AMA_Assignment Theory notes
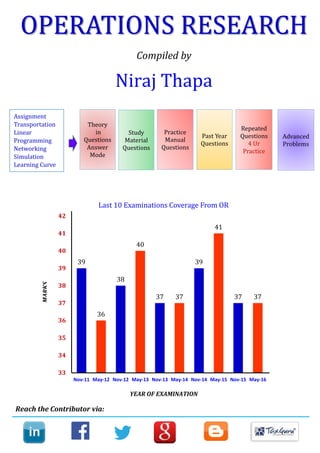
- 1. OPERATIONS RESEARCH Compiled by Niraj Thapa Reach the Contributor via: 39 36 38 40 37 37 39 41 37 37 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 Nov-11 May-12 Nov-12 May-13 Nov-13 May-14 Nov-14 May-15 Nov-15 May-16 Last 10 Examinations Coverage From OR Assignment Transportation Linear Programming Networking Simulation Learning Curve Theory in Questions Answer Mode Study Material Questions Practice Manual Questions Advanced Problems Repeated Questions 4 Ur Practice Past Year Questions MARKS YEAR OF EXAMINATION
- 2. 1 1 THE ASSIGNMENT PROBLEM 6 4 8 5 5 7 5 8 4 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Nov-11 May-12 Nov-12 May-13 Nov-13 May-14 Nov-14 May-15 Nov-15 May-16 Examwise Marks Disrtibution-Assignment MARKS YEAR OF EXAMINATION
- 3. 1 Let us start the topic with some questions relating to the topic. Issue 1: If in a printing press there is one machine and one operator is there to operate. How would the manager employ the worker? Obviously, the only operator shall operate the machine. Issue 2: If there are two machines in the press and two operators are engaged at different rates to operate them. Which operator should operate which machine for minimising the total cost? Issue 3: If there are n machines available and n persons are engaged at different rates to operate them. Which operator should be assigned to which machine to ensure maximum efficiency? The answer to Issue No.2 & 3 is based on the Principle of Assignment Technique (Hungarian Method). Assignment is optimal if it is in the interest of the press (i.e. the press should be able to maximise its total profit or minimise the total operating cost) The problem of assignment arises because available resources such as men, machines, etc. have varying degrees of efficiency for performing different activities An assignment is an act to allot the given number of jobs to operators. Assignment problem is one of the special cases of transportation problems. The objective of the assignment problem is to minimize the cost (i.e., maximising revenue/profits) or time of completing a number of jobs by a number of persons. An important characteristic of the assignment problem is the number of sources is equal to the number of destinations .It is explained in the following way. Only one job is assigned to person Each person is assigned with exactly one job The assignment problem involves following steps to get optimal solution. I. Initial Solution II. Optimality Test III. Assigning Jobs EXPLAINED I. Initial Solution The problem will specify jobs, operators and their associated costs. The no. of jobs should be equal to the no. of operators. It should be in matrix form. Start with a balanced minimisation* matrix. a) Row Reduction (The minimum cost of each row should be deducted from all cell cost of that row) b) Column Reduction (Deduct minimum cost of each column from all cost cell of that column) (Perform column operation in matrix obtained after Row Reduction) II. Optimality Test The matrix obtained after initial solution is to be tested for optimality. In this step the objective is to cover maximum zeros by drawing minimum no. of straight lines (straight lines means not diagonal lines) Then check whether the no. of straight lines drawn equals no. of row (column). If the answer is affirmative# then the solution is optimal. INTRODUCTION STEPS INVOLVED
- 4. 1 III. Assigning Jobs Start from the first row and see if there is single zero$ row, if yes then allot job over that zero by marking square sign over this zero and cross (X) all zeros against the column where is allotted. Repeat the same process for remaining rows and proceed in a similar way for all columns. Finally write the combination of operators/workers and job along with cost and take the total cost. The total cost will be minimum. 1) *Treatment of Unbalanced Maximisation Matrix A matrix is said to be balanced if No. of rows = No. of columns, otherwise it will be an unbalanced matrix. An unbalanced matrix is to be balanced by introducing a dummy row or column (whichever is necessary) so as to proceed further. A minimisation matrix has the objective of minimising cost or time. A matrix with the objective of maximising profit/revenue is a maximisation matrix. A maximisation matrix is to be converted in to the minimisation matrix by the following steps: a) Select the largest cell cost from the entire matrix b) Deduct all cell costs from the cell element selected in (a) above and proceed further. In case of unbalanced matrix with maximisation objective, we do have the options either to a) Minimise the matrix and then balance the matrix OR b) Balance the matrix and minimise the matrix (There will be no change in optimal solution) 2) # What if no. of straight lines drawn ≠ no. of rows (columns) In such cases the solution is to be improved before assigning jobs and should be tested for optimality. How to improve the matrix? Pick the minimum uncovered cell cost. (Uncovered element means such element not touched by st. line) Deduct the minimum cell cost from uncovered cells Add the said minimum cell cost to intersecting cells (Intersecting cell means two lines have met each other in that cell) In cells where there is single line (i.e. no intersection) no treatment is required. Copy the elements as it is in the upcoming matrix. 3) $ What if there are more than one zeros in a row/column? In such cases we shall move forward to next row and subsequent rows thereon and make allotment where there is one zero. If all rows are finished without any single zero and again we move forward column wise and proceed further. 4) What if few zeros are left uncovered either by square sign or cross sign (X) This case arises when tie appears. Select any one zero arbitrarily and assign it and mark two cross sign (X) against this zero in Row & Column. Now assign one remaining zero. 5) If a constant is added/multiplied/divided/ subtracted to every element of the matrix in an assignment problem then an assignment which minimises the total cost for the new matrix will also minimize the total cost matrix. (i.e. there will be no impact in final solution) ISSUES IN ABOVE STEPS
- 5. 1 STEPS IN ASSGNMENT PROBLEM AT A GLANCE Start Write the problem in matrix form Is it a balanced problem? Add Dummy Row/Column Is it a maximisation Problem? Convert it into a minimisation problem Obtain reduced cost matrix by Row & Column Operation Make assignments on one-to-one match basis considering zeros in Rows/columns Stop NO YES NO YES
