Chapter2 (JF302)
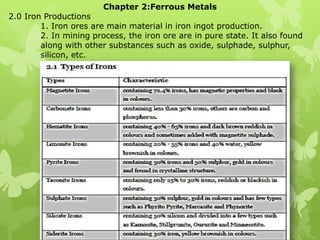
- 1. Chapter 2:Ferrous Metals 2.0 Iron Productions 1. Iron ores are main material in iron ingot production. 2. In mining process, the iron ore are in pure state. It also found along with other substances such as oxide, sulphade, sulphur, silicon, etc.
- 2. 2.2 Iron Ores Characteristics 1. GRADE – containing as much as possible iron oxide 2. COMPACTABILITY – not too compact or too brittle 3. PURITY – containing as less as possible impurities 4. SIMILARITY – containing similar composition to one another Limonite Hematite Magnetite Iron Ore Iron Ore Mining
- 3. 2.3 Iron Production Process Blast Furnace Iron Ore is smelted in the Blast Furnace in order to remove unwanted impurities such as rocks, clay and sand, and also to separate the Iron from the Oxygen. The result is Iron which is about 95% pure. The remaining impurities are other elements which can be removed later if necessary. A Blast Furnace is about 100ft. high and produces abut 1000 tons of molten Iron a day. It is made from steel.
- 4. 1. It’s divided into 2 parts : i. combustion chamber/ stove where the hot air from, blast into the furnace ii. fire bricks (furnace) to form a wide space (shaft) to accommodate and discharge the heat
- 16. The Blast Furnace Process 1. The Iron Ore, Coke and Limestone, (the Charge), is conveyed to the top of the Furnace.2. The Charge is stored in Bells until the timing is right for the charge to be dropped into the Furnace.3. Hot air is then blown through pipes called Tuyeres, to fire the mixture.4. The Coke burns to increase the temperature in the Furnace.
- 17. The Blast Furnace Process 5. The Limestone attracts the impurities in the Iron Ore and forms Slag. This Slag is lighter than the molten Iron and so floats on top of it.6. As the Furnace fills, the molten Iron is Tapped off. The Slag is also tapped off at regular intervals.Most Iron is taken straight from the Blast Furnace to the Steel Mill, but some is poured into buckets called Pigs. This Iron is called Pig Iron and is used to make Cast Iron.
- 18. Three important chemical processes in the blast furnace : i. carbon from the coke burning with oxygen in the air blast ii. oxide reduction to the irons iii. flushing the gauge and ashes from the iron ores using the limestone The disadvantages: i. high in cost and capital for operation ii. controlling iron composition are weak iii. small furnace using coke are incompetent, huge production from bigger furnace are no necessity. The output (products) of the blast furnace : i. the iron ingots contains 93% of basic irons, 3% - 5% of carbon, silica, sulphur, phosphorus and manganese. ii. besides, slags also can be used when separated from melting irons in the furnace such as road ways and building blocks
- 19. 2.4 Steel Production Basic Oxygen Process Furnace (BOP) (Using pure oxygen.)
- 20. The Water-Cooled Lance The Water-CooledLance provides the oxygen to the Furnace so that the temperature in the Furnace will increase. The Oxygen that comes through the Lance is extremely hot after coming through special heating ovens. The Lance has to be Water-Cooled so that it will not melt in the Furnace.
- 21. The Steel Shell The main body of the Basic Oxygen Furnace is made from Steel, as the material is strong and durable, or tough. The Steel Shell does not melt because of the Refractory Lining. The Refractory Lining The Refractory Lining is a special type of cement that has the ability to reflect heat. If you look at the back of an open fireplace, the cement you see on the back wall is a Refractory material, although it would not be of the same quality as the Refractory lining in a Furnace. The Refractory Lining has two purposes. The first is to keep the heat from the furnace in so that less energy is required to keep the Furnace at operating temperature. The second reason is to protect the Steel Shell of the Furnace.
