membrane models and biosynthesis
- 1. Membranes
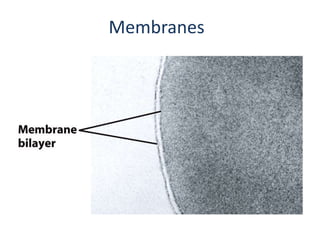
- 2. Membranes • Complex lipids form the membranes around cells and small structures within cells. • In aqueous solution, complex lipids spontaneously form into a lipid bilayer, with a back-to-back arrangement of lipid monolayers. – Polar (hydrophilic) head groups are in contact with the aqueous environment. – Nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails are buried within the bilayer – The arrangement of hydrocarbon tails in the interior can be rigid (if rich in saturated fatty acids) or fluid (if rich in unsaturated fatty acids).
- 3. • Reaction will take place spontaneously if the change in delta G is negative or exergonic. • In the case of the membrane the components must be arranged in such a way to minimize energetic costs
- 4. • Extensive hydrogen bonding in water molecules explains the hydrophobic effect seen in membrane • The aggregation of water around a single fatty acid chain causes a decrease in entropy • Therefore layers of polar or nonpolar motifs will cluster together, not always in a laminar fashion.
- 5. • Compartmentalization • Create gradients • Enzyme activity • Signal transduction • Selective passage Purpose
- 7. Composition: Proteins • Integral/transmembra ne • Peripheral – can be lipid anchored
- 8. Composition: Carbohydrates On external surface: glycoproteins & glycolipids
- 9. Figure 1.5 Early membrane models
- 10. Fluid Mosaic Model -Singer & Nicolson (1972) describe integral proteins, lateral diffusion of lipids and limited transverse diffusion Figure 1.6 The freeze-fracture technique reveals “bumps” in the membrane interior.
- 11. Figure 1.7 The Fluid Mosaic Model proposed by Singer and Nicolson • Lipids form a fluid bilayer • Bulk of the lipids form the bilayer • Lipids provide the solvent for the proteins • Most proteins are embedded and globular • It is a mosaic in that proteins are scattered across it or on its surface • Both integral and peripheral proteins exist • Lipids and proteins are amphipathic
- 12. Membrane Proteins are α- helical, globular and membrane spanning • Circular Dichroism: involves circular polarized light. It is present in absorption bans of chiral molecules. When circularly polarized light passes through an absorbing optically active medium, the speeds between right and left polarizations differ, as well as the wavelengths and the extent at which they’re absorbed. Alpha helices and beta sheets are optically active and have spectral signatures unique the them. • X-ray diffraction: is a tool used for identifying the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal. An X-rays beam will diffract once it hits the crystal and produce a 3-D picture, representing the density of the electrons within the crystals.
- 13. • Need 40-50 lipid molecules form single layer around protein • Lipids that surround protein are called the annulus • Protein-protein interaction
- 14. Paradigm shift: Lipid Rafts -Certain domains within the bilayer are not as 'fluid' and are enriched with proteins (some are anchoring), cholesterol and sphingolipids -Signaling domains called “liquid ordered” microdomains
- 16. 3° dimension • Asymmetry of membrane • Interacts with substances at the border • Cytoskeleton (actin- based)
- 17. 17 Lipid Biosynthesis keystone concepts: • Biosynthesis of fatty acids does not proceed as a simple reversal of fatty acid oxidation • These reactions are under tight control because the process is energetically expensive • Fatty acid synthesis and oxidation are coordinated and regulated together • Synthesis of storage and membrane lipids from fatty acids is determined by the metabolic needs of the organism • Cholesterol is synthesized from acetyl CoA and has several fates • Cholesterol and other lipids are transported through the blood as lipoproteins
- 18. Fatty Acid Biosynthesis While degradation of fatty acids takes place in mitochondria, the majority of fatty acid synthesis takes place in the cytosol. These two pathways have in common that they both involve acetyl CoA. – Acetyl CoA is the end product of each spiral of b-oxidation. – Fatty acids are synthesized two carbon atoms at a time – The source of these two carbons is the acetyl group of acetyl CoA. The key to fatty acid synthesis is a multienzyme complex called acyl carrier protein, ACP-SH.
