Anxiety Disorders
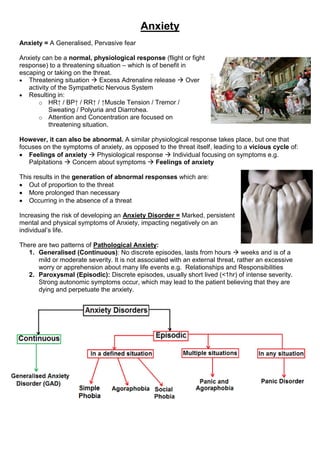
- 1. Anxiety Anxiety = A Generalised, Pervasive fear Anxiety can be a normal, physiological response (flight or fight response) to a threatening situation – which is of benefit in escaping or taking on the threat. Threatening situation Excess Adrenaline release Over activity of the Sympathetic Nervous System Resulting in: o HR↑ / BP↑ / RR↑ / ↑Muscle Tension / Tremor / Sweating / Polyuria and Diarrohea. o Attention and Concentration are focused on threatening situation. However, it can also be abnormal. A similar physiological response takes place, but one that focuses on the symptoms of anxiety, as opposed to the threat itself, leading to a vicious cycle of: Feelings of anxiety Physiological response Individual focusing on symptoms e.g. Palpitations Concern about symptoms Feelings of anxiety This results in the generation of abnormal responses which are: Out of proportion to the threat More prolonged than necessary Occurring in the absence of a threat Increasing the risk of developing an Anxiety Disorder = Marked, persistent mental and physical symptoms of Anxiety, impacting negatively on an individual’s life. There are two patterns of Pathological Anxiety: 1. Generalised (Continuous): No discrete episodes, lasts from hours weeks and is of a mild or moderate severity. It is not associated with an external threat, rather an excessive worry or apprehension about many life events e.g. Relationships and Responsibilities 2. Paroxysmal (Episodic): Discrete episodes, usually short lived (<1hr) of intense severity. Strong autonomic symptoms occur, which may lead to the patient believing that they are dying and perpetuate the anxiety.
- 2. Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD) Epidemiology: Lifetime risk is 4-5% and there is a 3% prevalence in the general population Aetiology: o Predisposing: FH / Twin Studies / Personality / Childhood upbringing o Precipitating: Relationships / Unemployment / Financial Problems / Ill health o Perpetuating: Continuing Stressful Events / Depression / Cycle of Anxiety DSM IV Criteria: o Excessive anxiety and worry about various ordinary events – more days than not for >6months <6months = Stress or Adjustment Disorder o 3/6 of the following associated symptoms: Restlessness / Fatigue / Irritability / Muscle Tension / cannot get to sleep or unsatisfying sleep / Poor concentration Other Symptoms: Palpitations / Hyperventilation / Nausea / Vomiting / Tremor / Erectile Dysfunction / Menstural discomfort and chronic stomach aches o Symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in: Social / Occupational / other important areas of functioning o Exclusion of direct physiological effects of substances or general medical conditions. Simple Phobia: Simple phobias are restricted to clearly specific objects or situations – other than those described in Agoraphobia. Epidemiology: Lifetime prevalence of 12.5%: o Mean onset of Animal phobia = 7 years o Situational phobias usually develop in early adulthood. Aeitiology: Most likely due to bad experiences classical conditioning, there is also robust evidence that there is a genetic component – as 1 in 3 first degree relatives suffer too. Clinically, they can be: o Situational = Public transportation / Flying / Driving / Tunnels / Bridges / Elevators o Natural = Heights (Acrophobia) / Storms / Water / Darkness (Scotophobia) o Blood- Injection = Seeing blood (Haematophobia) or injury, fear of needles (Trypanophobia) or invasive medical procedures o Animals: Spiders (Arachnophobia), Snakes, Mice, Dogs. o Others: Vomiting (Emetophobia), contracting illness e.g. AIDS or Clowns. Prognosis: Those that begin in childhood persist for many years, but those starting in adult life may improve with time. Social Phobia: Social phobia = Fear of social situations where the individual may be exposed to scrutiny by others, which may lead to humiliation or embarrassment. Epidemiology: The lifetime risk of developing it is12.1% Clinically: o This may be linked with an isolated fear of: Public Speaking / Eating in Public / Interacting with the opposite sex o Or it may involve almost all social activities outside of the home. Agoraphobia: Agoraphobia = ‘Fear of the Marketplace’ – a fear of entering crowded spaces e.g.: o Shops / Trains / Buses / Elevators, where immediate escape is difficult and/or immediate help may not be available if the individual suffers a panic attack.
- 3. Epidemiology: Lifetime risk if 1-2%, Two peaks: 15-30 years and 70-80 years Clinically: o At worst patients become housebound or refuse to leave the house without a friend or relative o There is a close relationship with panic disorder- up to 95% of patients with agoraphobia have a current or past history of panic disorder. Therefore it has its own classification too – of ‘Agoraphobia with Panic Attack’ (Episodic anxiety in multiple situations). Panic Disorder: Pan = Greek god, able to inspire fear in people and animals, whilst in lonely places. A Panic disorder = the presence of Panic attacks, that occur unpredictably and are not restricted to any particular situation or objective danger. Epidemiology: Prevalence of 7-9%, more common in Women, two peaks: 15-24 years and 45-55 years. Risk Factors: Urban living / Divorce / Limited Education / Physical or Sexual abuse Clinically: o Symptoms: Palpitations / Tachycardia / Sweating and Flushing / Trembling / Dyspnoea / Chest Discomfort / Nausea / Dizziness / Fainting / Depersonalisation o Panic attacks are particularly distressing, so much so that patient’s develop a fear of having further attacks = Anticipatory anxiety. o NB: Always ask about Agoraphobia as 95% of patients with Panic Disorder have it. DDx of Anxiety: Anxiety Disorders: o Continuous: Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD) o Episodic: Defined Situation: Simple Phobia / Agoraphobia / Social Phobia Multiple Situations: Agoraphobia + Panic Disorder Any Situation: Panic Disorder o Stress Reactions: o Acute Stress Reactions o Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder o Adjustment Disorder o Obsessive Compulsive Disorder o Psychiatric disorders: o Depression o Psychosis o Substance misuse or Withdrawal: o Caffeine / Cocaine / Cannabis / Theophylline / Amphetamines / Steroids o Organic Medical Conditions: o Thyrotoxicosis / Hypoparathyroidism / Phaeochromocytoma / Hypoglycaemia / Arrythmias / Meniere’s disease / Temporal Lobe Epilepsy / Respiratory disease / Carcinoid. References: Geddes, J. Psychiatry: 4th Edition Oxford University Press; 2012 Semple, D. Oxford Handbook of Psychiatry: 2nd Edition. Oxford University Press; 2009 Bourke, Castle and Cameron. Crash Course Psychiatry. 3rd Edition. Mosby Elsevier; 2008