Test PDF 5
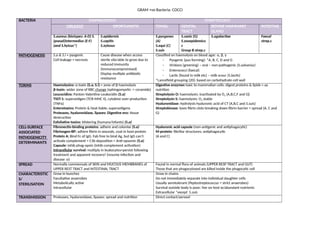
- 1. GRAM +ve Bacteria: COCCI BACTERIA STAPHILOCOCCI STREPTOCOCCI VIRULENT OPORTUNISTIC TONSIL GENITAL TRACT BOVINE MAMMARY GLAND INTESTINE S.aureus (biotypes: A-D) S. (pseud)intermedius (E-F) (and S.hyicus*) S.epidermis S.capits S.xylosus S.pyogenes (A) S.equi (C) S.suis S.canis (G) S.zooepidemicu s Group B strep.c S.agalactae Faecal strep.c PATHOGENESIS S.a & S.i = pyogenic Cell leakage = necrosis Cause disease when access sterile site/able to grow due to reduced immunity (immunocompromised) Display multple antbiotc resistance Classifed on haemolysis on blood agar: α, β, γ - Pyogenic (pus forming): *A, B, C, D and G - Viridans (greening) – oral – non-pathogenic (S.salvarius) - Enterococci (faecal) - Lactc (found in milk etc) – milk scour (S.lacts) *Lancefeld grouping (20): based on carbohydrate cell wall TOXINS Haemolysins: α-toxin (S.a; S.i) = zone of β-haemolysis β-toxin: wider zone of RBC change (sphingomyelin -> ceramide) Leucocidins: Panton-Valentne Leukocidin (S.a) TSST-1: superantgen (TCR-MHC II), cytokine over-producton (TNFα) Enterotoxins: Protein & heat liable; superantgens Proteases, hyaluronidase, lipases: Digestve enz: tssue destructon Exfoliatve toxins: blistering (humans/infants) (S.a) Digestve enzymes toxic to mammalian cells: digest proteins & lipids = aa nutriton Streptolysin O: haemolysin; inactvated by O2 (A,B,C,F and G) Streptolysin S: haemolysin; O2 stable Hyaluronidase: hydrolysis hyaluronic acid of CT (A,B,C and S.suis) Streptokinase: lyses fbrin clots breaking down fbrin barrier = spread (A, C and G) CELL-SURFACE ASSOCIATED PATHOGENICITY DETERMINANTS Fibronectn-binding proteins: adhere and colonise (S.a) Fibrinogen-BP: adhere fbrin in wounds, coat in host-protein Protein A: Bind Fc of IgG. Fab free to bind Ag, but IgG can’t actvate complement = C3b depositon = Ant-opsonin (S.a) Capsule: inhib phag-opsin (inhib complement actvaton) Intracellular survival: multply in leukocytes=persist following treatment and apparent recovery! (resume infecton and disease :o) Hyaluronic acid capsule (non-antgenic and antphagocytc) M-protein: fbrillar structures; antphagocytc (A and C) SPREAD Normally commensals of SKIN and MUCOUS MEMBRANES of UPPER REST TRACT and INTESTINAL TRACT Found in normal fora of animals (UPPER RESP TRACT and GUT) Those that are phagocytosed are killed inside the phagocytc cell CHARACTERISTIC S/ STERILISATION Grow in bunches Facultatve anaerobes Metabolically actve Intracellular Grow in chains Do not immediately separate into individual daughter cells Usually aerotolerant (Peptostreptococcus = strict anaerobes) Survival outside body is poor: live on host w/abundant nutrients Extracellular *except S.suis TRANSMISSION Proteases, hyaluronidase, lipases: spread and nutriton Direct contact/aerosol
- 2. GRAM +ve Bacteria: COCCI DIAGNOSIS Catalase(DNase)+ve Coagulase +ve (bound coagulase) S.hyicus: Catalase(DNase)+ve But Coagulase –ve Catalase (DNase) +ve Coagulase–ve Adheres to plastc Catalase –ve = Do not split H2O2 (no O2 release) While can be most aggressive pathogens; β-haemolytc strep.c of Lancefeld groups A,C and G remain sensitve to Penicillin G and other penicillins. Resistance unknown/