- 22. The Molten Metal The Molten Metal at the bottom of the Furnace is the Steel. The Steel is below the Slag as it is heavier or denser. The Molten Steel is removed from the Furnace when the Steel is of the correct consistency, through the Tap Hole. The Slag The Slag which sits on top of the Molten Metal, because it is less dense, is the waste material from the process of creating Steel. It consists of the impurities, that is most materials other than Iron and Carbon which were put into the Furnace at the start when the Furnace was being Charged. The Slag is removed from the Furnace when the time is ready. The slag
- 23. The Tap hole The Tap hole is used to remove the Molten Steel from the Furnace when it is of the right consistency. During the process of manufacturing the Tap Hole is "plugged" so as not to allow heat to escape from the Furnace. The Converter Fumes The Converter Fumes has two purposes. The first is to trap the dangerous gases that the Basic Oxygen Process produces so that they cannot escape into the atmosphere to poison people or create Acid Rain. The gases are "cleaned" or put to other uses. One important use of the gases is to heat the Oxygen that is going through the Water-Cooled Lance. The second purpose is to reduce the amount of heat loss in the Furnace.
- 24. The Basic Oxygen Process 1. Scrap Charging Scrap Iron and Steel are tipped into the Furnace. The Iron and Steel comes from old or scraped cars, bridges, buildings, etc. Also used is Iron or Steel that when manufactured into a product was not of good enough quality to be used for its intended purpose. 2. Molten Iron Charging Molten Iron, which comes straight from the Blast Furnace is then tipped into the Furnace. The Furnace is now ready for the blow.
- 25. 3. The Blow The Converter Fume is lowered onto the Furnace. The water cooled lanceis then lowered. This carries the hot Oxygen to the surface of the hot metal, increasing the temperature in the Furnace and melting all of the metal. The Oxygen combines with the impurities to form oxides in the form of gases and slag. 4. Sampling During the ‘Blow’ the temperature of the Furnace is monitored, and at regular intervals samples of the molten metal are taken to be analyses. When the Steel is of the right composition, then the Steel workers can move onto the next stage.
- 26. 5. Pouring When the Steel is of the right composition the Converter fume and the water cooled Lance are removed. The molten Steel is then poured out the Tap hole by turning the Furnace to one side. The Steel is then cast into ingots, or processed by continuous casting. 6. Slagging When all of the Steel has been poured out, the Furnace is turned upside down, in the opposite direction to that when pouring, and the Slag is removed.
- 27. 2.5 Steel Production Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) This furnace has high ability in production and easier to handle. Low in oxygen rates made it suitable in producing steel alloy because the metal did not react with the oxygen in the furnace. This furnace used widely and suitable for upgrading the steel, produces tool steel and high quality alloy steel. It can produce up to 120 tones of steels within 4 hours.
- 28. Electric Arc Furnace Diagram
- 30. Electric Arc Furnace operation 1. Charging Charge materials which containing steel scraps, iron ores, oxide irons and limestone were added into the furnace. Electric current flow to the carbon electrode to supply the electric arc.
- 31. 2. Melting The electric arc will melted the oxidize charge materials. Silicon, manganese and phosphorus will start to oxidize and combined with limestone to form slags. Only the carbon electrodes are burning, therefore there is no metal lost.
- 32. 3. Slagging The limestone, fluorspars and oxide irons are added to form slags. After the reaction, it will form the needed steel compositions. Sulphur then added to the slags as calcium sulphade. The reaction are shown as below : FeS + CaO + C CaS + Fe + CO
- 33. 4. Finishing or tapping The steel oxidized by aluminum, ferro-silicon or ferro-manganese to retracted the steels. Slags will be plucked or poured start from its surface and then will be separated or tapped through a hole/ exit channel by leaning the furnace.
- 34. The advantages of electric arc furnace : i. blazing process can be controlled and arranged efficiently ii. no oxidation gases, so can produce high quality steels iii. the temperature can be control accurately iv. free from soils and smokes
- 36. 2.6 Plain Carbon Steel Plain carbon steel is an iron carbon alloy containing 0.02 to 2% carbon. All commercial plain carbon steels contains manganese, sulphur, phosphorus and silicon impurities.
