Chickenpox
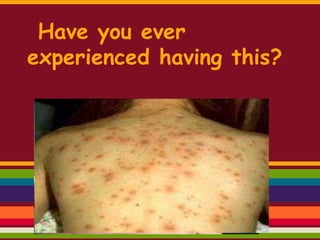
- 1. Have you ever experienced having this?
- 3. Before we begin with the discussion..... I shall share with you people a true to life story...
- 4. CHICKEN POX Patricia Librea Ricki Literal Mary Macaldo Sam Madriñan Kristine Olmo
- 5. What is Chickenpox? • Also called VARICELLA • It is a contagious viral disease characterized by an eruption of vesicles (blisters) in the skin.
- 8. What causes chickenpox? • Varicella-Zoster Virus
- 9. How do we acquire the disease? • Direct skin-to-skin contact • Via respiratory droplets like coughing and sneezing from the infected individual
- 10. Common age group affected: • Children • Before Vaccine was available:Children between 5-9 years old. • Between 2 and 6 years old.
- 11. Attack Rate: • 90% among susceptible persons • 70-90% among susceptible siblings (Household) • Infants under 6 months old. • Pregnant women. • Older patients have a higher risk for complications of chickenpox.
- 12. Which gender is more likely to be infected with the disease? • Gender doesn't matter when it comes to infection of chickenpox. But women are more likely to develop shingles which occurs in people who have had chickenpox. *Shingles -reactivation of the virus from chickenpox
- 13. Shingles
- 14. Usually occurring... • About 97% of adults in temperate climates have antibodies to chickenpox by their early 20's. • Usually occurs during epidemics *antibodies - large Y-shaped proteins, recruited by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects like bacterias and viruses.
- 15. Complications: • Itching - the most common complications of the varicella infection that is very distressing particularly for small children. • Secondary infection and scarring • Ear Infection • Bacterial Superinfection
- 16. Complications: • Reye Syndrome - It is a side effect of aspirin therapy. • Zoster Ophtalmicus • Ramsay Hunt Syndrome • Postherpetic Neuralgia (PHN) • Pneumonia
- 17. Signs and Symptoms • Red, itchy rash initially resembling insect bites on your face, scalp, chest, and back. • Fever • Abdominal pain or loss of appetite • Mild headache • General feeling of unease and discomfort • Dry cough • Common cold
- 18. Diagnosis: 1. Verify if you have the symptoms of chickenpox first. What else could it be if not chickenpox? -Insect bites -Other viral illness -Contact Dermatitis
- 19. 2. Frankly, you do not need to see the doctor for straightforward cases but with the exceptions of : • You are not sure about the diagnosis after two or three days have passed • An infant 2 months or younger catches chickenpox
- 20. • Your child has a weakened immune system such as from an immune disorder or from taking steroid medication • The mother of a newborn baby breaks out in chickenpox less than 3 days after the birth • Your child has fever more than five days
- 21. • Your child develops a moderate to severe cough • Severe headaches develop even when fever is controlled (high fever can cause headaches) • Significant dizziness (spinning feeling) occurs
- 22. • Severe headaches with vomiting and stiff painful back of the neck or spine • Any spots become infected with redness spreading outward from the spot with puss draining out
- 23. • Your child has spots on the upper or lower eyelids or has red, painful eyes • You are pregnant, are exposed to chickenpox, and have never had the illness or the vaccine
- 24. How long is the disease contagious? • The disease is contagious starting the day before fever or spots appear, until 24 hours after all the blisters have crusted over. This usually takes about 7 days from beginning to end.
- 25. Treatment: • Apply cold compress to blisters. • Cool water baths (every 3-4 hours) adding baking soda to calm itching. • Acyclovir (Zofirax) is the only FDA (food and drug administration) approved treatment for chickenpox. • Treat fever with acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen.
- 26. Treatment: • Do not scratching to avoid future scarring. One way to avoid scratching is to keep fingernails clean and short. • If the skin is sore and aggravated, dress appropriately so they don't get too hot or too cold. • Loose-fitting, smooth, cotton fabrics and will help stop the skin from becoming sore and irritated.
- 27. Treatment: • Occasionally a child will develop blisters in the mouth, making eating or drinking painful. • A person should be encouraged to drink fluids to prevent dehydration. • To alleviate pain, provide cold fluids and soft bland food. Avoid any foods that are spicy, hot or acidic (Like orange juice)
- 28. Treatment • Benadryl helps decrease the itching • Oatmeal baths : Aveeno or other brands can be purchased at the store. This can soothe itching. • Never use aspirin during a chickenpox infection
- 29. Prognosis Is it curable? • Chickenpox can be cured but it takes time • Incubation period: 10-21 days
- 30. Prognosis Is it fatal? • Can be a fatal disease. Some people die because of chickenpox. • Most children completely recover in a week. But it can be severe for babies, adolescents, pregnant women
- 31. Prevention • Varicella vaccine Note: Not 100 % effective at preventing the disease but vaccinated people who develop chickenpox usually develop a milder case than unvaccinated people
- 32. Prevention For chickenpox prevention, the vaccine should be used in the following groups of people: • Children from 12 months to 13 years old: Single dose • People 13 and older: Two doses of vaccine with 4-8 weeks apart
- 33. Prevention • The chickenpox vaccine may be given at the same time as other vaccines. • No vaccine is 100% effective in preventing the disease. • About 8-9 out of 10 people who are vaccinated are completely protected from chickenpox.
- 34. Prevention • If a vaccinated person does get chickenpox, it is usually a very mild case with fewer skin lesions (Usually less than 50) lasting only a few days, no fever or a low fever, and few other symptoms.
- 35. QUIZ!!!
- 36. I. Identification 1. What is the other name for chickenpox? 2. It is the virus that causes chickenpox. 3. These are the common age group affected by the disease.
- 37. 4-6. Give 3 symptoms of chickenpox. 7-8. Give two ways on how we can acquire chickenpox. 9. It is the most common complication of the infection that is very distressing particularly for small children.
- 38. 10. It is the only FDA (food and drug administration) approved treatment, an anti-viral drug used for chickenpox 11. It is a kind of drug which when intake into the body, may have a risk of having Reye's syndrome. 12. How many days is the incubation period?
- 39. II. True or False 13. The older the patient, the higher the risk for complications from either chickenpox or shingles. 14. The chickenpox vaccine should not be given at the same time as other vaccines. 15. If a child has already taken a chickenpox vaccine, he/she will not be infected with chickenpox anymore.
- 40. ANSWER KEY: 1. Varicella 2. Varicella-Zoster Virus 3. Children 4. - 6. Fever, abdominal pain, mild headache, general feeling of unease, dry cough, common cold, general malaise
- 41. ANSWER KEY: 7. - 8. Direct skin to skin contact, via respiratory droplets (coughing, sneezing) 9. Itching 10. Acyclovir (Zofirax) 11. Aspirin 12. 10-21 days 13. True 14. False 15. False
