. 2. Lateral sacral arteries: from the internal iliac artery. www.abondok.jeeran.com
- 4. Dr Adel Bondok 4 VERTEBRAL CANAL Veins Draining the Vertebral Column and Spinal Cord: Into the internal and external vertebral venous plexus which drain into the: 1. Cervical Region: into the vertebral vein 2. Thoracic Region: into the posterior intercostal veins then to azygos and hemiazygos veins then to the superior vena cava. 3. Lumbar vertebrae, Sacrum and Coccyx: into the a. Lumbar veins: which drain into the inferior vena cava. b. Lateral sacral veins: which drain into the internal iliac veins INTERVERTEBRAL DISC Position: The discs lie between the vertebral bodies and are fused with them. Structure:The intervertebral discs consist of 2 parts: 1. An outer fibrous ring: annulus fibrosus formed of crisscrossed, tight collagen fibers connecting the adjacent vertebrae 2. Spongy center: nucleus pulposus in the middle of the intervertebral disc. It is comprised of 80% water . Function: the intervertebral discs function like a shock absorber. The spongy center absorbs pressures exerted upon the vertebre. Changes in the water content: Compression forces develop in the spinal column during movements are absorbed and distributed by the intervertebral discs. These compression forces force the water to go out of the intervertebral disc, making it thinner. When the pressure is relieved, for example during sleep, the disc takes up water again and becomes thicker. This mechanism explains why a person’s height may vary by 1-2 cm in the course of a day depending on load and strain on the spine. Aging: Due to the natural aging process, intervertebral discs lose their capacity to take up water, resulting in a drop in the swelling capacity of the spongy center. As the intervertebral disc becomes less elastic and thinner, the adjacent vertebrae move closer together. This results in bone-on-bone reactions involving formation of osteophytes (new bony substance) at the epiphyses of the vertebral bodies – a sign of the degeneration (wearing down) of the intervertebral disc (osteochondrosis, spondylosis). Blood Supply: The intervertebral disc doesn't contain blood vessels after the fourth year of life, and is supplied with nutrients via diffusion. Metabolic exchange takes place through the porous bony structures of the vertebral bodies by way of diffusion from the marrow spaces of the vertebrae. www.abondok.jeeran.com
- 5. Dr Adel Bondok 5 VERTEBRAL CANAL LABEL THE FIGURES www.abondok.jeeran.com