- 37. 2.6.1 Iron-Carbon Phase Equilibrium Diagram 1. The Iron-Carbon Phase Diagram are a phase diagram that shows the connection between amount of carbon and the changes of internal structure by irons and steels while heated until reaching their melting point. 2. Only ferrous metals could show the changes while it is heated. 3. First stage/ phase called lower critical temperature and the second stage of changes called upper critical temperature. 4. The levels of lower critical temperature for every eutectoid steels (0.8% carbon) are the same which it is about 723°C. 5. However, the upper critical temperatures are different depends on the amount of carbon. The higher the amount (more than 0.8%), the higher the temperature.
- 38. 2.6.1.1 Irons, Steels and Cast Irons in the Iron-Carbon Phase Equilibrium Diagram 1. Between the temperature of 1400˚C and 1537˚C, the solid irons exist in body-centered cubic (BCC) and called as pearlite. 2. The temperature between 910˚C and 1400˚C, the crystalline structures are face-centered cubic (FCC) called austenite. 3. The temperature 910˚C and below, the iron structures are body–centered cubic (BCC) called ferrite. 4. At 1125˚C, cementite dissolvability in austenite irons is limited at 2% carbon only. 5. Cementite solid solutions in austenite called ferrite. 6. Eutectoid composition for ferrite and cementite called pearlite which containing a lamellar structure consisting of alternate layers of cementite and ferrite. 7. Ferrite and cementite only transformed from austenite with slow cooling process. But with fast cooling process, the martensite will transformed from austenite.
- 40. Fig 2: Microstructure for various phase of steel
- 43. A pearlite has a variable hardnessPearlite
- 46. Medium carbon steel Contains 0.3 – 0.8% carbon High strength and ductility after heat treatment, stability, tough and tensile strength Applications : railways, wheels, shafts, gears, bolts It can be quenched to form martensite and bainite if using media for quenching such as water and brine
- 47. High carbon steel Contains more than 0.8% carbon (>0.8% C) Low in strength, high in hardness and wear resistance after heat treatment Applications : moulds, hammers, knives, milling cutters Also known as tool steel Tempering process can accelerate martensite formation and maintain the low strength properties
- 48. 2.9 Alloy Steels 1. Alloy steel may be defined as carbon steel to which one or more elements are added to get some beneficial effects. 2. Main purposes : i. to improve the quality of steels ii. to improve steel characteristics iii. to make it suitable for engineering works iv. to make it easier for heat treatment process
- 49. 3. The commonly added elements to achieve these properties : i. increase tensile strength ii. increase hardness and toughness iii. higher hardenability iv. changeability for critical temperature v. increase wear and abrasive resistance vi. higher corrosion and oxidation resistance vii. maintaining higher hardness (red hardness) at temperatures up to 600 ˚C, due to the presence of alloy carbides viii. higher temperability, and maintain the hardness and strength at elevated temperatures (creep strength)
- 51. increase the machineability in finishing process
- 53. act as oxidation agent at higher temperature
- 55. increase the critical temperature for heat treatment
- 57. 2.10 Cast Irons 1. An alloy of iron and carbon containing 2 – 4% carbon. 2. Carbon content form in two ways: a) cementite (Fe3C) b) graphite (Fe+C) as free carbon when the cementite is decomposed 2.10.1 Factors In Carbon Forming Cooling / Solidifying Process Rate The cooling rate depends on the thickness and type of die/mould. 1. Slow cooling : caused the carbon separated as graphite, producing grey cast iron 2. Rapid cooling : prevent the change of graphite and maintain it hardness and difficult to machined, producing white cast iron Heat Treatment 1. With long heating process, white cast iron will be forming graphite structure and are used to produce malleable steel. High Carbon Contents 1. With high carbon contents, the cast irons will have the tendency to solidify as grey cast irons. 2. The strength and hardness of irons increased with the increasing of carbon.
- 58. 2.10.2 Alloying Elements Silicon - The higher silicon contents, causing higher resistance and good magnetic properties Sulphur - Causing the cast irons to be harden, embrittle and weak Phosphorus - Increasing strength, hardness and improving the resistance of corrosion Manganese - Causing strength, toughness and high wear resistance, hard to machine because of the hardness 2.10.3 The Advantages of Cast Irons Widely used in industries as for : i. cheaper and machineable ii. low melting point (1140˚C - 1200˚C) compared to steels iii. liquidity and formability in casting iv. wear resistance and moistureability
- 59. 2.10.4 Structures, Properties and the Usages of Cast Irons