- 19. 19 comparison to b-oxidation • Different pathway • Different enzymes • Different parts of the cell – b-oxidation is in the mitochondria – Fatty acid synthesis is in the cytosol
- 21. Fatty Acid Biosynthesis • Synthesis takes place in the cytosol • Intermediates covalently linked to acyl carrier protein • Activation of each acetyl CoA. • acetyl CoA + CO2 Malonyl CoA • Four-step repeating cycle, extension by 2-carbons / cycle – Condensation – Reduction – Dehydration – reduction
- 22. 22 First Activation: Irreversible formation of malonyl- CoA by acetyl-CoA carboxylase
- 23. Reaction catalyzed by acetyl-CoA carboxylase
- 24. Malonyl CoA • Malonyl CoA is synthesized by the action of acetylCoA carboxylase. • Biotin is a required cofactor. • This is an irreversible reaction. • Acetyl CoA carboxylation is a rate-limiting step of FA biosynthesis. • AcetylCoA carboxylase is under allosteric regulation. Palmitate is a negative effector.
- 26. 26 Fatty Acid Synthase complex • Multienzyme Complex with 7 different active sites • 4 repeated steps include: Condensation, Reduction, Dehydration, and Reduction (NADPH electron carrier) • Saturated acyl group produced is the substrate for additional rounds of the pathway
- 27. Fatty Acid Biosynthesis The biosynthesis of fatty acids. – ACP has a side chain that carries the growing fatty acid – ACP rotates counterclockwise, and its side chain sweeps over the multienzyme system (empty spheres).
- 28. Fatty Acid Synthase (FAS) • FAS is a polypeptide chain with multiple domains, each with distinct enzyme activities required for fatty acid biosynthesis. • ACP: Recall that CoA is used as an activator for β-oxidation. For fatty acid biosynthesis, the activator is a protein called the acyl carrier protein (ACP). It is part of the FAS complex. The acyl groups get anchored to the CoA group of ACP by a thioester linkage • Condensing enzyme/β-ketoacyl synthase (KS). Also part of FAS, has a cysteine SH that participates in thioester linkage with the carboxylate group of the fatty acid. • During FA biosynthesis, the growing FA chain alternates between K-SH and ACP-SH
- 29. 29 saturated acyl group is the substrate for additional rounds of the pathway •Reducing agent is NADPH
- 30. Stepwise reaction 1. The acetyl group gets transferred from CoA to ACP by malonyl/acetyl-CoA-ACP transferase. 2. The acetyl (acyl) group next gets transferred to the β-ketoacyl-ACP synthase (KS) of FAS complex. 3. Next, the malonyl group gets transferred from CoA to ACP by malonyl/acetyl CoA ACP transferase. • This results in both arms of FAS occupied 4. The COO group of malonyl ACP is removed as CO2, the acetyl group gets transferred to the alpha carbon of malonyl ACP. This results in acetoacetyl-ACP
- 32. Repeat cycles for elongation • The result of the first cycle of fatty acid biosynthesis is a four carbon chain associated to the ACP arm. • This chain gets transferred to the KS. • A new malonyl CoA is introduced on the ACP arm. • The reactions proceed as before. For each cycle the acyl group transferred to the malonyl CoA is 2-carbons longer the previous cycle. • At the end of 7 cycles a 16 carbon chain is attached to the ACP arm (palmitoyl ACP). • The C16 unit is hydrolyzed from ACP yielding free palmitate Net reaction: Acetyl CoA + 7 malonyl CoA + 14 NADPH + 14 H+ Palmitate + 7 CO2 + 8 CoA + 14 NADP+ + 6H2O
- 33. Chem 674 De Novo to Palmitate:
- 34. Fatty Acid Biosynthesis – Higher fatty acids, for example C18 (stearic acid), are obtained by addition of one or more additional C2 fragments by a different enzyme system. – Unsaturated fatty acids are synthesized from saturated fatty acids by enzyme-catalyzed oxidation at the appropriate point on the hydrocarbon chain.
- 35. 35 long chain saturated FA’s are made from palmitate • In the sER and mitochondria • CoA is the acyl carrier • Similar mechanism to FAS
- 36. 36 desaturation of FA’s requires a mixed-function oxidase • Mammalian liver cells desaturate fatty acids on sER • Mammals can only make ω9 or higher fatty acids • Plants can make ω6 and ω3 fatty acids in their sER and chloroplasts
- 37. Cholesterol All carbon atoms of cholesterol and of all steroids synthesized from it are derived from the two-carbon acetyl group of acetyl CoA. • Synthesis starts with reaction of three molecules of acetyl CoA to form the six-carbon compound 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA (HMG-CoA). • The enzyme HMG-CoA reductase then catalyzes the reduction of the thioester group to a primary alcohol.
- 38. 38 3 acetates condense mevalonate to isoprene conversion 6 isoprenes polymerize cyclization Cholesterol biosynthesis
- 39. 39 Fates of cholesterol • Synthesis in the liver • Exported as: bile acids, cholesteryl esters • Needed for membrane synthesis, hormone precursors, Vitamin D • Insoluble in water • Cholesteryl esters (CE’s) are transported in lipoprotein particles or stored in the liver.