Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
SPORE AND CONE BEARING PLANTS, VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION

SPORE AND CONE BEARING PLANTS, VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION
Viewers also liked (19)
C. Medio LA EDAD MODERNA Y LA EDAD CONTEMPORÁNEA Tercer ciclo E. Primaria

C. Medio LA EDAD MODERNA Y LA EDAD CONTEMPORÁNEA Tercer ciclo E. Primaria
Similar to Unit 4 diagram
Similar to Unit 4 diagram (20)
Plants: Parts, Photosynthesis, Reproduction REINO LA PUEBLA

Plants: Parts, Photosynthesis, Reproduction REINO LA PUEBLA
More from rafael yuste muñoz
More from rafael yuste muñoz (20)
Natural science 2_unit_1_how_my_body_works_worksheet

Natural science 2_unit_1_how_my_body_works_worksheet
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx

ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx
Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf

Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf
NO1 Top Black Magic Specialist In Lahore Black magic In Pakistan Kala Ilam Ex...

NO1 Top Black Magic Specialist In Lahore Black magic In Pakistan Kala Ilam Ex...
ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.

ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.
Beyond_Borders_Understanding_Anime_and_Manga_Fandom_A_Comprehensive_Audience_...

Beyond_Borders_Understanding_Anime_and_Manga_Fandom_A_Comprehensive_Audience_...
Unit 3 Emotional Intelligence and Spiritual Intelligence.pdf

Unit 3 Emotional Intelligence and Spiritual Intelligence.pdf
Fostering Friendships - Enhancing Social Bonds in the Classroom

Fostering Friendships - Enhancing Social Bonds in the Classroom
This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.

This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.
UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf

UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf
Exploring_the_Narrative_Style_of_Amitav_Ghoshs_Gun_Island.pptx

Exploring_the_Narrative_Style_of_Amitav_Ghoshs_Gun_Island.pptx
Unit 4 diagram
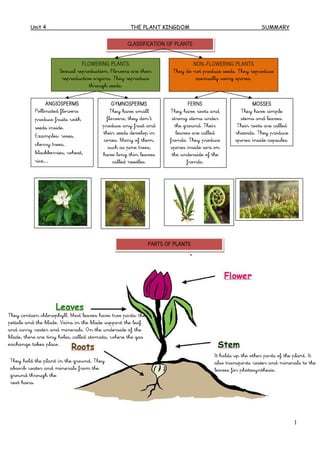
- 1. Unit 4 THE PLANT KINGDOM SUMMARY 1 CLASSIFICATION OF PLANTS FLOWERING PLANTS Sexual reproduction. Flowers are their reproductive organs. They reproduce through seeds. NON-FLOWERING PLANTS They do not produce seeds. They reproduce asexually using spores. ANGIOSPERMS Pollinated flowers produce fruits with seeds inside. Examples: roses, cherry trees, blackberries, wheat, rice,… GYMNOSPERMS They have small flowers, they don’t produce any fruit and their seeds develop in cones. Many of them, such as pine trees, have long thin leaves called needles. FERNS They have roots and strong stems under the ground. Their leaves are called fronds. They produce spores inside sori on the underside of the fronds. MOSSES They have simple stems and leaves. Their roots are called rhizoids. They produce spores inside capsules. PARTS OF PLANTS They hold the plant in the ground. They absorb water and minerals from the ground through the root hairs. It holds up the other parts of the plant. It also transports water and minerals to the leaves for photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll. Most leaves have two parts: the petiole and the blade. Veins in the blade support the leaf and carry water and minerals. On the underside of the blade, there are tiny holes, called stomata, where the gas exchange takes place.
- 2. Unit 4 THE PLANT KINGDOM SUMMARY 2 Plants make their own food through the process called photosynthesis. 1. The roots absorb water and minerals from the soil. 2. Xylem cells transport this mixture of water and minerals, called raw sap, through the stem to the leaves. 3. Leaves absorb carbon dioxide through their stomata. In the chloroplasts, chlorophyll collects solar energy to transform water, minerals and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen. 4. Phloem cells carry the glucose, the plants’ food, through the stem to all the parts of the plant. - PHOTOSYNTHESIS is very important because: 1. It gives us oxygen to breathe. 2. It consumes carbon dioxide. 3. It transforms water and minerals into food. Animals can feed on plants to get energy to live. Plants consume oxygen and produce it too. Plants produce oxygen through the photosynthesis during the day. They produce more oxygen than they need and expel it through the stomata. At night, when photosynthesis stops, plants release carbon dioxide. PLANT NUTRITION PLANT RESPIRATION