- 6. 1 Question -1 Prescribe the steps to be followed to solve an assignment problem. Answer: The steps involved in assignment problem can be solved by following steps: Step-1: Take a balanced minimization matrix and perform Row Reduction Operation by subtracting the minimum cost of each row from all cell cost of that row and conduct Column Reduction Operation by deducting minimum cost of each column from all cost cell of that column. Step-2: The matrix obtained after initial solution is to be tested for optimality. In this step the objective is to cover maximum zeros by drawing minimum no. of straight lines (straight lines mean not diagonal lines) Then check whether the no. of straight lines drawn equals no. of row (column). If the answer is affirmative then the solution is optimal Step-3: Assigning Jobs Start from the first row and see if there is single zero row, if yes then allot job over that zero by marking square sign over this zero and cross (X) all zeros against the column where is allotted. Repeat the same process for remaining rows and proceed in a similar way for all columns. Finally write the combination of operators/workers and job along with cost and take the total cost. The total cost will be minimum. (Read Introduction portion for detailed study) Question -2 Explain following statement “Assignment is special case of transportation problem; it can also be solved by transportation methods” Answer: The assignment problem is special case of transportation problem; it can also be solved by transportation method. But the solution obtained by applying this method would be severely degenerate. This is because the optimality test in the transportation method requires that there must be m+n-1 allocations/assignments. But due to the special structure of assignment problem of order n × n, any solution cannot have more than n assignments. Thus, the assignment problem is naturally degenerate. In order to remove degeneracy, (n-1)* number of dummy allocations will be required in order to proceed with the transportation method. Thus, the problem of degeneracy at each solution makes the transportation method computationally inefficient for solving an assignment problem. (*) m+n-1-n n+n-1 – n 2n-1 - n n-1 Question -3 In an assignment problem to assign jobs to men to minimize the time taken, suppose that one man does not know how to do a particular job, how will you eliminate this allocation from the solution? Answer: The objective of assignment problem is to minimize time the total time take to perform a particular task or to minimize the overall cost so, in an assignment minimization problem, if one task cannot be assigned to one person, introduce a prohibitively large cost for that allocation, say M, where M has a high the value. Then, while doing the row minimum and column minimum operations, automatically this allocation will get eliminated. THEORY QUESTIONS [EXAM-SM-PM-RTP-OTHERS]
- 7. 1 Question -4 Just after row and column minimum operations, we find that a particular row has 2 zeros. Does this imply that the 2 corresponding numbers in the original matrix before any operation were equal? Why? Answer: Under the Hungarian Assignment Method, the prerequisite to assign any job is that each row and column must have a zero value in its corresponding cells. If any row or column does not have any zero value then to obtain zero value, each cell values in the row or column is subtracted by the corresponding minimum cell value of respective rows or columns by performing row or column operation. This means if any row or column have two or more cells having same minimum value then these row or column will have more than one zero. However, having two zeros does not necessarily imply two equal values in the original assignment matrix just before row and column operations. Two zeroes in a same row can also be possible by two different operations i.e. one zero from row operation and one zero from column operation. Question -5 Under the usual notation, where a32 means the element at the intersection of the 3rd row and 2nd column, we have, in a 4 × 4 assignment. What can you conclude about the remaining assignments? Why? Answer: The order of matrix in the assignment problem is 4 × 4. The total assignment (allocations) will be four. In the assignment problem when any allocation is made in any cell then the corresponding row and column become unavailable for further allocation. Hence, these corresponding row and column are crossed mark to show unavailability. In the given assignment matrix two allocations have been made in a24 (2nd row and 4th column) and a32 (3rd row and 2nd column). This implies that 2nd and 3rd row and 4th and 2nd column are unavailable for further allocation. Therefore, the other allocations are at either at a11 and a43 or at a13 and a41. Question -6 Explain the following terms: a) Balanced Problem b) Unbalanced Prob. c) Dummy d) Infeasible Assignment e) Maximisation Prob. Answer: Balanced Problem An assignment problem is said to be balanced if the no. of rows = no. of columns (i.e. No. of jobs = no. of workers) Unbalanced Problem If in an assignment problem the no. of rows is not equal to no. of columns the problem is said to be unbalanced problem. Here, no. of facilities is not equal to the no. of jobs. Such matrix is to be balanced by inserting requisite no. of dummy row(s)/column(s). Dummy A dummy is an imaginary job/facility with all cell element being Zero which is introduced to make an unbalanced problem balanced. In case final allotment is in dummy row/column, then it and indication that the particular operator has not been assigned any task. Infeasible Assignment Sometimes, it happens that a particular person is unable to perform a specific job/task or a specific job cannot be performed in a particular machine. In such cells a very high cost is assigned so as to avoid the infeasibility and continue the solution. Maximisation Problem In a maximisation problem the objective is to maximise the sales/revenue/profit. This is to be converted into minimisation problem. A maximisation matrix is to be converted in to the minimisation matrix by the following steps: a) Select the largest cell cost from the entire matrix b) Deduct all cell costs from the cell element selected in (a) above.
